India’s Transition Towards Workforce Formalization - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India’s Transition Towards Workforce Formalization
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>India's Journey Towards Workforce Formalization</h4><p>India's economy is undergoing a significant transformation towards <strong>workforce formalization</strong>. This shift is redefining job structures, enhancing employment security, and expanding social benefits for millions of workers across the nation.</p><p>The primary goal of this transition is to ensure a larger segment of the population is covered by comprehensive <strong>social security systems</strong>. This integration offers greater economic stability and a more secure future for individuals and their families.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This formalization drive, significantly supported by the <strong>Employee’s Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO)</strong>, plays a crucial role in boosting economic stability by bringing more workers under its protective social security umbrella.</p></div><h4>Understanding EPFO and its Role</h4><p>The <strong>Employee’s Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO)</strong> stands as one of the world’s largest social security organizations. It is dedicated to providing a wide array of social security benefits to millions of workers throughout India.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Establishment:</strong> EPFO was established under the <strong>Employees’ Provident Funds & Miscellaneous Provisions Act of 1952</strong>.</p><p><strong>Reach:</strong> As per EPFO’s Annual Report 2022-23, it manages over <strong>29.88 crore accounts</strong>, highlighting its extensive reach and the vast scale of financial transactions it oversees.</p><p><strong>Administrative Control:</strong> The EPFO operates under the administrative control of the <strong>Ministry of Labour & Employment, Government of India</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Benefits Provided by EPFO</h4><p>EPFO ensures long-term financial security for its members through several crucial schemes and provisions:</p><ul><li><strong>Retirement Funds:</strong> Provides a robust system for retirement savings.</li><li><strong>Insurance:</strong> Offers insurance coverage under the <strong>Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance (EDLI) Scheme, 1976</strong>.</li><li><strong>Monthly Pensions:</strong> Facilitates monthly pension payouts via the <strong>Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS), 1995</strong>.</li><li><strong>Partial Withdrawals:</strong> Allows partial withdrawals under the <strong>Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) Scheme, 1952</strong>, for emergencies, education, or home purchases, making it a versatile financial tool.</li></ul><h4>EPFO's Contribution to Increased Formalization</h4><p>EPFO data clearly illustrates a significant surge in workforce formalization:</p><ul><li><strong>Membership Growth:</strong> From <strong>2017 to 2024</strong>, over <strong>6.91 crore members</strong> joined EPFO.</li><li><strong>Record New Registrations:</strong> The fiscal year <strong>2022-23</strong> witnessed a record <strong>1.38 crore new members</strong> registering.</li><li><strong>Steady Monthly Additions:</strong> In <strong>July 2024</strong> alone, nearly <strong>20 lakh new members</strong> were added, indicating a consistent increase in monthly registrations.</li><li><strong>Fund Transfers:</strong> Many members consistently transfer their funds when changing jobs, ensuring uninterrupted access to their social security benefits.</li><li><strong>Youth and First-time Job Seekers:</strong> A substantial portion of new EPFO members are <strong>youth</strong>, with many being <strong>first-time job seekers</strong>, signifying a growing formal entry into the workforce.</li><li><strong>Inclusive Workforce:</strong> An increasing number of <strong>female workers</strong> are registering with EPFO, reflecting a positive trend towards a more inclusive and formalized workforce.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>These recent EPFO registration figures underscore the expansion of <strong>formal jobs</strong> in India, providing more employees with essential benefits such as <strong>job security, retirement savings, and insurance</strong>.</p></div><h4>Addressing Gender Inequality in Formal Employment</h4><p>Despite progress, <strong>women</strong> continue to face disproportionate barriers to securing formal employment. These challenges are multifaceted and include:</p><ul><li><strong>Socio-cultural Constraints:</strong> Traditional societal norms and expectations.</li><li><strong>Lack of Childcare Services:</strong> Insufficient support systems for working mothers.</li><li><strong>Gender Bias:</strong> Prejudices and discrimination prevalent in the workplace.</li></ul><h4>India’s Initiatives for Workforce Formalization</h4><p>The Government of India has launched several key initiatives to accelerate the formalization of its workforce:</p><ul><li><strong>e-Shram Portal:</strong> A national database for unorganized workers to avail social security benefits.</li><li><strong>Udyam Portal:</strong> Simplifies registration for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), encouraging formal business operations.</li><li><strong>Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-dhan Yojana:</strong> A pension scheme for unorganized workers.</li></ul><h4>Labour Reforms for Formalization</h4><p>The government has undertaken significant <strong>labour reforms</strong> to modernize archaic laws and promote formal employment:</p><ul><li><strong>Social Security Code, 2020:</strong> Consolidates laws relating to social security.</li><li><strong>Industrial Relations Code, 2020:</strong> Simplifies regulations concerning trade unions, industrial disputes, and standing orders.</li><li><strong>Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020:</strong> Focuses on safety, health, and working conditions of workers.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>These <strong>labour codes</strong> aim to simplify existing labour laws, enhance working conditions, and streamline the process for businesses to hire formally, thereby reducing informality.</p></div><h4>Government Digital Payment Systems</h4><p>Government initiatives like <strong>Goods and Services Tax (GST)</strong> and <strong>Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)</strong> are instrumental in reducing informality. They encourage businesses to operate with greater transparency and contribute effectively to the tax system, fostering a more formalized economy.</p>
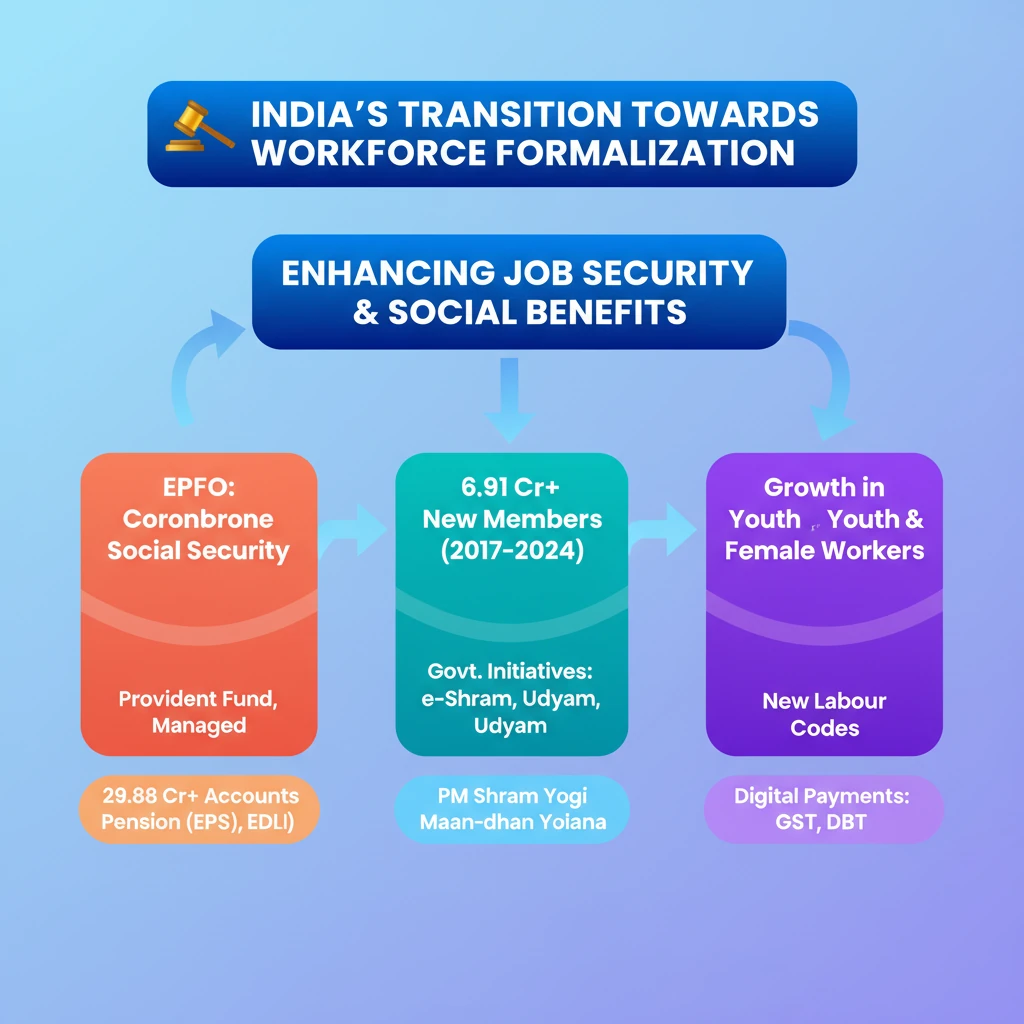
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India is experiencing a significant transition towards workforce formalization, enhancing job security and social benefits.
- •EPFO is a crucial institution, managing over 29.88 crore accounts and providing retirement funds, pensions (EPS), and insurance (EDLI).
- •EPFO has seen substantial growth, with over 6.91 crore new members (2017-2024), including a notable increase in youth and female workers.
- •Government initiatives like e-Shram, Udyam Portal, PM Shram Yogi Maan-dhan Yojana, and new Labour Codes are driving formalization.
- •Digital payment systems like GST and DBT also contribute by promoting transparency in economic transactions.
- •Challenges like gender inequality in formal employment persist due to socio-cultural constraints and lack of support services.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•EPFO’s Annual Report 2022-23 (as cited in source)