What is Decarbonisation of the Steel Sector? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Decarbonisation of the Steel Sector?
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Decarbonisation of the Steel Sector</h4><p><strong>Decarbonisation of the Steel Sector</strong> refers to the critical process of reducing <strong>carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>) emissions</strong> and the overall <strong>carbon footprint</strong> associated with steel production.</p><p>This initiative is fundamental to producing <strong>Green Steel</strong>, which is manufactured with significantly lower or zero carbon emissions.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary goal is to mitigate <strong>climate change</strong> and ensure <strong>sustainability</strong> within one of the world's most energy-intensive industries.</p></div><h4>India's Steel Industry: A Global Perspective</h4><p><strong>India</strong> holds the position of the <strong>second-largest crude steel producer globally</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>As of <strong>FY 2023-24</strong>, India's crude steel capacity reached <strong>179.5 million tonnes</strong>. It is also the <strong>largest producer of sponge iron</strong>, with a capacity of <strong>55 million tonnes</strong>.</p></div><p>Despite its significant production, India's <strong>per capita steel consumption</strong> is relatively low at <strong>97.7 kg (FY 2024)</strong>, compared to the global average of <strong>221.8 kg (2022)</strong>.</p><p>The <strong>National Steel Policy 2017</strong> aims to boost this consumption to <strong>160 kg by 2030</strong>, anticipating substantial growth.</p><p>Currently, India remains a <strong>net importer of steel</strong>. There was a <strong>25% increase in imports</strong> and a <strong>7% decrease in exports</strong> during the <strong>April to August (FY25)</strong> period.</p><h4>India's Commitment to Climate Action</h4><p>India is deeply committed to a <strong>low-carbon development pathway</strong>, despite its relatively small historical contribution to global <strong>Greenhouse Gas (GHG) accumulation</strong> (only <strong>4%</strong>).</p><p>This commitment is significant, especially considering India houses <strong>17% of the global population</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>India's <strong>Revised Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)</strong> prominently feature a focus on expanding <strong>renewable energy</strong> and actively <strong>greening industrial sectors</strong>.</p></div><p>To achieve its ambitious <strong>net-zero target by 2070</strong>, the entire industrial sector, including the critical <strong>steel industry</strong>, must undergo comprehensive decarbonisation.</p><h4>Why Decarbonising Steel is Crucial for India</h4><p>The <strong>steel industry</strong> is a major contributor to India's overall emissions, accounting for approximately <strong>10-12% of the country's total emissions</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Therefore, its decarbonisation is not just an industrial upgrade but a fundamental requirement for India to successfully meet its national and international <strong>climate goals</strong>.</p></div><p>Recognizing this urgency, the <strong>Ministry of Steel</strong> has established <strong>14 dedicated task forces</strong>.</p><p>These task forces are focused on:</p><ul><li><strong>Incentivizing green steel production</strong>.</li><li>Enabling various <strong>decarbonisation levers</strong> (e.g., technology, policy).</li><li>Providing robust support for the sector's <strong>transition</strong> towards cleaner production methods.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
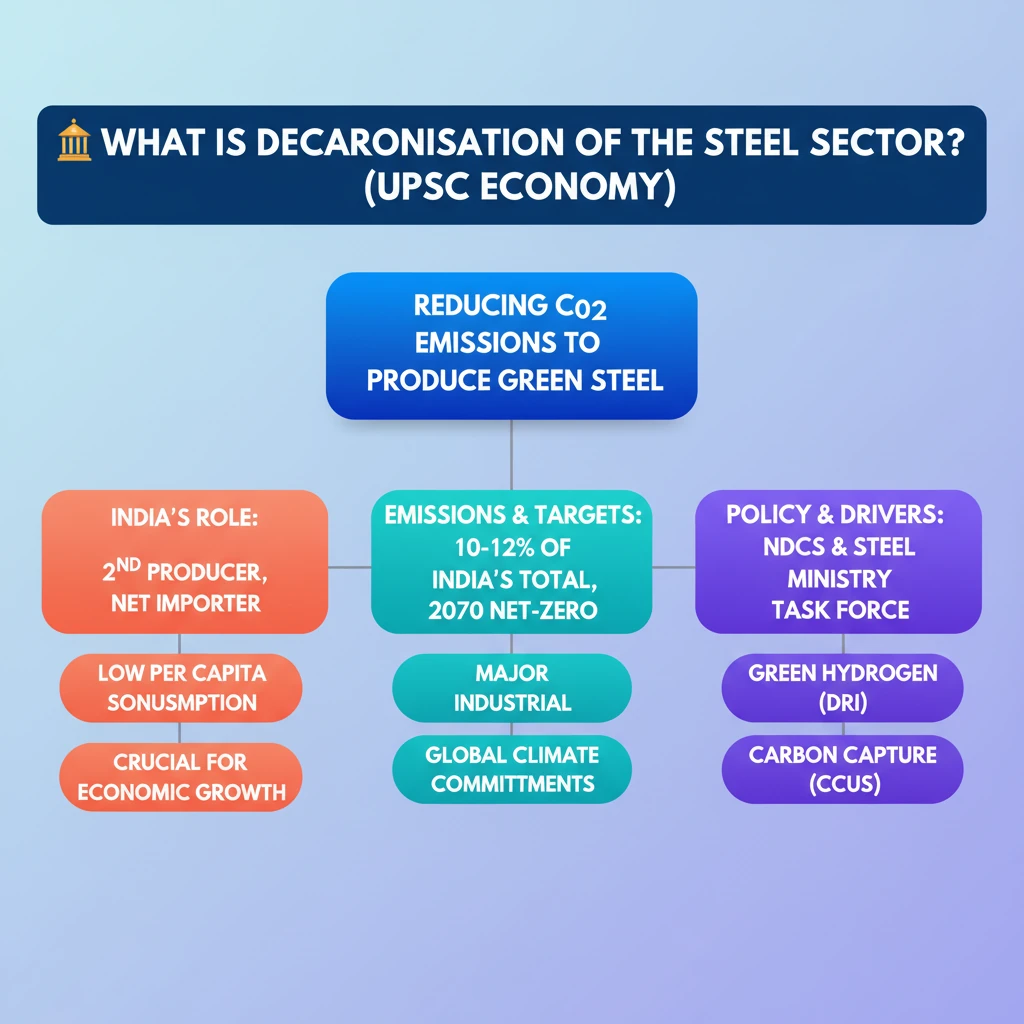
- •Decarbonisation of steel aims to reduce CO2 emissions and produce Green Steel.
- •India is the 2nd largest crude steel producer but a net importer, with low per capita consumption.
- •Steel sector contributes 10-12% of India's total emissions, making decarbonisation crucial for 2070 net-zero target.
- •India's NDCs and Ministry of Steel task forces are driving this transition.
- •Key technologies include green hydrogen-based DRI and Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS).
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content