Employment, Skill Development and Innovation - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Employment, Skill Development and Innovation
Medium⏱️ 15 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
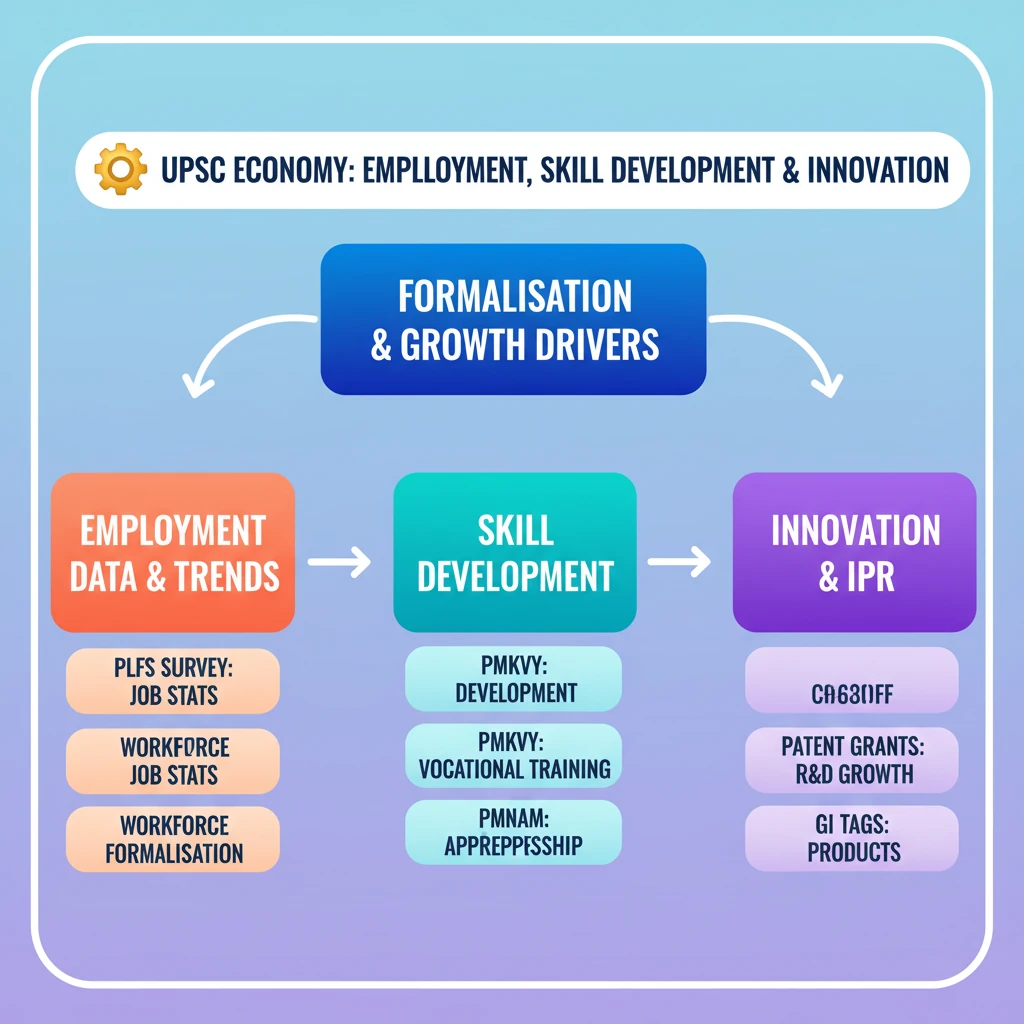
<h4>India's Transition Towards Workforce Formalisation</h4><p>India is experiencing a significant shift towards the <strong>formalisation of its workforce</strong>. This process involves moving workers from the informal sector, characterized by lack of social security and regulatory oversight, into the formal sector.</p><p>Formalisation often leads to better working conditions, social security benefits, and adherence to labor laws. It is a crucial indicator of economic development and improved living standards for workers.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Drivers of Formalisation:</strong></p><ul><li>Government initiatives promoting registration and compliance.</li><li>Growth of organized industries and services.</li><li>Increased awareness among workers about their rights.</li></ul></div><h4>Central Trade Unions (CTUs) Demand for Labour Welfare</h4><p><strong>Central Trade Unions (CTUs)</strong> play a vital role in advocating for the rights and welfare of workers in India. They represent a large segment of the organized and unorganized labor force.</p><p>CTUs consistently demand better working conditions, fair wages, social security, and protection against exploitation. Their collective bargaining power influences labor policy formulation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Common Demands by CTUs:</strong></p><ul><li>Implementation of a <strong>universal minimum wage</strong>.</li><li>Strengthening of <strong>social security schemes</strong> like EPF and ESI.</li><li>Protection of <strong>trade union rights</strong> and collective bargaining.</li><li>Ensuring job security and preventing arbitrary retrenchment.</li></ul></div><h4>Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Report</h4><p>The <strong>Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)</strong> is a crucial survey conducted by the <strong>National Sample Survey Office (NSSO)</strong> under the <strong>Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)</strong>.</p><p>It provides estimates of key employment and unemployment indicators in India. These indicators include the <strong>Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR)</strong>, <strong>Worker Population Ratio (WPR)</strong>, and <strong>Unemployment Rate (UR)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Purpose of PLFS:</strong></p><ul><li>To estimate employment and unemployment indicators in both usual status and current weekly status.</li><li>To assess the labor force dynamics in both rural and urban areas.</li><li>To provide data for policy formulation related to employment and skill development.</li></ul></div><h4>India Grants Record Patents</h4><p>India has witnessed a significant increase in the number of <strong>patents granted</strong>, indicating a growing focus on innovation and research and development (R&D) within the country.</p><p>A patent grants exclusive rights to an inventor for a limited period, preventing others from making, using, or selling the invention without permission. This incentivizes innovation.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> Record patent grants reflect India's progress in its <strong>innovation ecosystem</strong>, a key aspect of economic growth and global competitiveness (GS Paper III - Economy, Science & Technology).</p></div><h4>India’s Geographical Indication Landscape</h4><p>A <strong>Geographical Indication (GI) tag</strong> is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. India's GI landscape is expanding.</p><p>GI tags protect the unique identity of products, prevent misuse of names, and promote the economic prosperity of producers in a specific region. Examples include <strong>Darjeeling Tea</strong> and <strong>Kanchipuram Silk</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Benefits of GI Tags:</strong></p><ul><li>Confers <strong>legal protection</strong> to GI products in India.</li><li>Prevents <strong>unauthorized use</strong> of a registered GI by others.</li><li>Promotes the <strong>economic prosperity</strong> of the producers of GI goods.</li><li>Helps in <strong>export promotion</strong> and international recognition.</li></ul></div><h4>PM Internship Scheme</h4><p>The <strong>Prime Minister's National Apprenticeship Mela (PMNAM)</strong>, often referred to as a PM Internship Scheme, is an initiative aimed at boosting apprenticeship opportunities in India.</p><p>The scheme connects aspiring individuals with companies seeking to onboard apprentices, providing practical training and enhancing employability. It focuses on skill development and industry readiness.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Objectives of PMNAM:</strong></p><ul><li>To provide <strong>on-the-job training</strong> to youth.</li><li>To bridge the gap between academic learning and industry requirements.</li><li>To enhance the <strong>employability</strong> of the Indian workforce.</li><li>To promote a culture of apprenticeship across various sectors.</li></ul></div><h4>Global Innovation Index 2024</h4><p>The <strong>Global Innovation Index (GII)</strong> is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation. It is published by the <strong>World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)</strong>.</p><p>India's performance in the GII is closely watched as it reflects the country's innovation ecosystem, including R&D investment, intellectual property, and technological output.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> India's consistent improvement in GII rankings can be cited in answers related to economic reforms, 'Make in India', and boosting indigenous innovation (GS Paper III).</p></div><h4>PRAVAH Portal</h4><p>The <strong>PRAVAH Portal</strong> (Platform for Regulatory Application, Vetting and Authorisation) is an initiative launched by the <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong>.</p><p>Its primary objective is to streamline and expedite the application and approval processes for various regulatory clearances and authorizations required from the RBI. This enhances ease of doing business.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Features of PRAVAH Portal:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Online application submission</strong> for various licenses and authorizations.</li><li><strong>Transparency</strong> in the application tracking process.</li><li><strong>Reduced processing time</strong> for regulatory approvals.</li><li>A single platform for all RBI regulatory clearances.</li></ul></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Workforce formalisation is crucial for social security and economic development.
- •PLFS provides vital data on employment trends and unemployment rates.
- •India's innovation ecosystem is growing, reflected in record patent grants and GII ranking.
- •GI tags protect unique regional products and boost local economies.
- •Government schemes like PMKVY and PMNAM are key to skill development and employability.
- •PRAVAH Portal streamlines RBI regulatory approvals, enhancing ease of doing business.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) - PLFS Reports
•World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) - Global Innovation Index Reports
•Controller General of Patents, Designs & Trade Marks (CGPDTM) - Annual Reports
•Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) - PMKVY Guidelines
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) - Press Releases and Notifications on PRAVAH Portal