Balance of Payments: Components & Current/Capital Accounts - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Balance of Payments: Components & Current/Capital Accounts
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
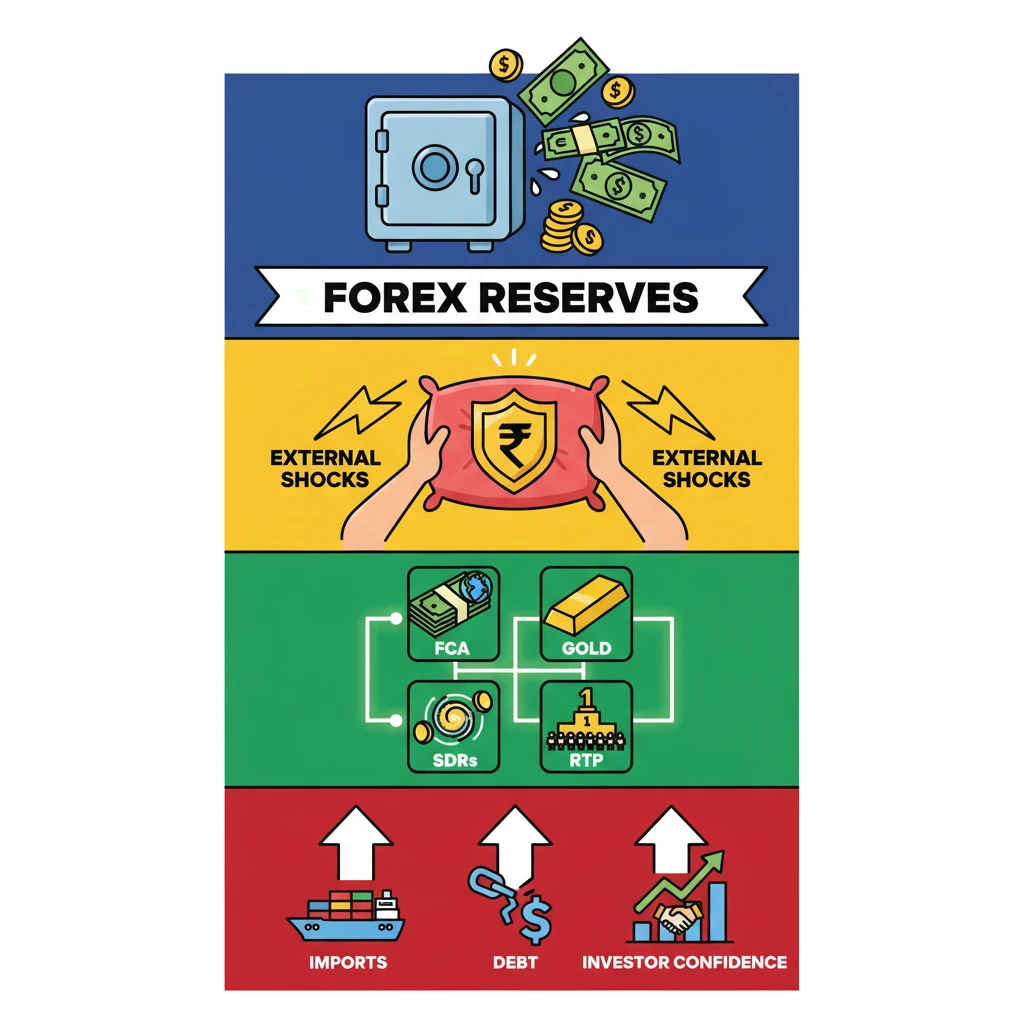
<h4>Understanding Forex Reserves: India's Financial Shield</h4><p><strong>Indian forex reserves</strong> are crucial assets held by the <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong>. These reserves are primarily denominated in foreign currencies.</p><p>Their main purpose is to act as a <strong>financial cushion</strong>, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet India's external obligations and to stabilize the nation’s economy and its currency, the <strong>Indian Rupee</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Role:</strong> Forex reserves are vital for maintaining <strong>macroeconomic stability</strong> and investor confidence in the Indian economy.</p></div><h4>Components of Indian Forex Reserves</h4><p>The Indian forex reserves are composed of several key elements, with foreign currencies being the most significant part.</p><h5>Foreign Currencies Assets (FCA)</h5><p>The bulk of India's forex reserves consists of <strong>foreign currencies</strong>. These typically include major global currencies like the <strong>US Dollar (USD)</strong>, <strong>Euro (EUR)</strong>, and <strong>British Pound (GBP)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Purpose of FCAs:</strong> These currencies provide essential liquidity, facilitating international trade transactions, payments for imports, and managing external debt.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> While the <strong>US Dollar</strong> forms the largest share, the composition of FCAs can change based on RBI's diversification strategy and global currency movements. This impacts India's vulnerability to specific currency fluctuations.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Forex reserves are foreign currency assets held by the RBI, primarily USD, EUR, GBP.
- •They act as a financial cushion for external obligations and currency stabilization.
- •Key components include Foreign Currency Assets, Gold, SDRs, and Reserve Tranche Position.
- •Reserves are crucial for financing imports, managing external debt, and boosting investor confidence.
- •The 1991 BoP crisis highlighted the critical importance of maintaining sufficient forex reserves.
- •RBI actively manages reserves for exchange rate stability and macroeconomic resilience.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Annual Reports/Bulletins
•Economic Survey of India