INTERNATIONALISATION OF RUPEE - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
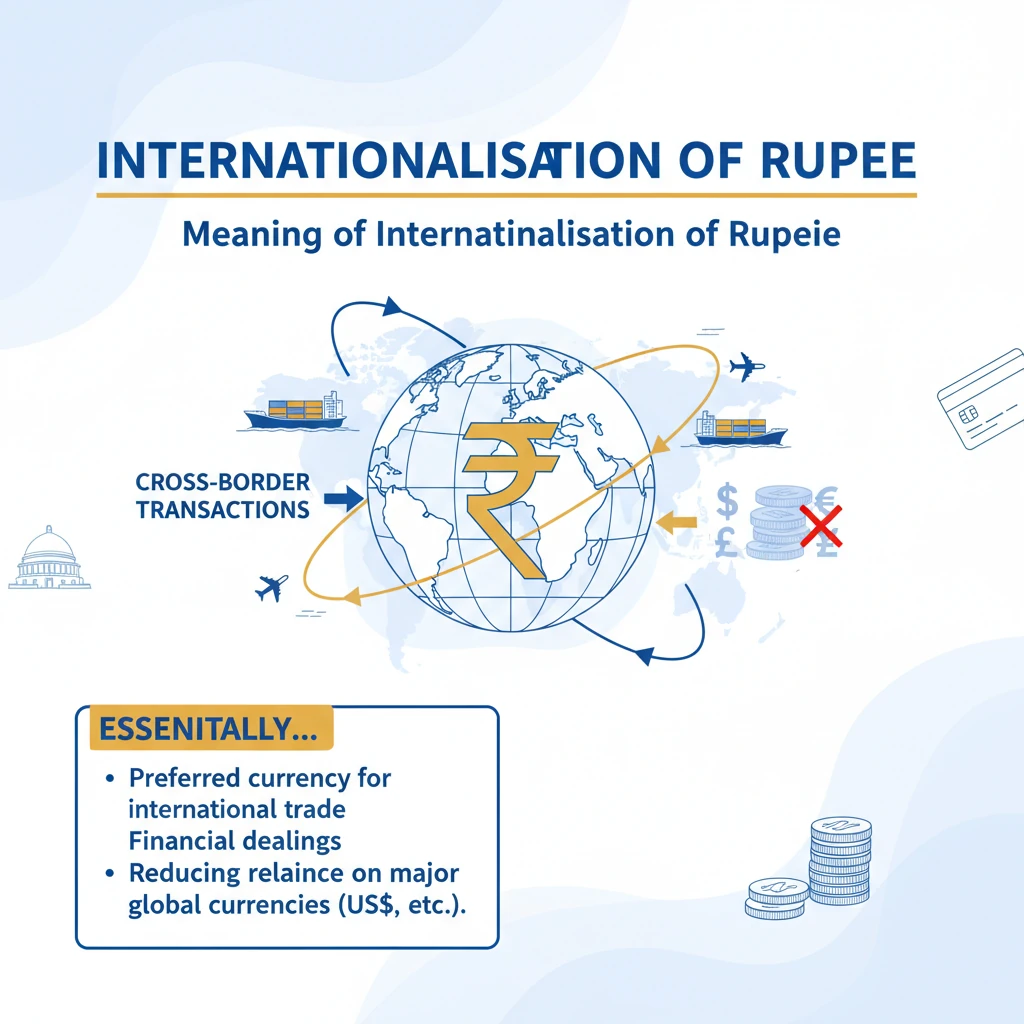
INTERNATIONALISATION OF RUPEE
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
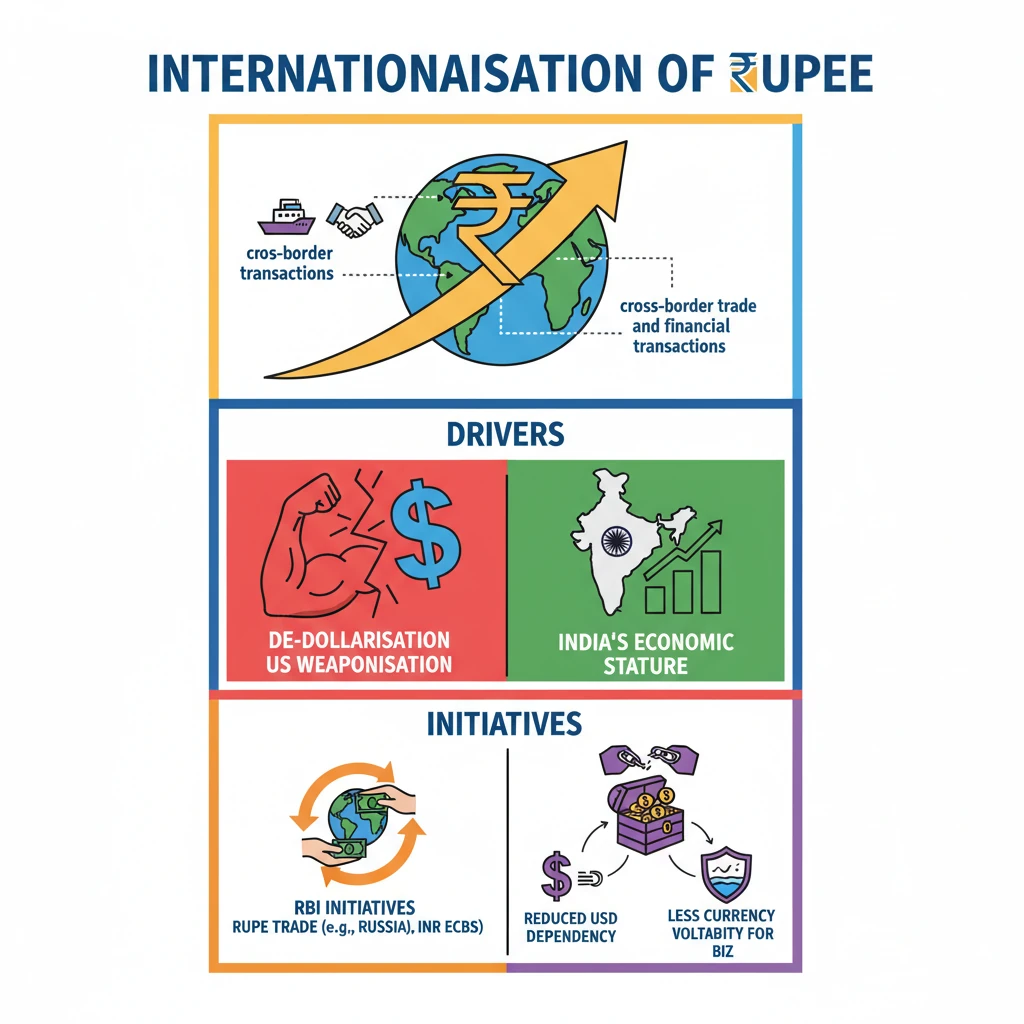
<h4>Meaning of Internationalisation of Rupee</h4><p>The <strong>internationalisation of the Rupee</strong> refers to increasing its usage in <strong>cross-border transactions</strong>. This means the Indian Rupee would be accepted and used more widely outside India for various economic activities.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Essentially, it involves promoting the Rupee as a preferred currency for international trade and financial dealings, reducing reliance on major global currencies like the US Dollar.</p></div><h4>What Internationalisation Entails</h4><p>The process of internationalising the Rupee involves its greater acceptance and utility in several key areas:</p><ul><li><strong>Rupee for import and export:</strong> Indian businesses and their international partners would increasingly use the Rupee to settle trade transactions for goods and services.</li><li><strong>Rupee for current and capital account transactions:</strong> The Rupee would be used for a wider range of financial flows, including remittances, investments, and loans.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>Currently, the <strong>Indian Rupee is fully convertible in the current account</strong>, meaning there are no restrictions on foreign exchange for trade in goods, services, and remittances. However, it is <strong>partially convertible in the capital account</strong>, with certain limitations on financial flows like foreign investments and borrowings.</p></div><h4>Why Internationalisation is Needed</h4><p>Several factors highlight the urgent need for the internationalisation of the Indian Rupee:</p><ul><li><strong>Weaponisation of USD by US:</strong> The use of the <strong>US Dollar</strong> as a tool for imposing <strong>sanctions</strong> by the United States has prompted many countries to seek alternatives to reduce geopolitical risks.</li><li><strong>Wave of de-dollarisation:</strong> There is a growing global trend among nations to reduce their dependency on the <strong>US Dollar</strong> and diversify their foreign exchange reserves and trade settlements.</li><li><strong>Increasing internationalisation of Chinese Renminbi:</strong> China's proactive efforts to internationalise its currency, the <strong>Renminbi</strong>, demonstrate the strategic benefits of such a move, putting pressure on other economies like India to follow suit.</li><li><strong>India’s minimal share in global forex market turnover:</strong> India accounts for only about <strong>1.7%</strong> of the global foreign exchange market turnover, indicating a limited international presence for its currency.</li></ul><h4>RBI's Initiatives Towards Internationalisation</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> has taken several concrete steps to promote the use of the Indian Rupee internationally:</p><ul><li><strong>Indian currency in cross-border trade:</strong> This has been identified as a <strong>key component</strong> in India's <strong>Foreign Trade Policy (2022)</strong>, signaling a strategic shift towards Rupee-based trade.</li><li><strong>Mechanism introduced for rupee trade settlement with Russia:</strong> A specific framework was established to facilitate trade settlements with <strong>Russia</strong> in Indian Rupees, bypassing the need for third-country currencies.</li><li><strong>Vostro accounts for trade settlement:</strong> Banks from partner countries are allowed to open <strong>Special Rupee Vostro Accounts</strong> in India. These accounts enable the settlement of trade transactions directly in Rupees.</li><li><strong>Circular on “International Trade Settlement in Indian Rupees” (2022):</strong> The RBI issued a comprehensive circular outlining the operational framework for international trade settlements using the Indian Rupee.</li><li><strong>External commercial borrowings (ECBs) in INR enabled:</strong> Indian entities are now permitted to raise <strong>External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)</strong> denominated in Indian Rupees, further integrating the currency into international finance.</li></ul><h4>Significance and Benefits</h4><p>The internationalisation of the Rupee offers numerous advantages for the Indian economy:</p><ul><li><strong>Reduced dependency on USD:</strong> It lessens India's reliance on the <strong>US Dollar</strong>, mitigating risks associated with its volatility and geopolitical weaponisation.</li><li><strong>Strengthening India’s forex reserves:</strong> Greater use of the Rupee in trade reduces the need to hold large dollar reserves, potentially freeing up these reserves for other strategic uses.</li><li><strong>Better bargaining power of Indian businesses:</strong> Indian exporters and importers can negotiate better terms when transacting in their home currency, reducing currency conversion costs and risks.</li><li><strong>Less exposure to currency volatility:</strong> Businesses face reduced exposure to exchange rate fluctuations between the Rupee and other major currencies, leading to more predictable pricing and profits.</li><li><strong>Enhanced global standing:</strong> A more internationalised Rupee reflects India's growing economic influence and strengthens its position in the global financial architecture.</li></ul><h4>Key Challenges in Internationalisation</h4><p>Despite the benefits, several challenges hinder the full internationalisation of the Rupee:</p><ul><li><strong>Limited full convertibility:</strong> The <strong>partial convertibility in the capital account</strong> restricts the free flow of capital, which is crucial for a truly international currency.</li><li><strong>Less need for other countries to hold INR:</strong> Without widespread acceptance and utility, other countries have limited incentives to hold significant reserves of Indian Rupees.</li><li><strong>Limited share in global exports:</strong> India's relatively small share in global exports means there is less natural demand for the Rupee for trade settlement purposes.</li><li><strong>Rupee may become more vulnerable to external shocks:</strong> Increased international exposure could make the Rupee more susceptible to global economic and financial shocks.</li><li><strong>India’s lesser control on rupee supply:</strong> As the Rupee becomes an international currency, the RBI might have less direct control over its supply in global markets, impacting monetary policy effectiveness.</li></ul><h4>Steps for Further Internationalisation</h4><p>To overcome challenges and accelerate the internationalisation process, several strategic steps can be taken:</p><ul><li><strong>More liberalised settlements in INR:</strong> Both within India and overseas, policies should be further liberalised to encourage and simplify Rupee-denominated transactions.</li><li><strong>India must expand its reach in the global financial market:</strong> Increasing India's presence and influence in international financial institutions and markets will boost confidence in the Rupee.</li><li><strong>Transition to an export-oriented economy:</strong> Reducing the <strong>trade deficit</strong> by boosting exports will create more natural demand for the Rupee globally.</li></ul>
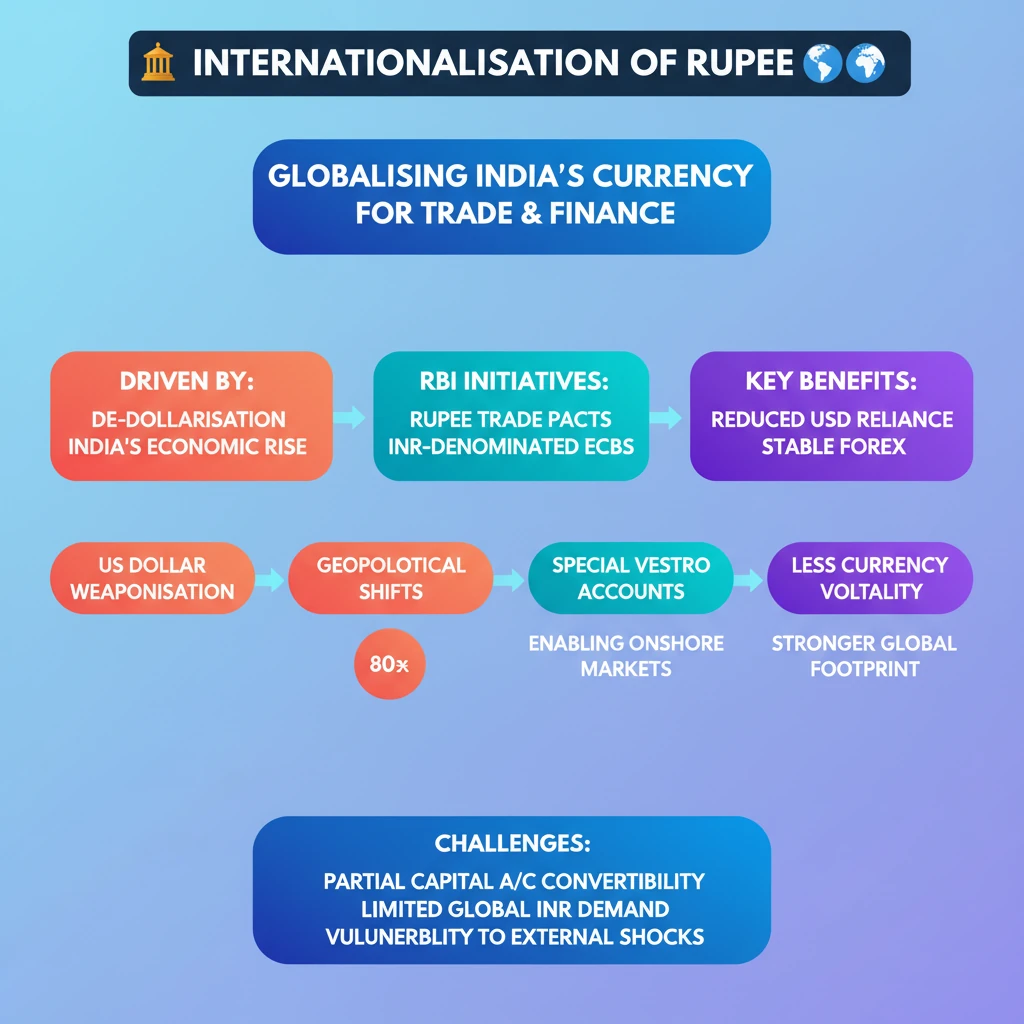
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Internationalisation of Rupee means increasing its use in cross-border trade and financial transactions.
- •It is driven by de-dollarisation trends, US dollar weaponisation, and India's growing economic stature.
- •RBI initiatives include Rupee trade settlement mechanisms (e.g., with Russia) and enabling INR-denominated ECBs.
- •Benefits include reduced USD dependency, stronger forex reserves, and less currency volatility for businesses.
- •Challenges involve partial capital account convertibility, limited global demand for INR, and potential vulnerability to external shocks.
- •Key steps include further liberalisation of Rupee settlements and boosting India's global export share.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) official circulars and press releases (e.g., International Trade Settlement in Indian Rupees, July 2022)
•Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Foreign Trade Policy (2022)
•Reports of the Committee on Capital Account Convertibility (Tarapore Committee)