Taxation and Financial Reforms - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Taxation and Financial Reforms
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Taxation and Financial Reforms: An Overview</h4><p>The government has implemented several significant <strong>taxation and financial reforms</strong> aimed at easing compliance burdens, promoting domestic manufacturing, and improving public welfare. These reforms touch upon various aspects of direct and indirect taxation.</p><h4>Reforms in Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)</h4><p>A notable reform involves the <strong>Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)</strong> mechanism, specifically for <strong>rent payments</strong>. This adjustment seeks to streamline tax procedures for a large segment of taxpayers.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The threshold for <strong>TDS on Rent</strong> has been significantly increased from <strong>₹2.4 lakh</strong> to <strong>₹6 lakh</strong> per annum. This change directly impacts individuals and entities involved in rental transactions.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>This enhancement is designed to substantially reduce the <strong>tax compliance burden</strong> on a large number of taxpayers, simplifying their financial obligations and administrative tasks.</p></div><h4>Extension of Time Limit for Updated Tax Returns</h4><p>Another key financial reform focuses on providing greater flexibility for taxpayers to rectify their tax filings. The government has extended the window for submitting <strong>updated tax returns</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The time limit for filing <strong>updated tax returns</strong> has been extended from <strong>2 years</strong> to <strong>4 years</strong> from the end of the relevant assessment year. This provides a longer period for corrections.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>This extension is intended to facilitate <strong>voluntary tax compliance</strong>, allowing taxpayers more time to ensure accuracy and avoid penalties for past errors or omissions.</p></div><h4>Exemptions in Basic Customs Duty (BCD)</h4><p>To bolster public health and domestic industry, several critical exemptions have been introduced for <strong>Basic Customs Duty (BCD)</strong>. These exemptions target specific sectors and products.</p><h4>BCD Exemption for Life-Saving Drugs</h4><p>In a humanitarian move, the government has granted full exemption from <strong>Basic Customs Duty (BCD)</strong> for essential medical supplies. This aims to make critical treatments more accessible and affordable.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>36 life-saving drugs</strong> used for treating severe conditions such as <strong>cancer</strong>, various <strong>chronic diseases</strong>, and <strong>rare diseases</strong> are now fully exempted from BCD.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>This reform aligns with India's public health goals and can be cited in answers related to healthcare accessibility and social welfare in <strong>GS Paper II (Social Justice)</strong>.</p></div><h4>BCD Exemption for Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing</h4><p>To accelerate the transition to green energy and boost local manufacturing capabilities, exemptions have been provided for components crucial to the <strong>electric vehicle (EV)</strong> and mobile device sectors.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Capital goods</strong> used in the manufacturing of <strong>Lithium-Ion batteries</strong> for both <strong>Electric Vehicles (EVs)</strong> and <strong>mobile devices</strong> have been fully exempted from BCD.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>This exemption is a strategic move to boost <strong>domestic production</strong> of these critical components, reducing reliance on imports and fostering a self-reliant energy ecosystem.</p></div><h4>BCD Exemption for Textile and Electronics Sector Components</h4><p>Further strengthening the 'Make in India' initiative, specific components for key industrial sectors have also received customs duty exemptions. This targets two significant manufacturing areas.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Components for the <strong>textile sector</strong> and the <strong>electronics sector</strong> have been exempted from BCD. This is designed to support indigenous manufacturing and value addition.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary objective of these exemptions is to encourage <strong>local manufacturing</strong>, thereby reducing India's <strong>dependency on imports</strong> for crucial industrial inputs and fostering job creation.</p></div>
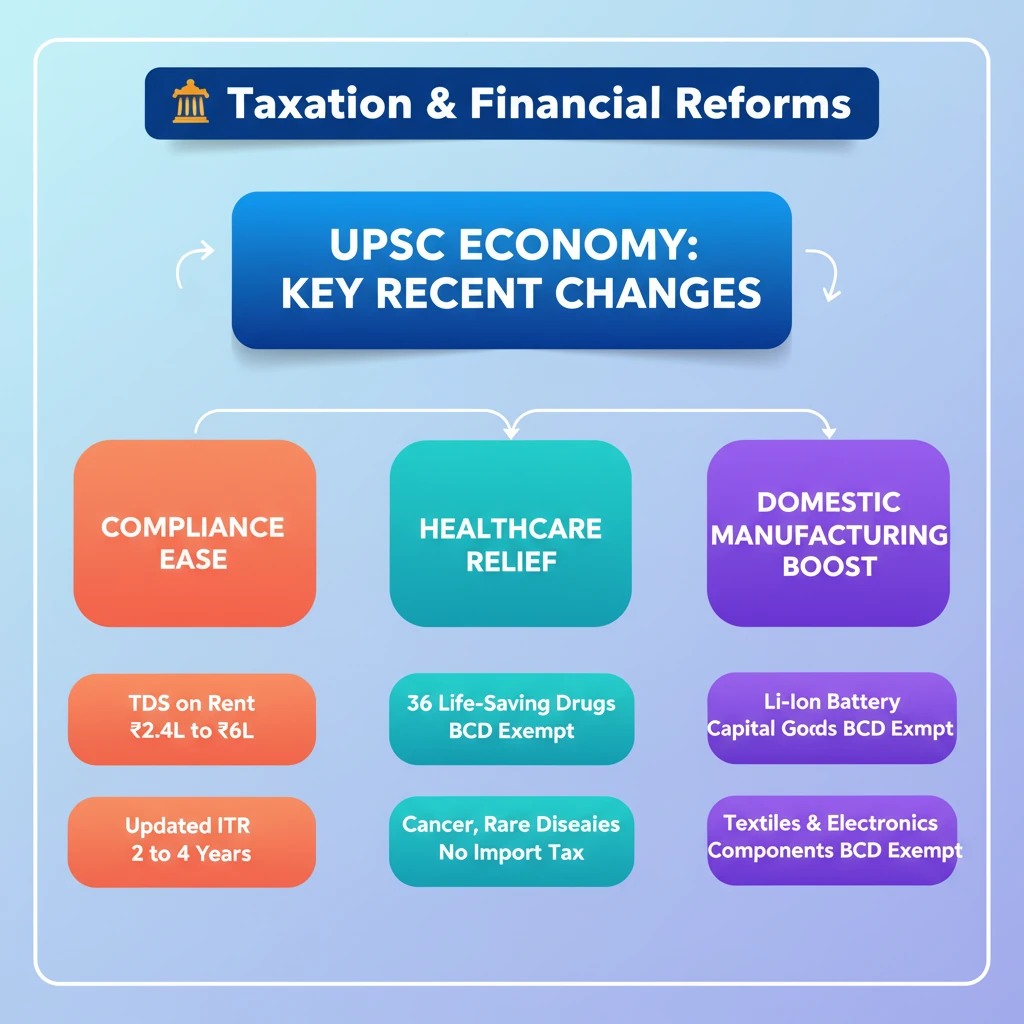
💡 Key Takeaways
- •TDS on Rent limit increased from ₹2.4 lakh to ₹6 lakh, easing compliance for many.
- •Time limit for updated tax returns extended from 2 years to 4 years, promoting voluntary compliance.
- •36 life-saving drugs for cancer, chronic, and rare diseases fully exempted from Basic Customs Duty (BCD).
- •BCD exemption for Lithium-Ion battery manufacturing capital goods boosts EV/mobile domestic production.
- •Textile and electronics sector components also exempted from BCD to encourage local manufacturing and reduce import dependency.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Union Budget documents (general knowledge of where such reforms originate)
•Ministry of Finance official releases (general knowledge)