India Surpasses USD 1 Trillion in FDI - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
India Surpasses USD 1 Trillion in FDI
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
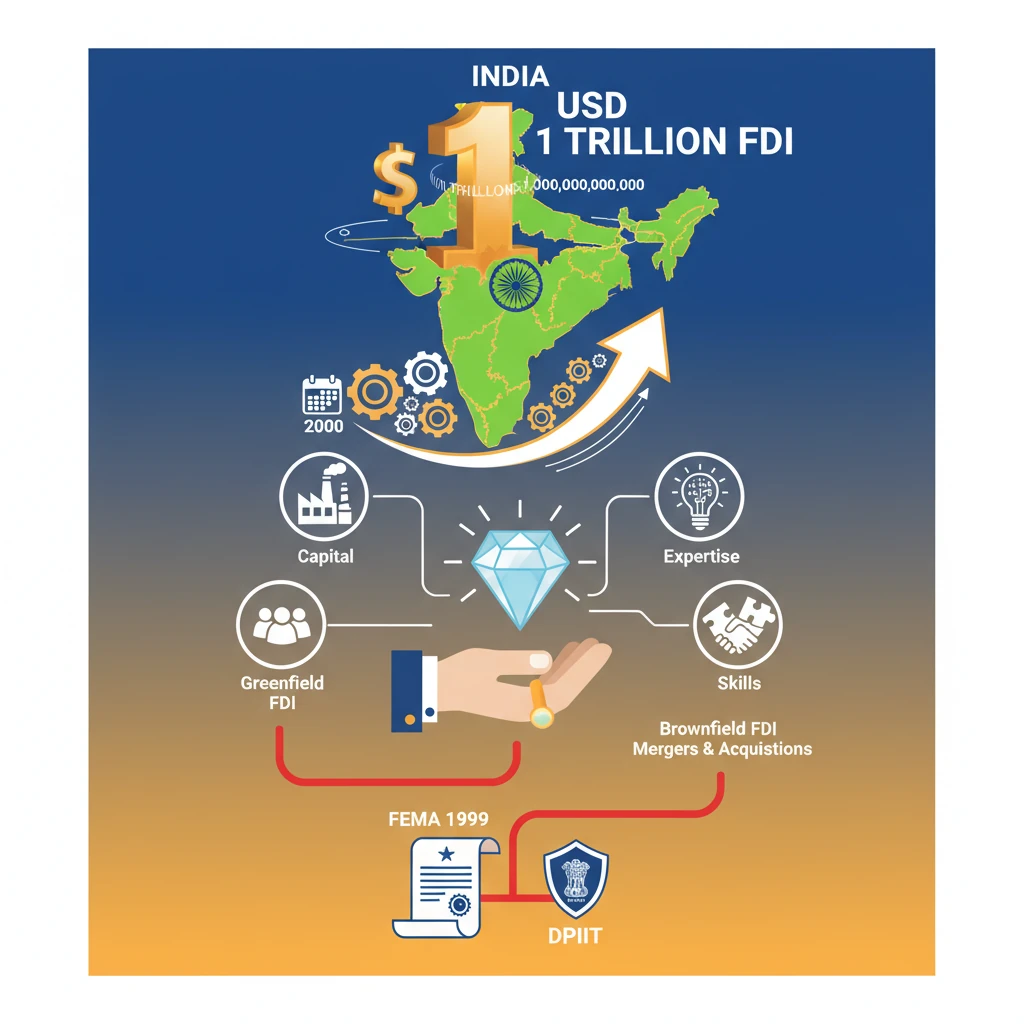
<h4>India's Milestone in Global Investment</h4><p>India has achieved a significant milestone, surpassing <strong>USD 1 trillion</strong> in <strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</strong> inflows. This cumulative figure has been recorded <strong>since the year 2000</strong>.</p><p>This remarkable achievement underscores India's increasing attractiveness as a <strong>global investment hub</strong>. It reflects the nation's growing economic potential and stable policy environment.</p><div class='highlight-box'>India has accumulated over <strong>USD 1 Trillion in FDI inflows</strong> since <strong>2000</strong>, signifying its emergence as a preferred destination for global capital.</div><h4>Understanding Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</h4><p><strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</strong> is a crucial form of international investment. It involves an entity from one country making a direct investment into a business in another country.</p><p>The defining characteristic of FDI is the establishment of a <strong>controlling interest</strong>. This implies a long-term relationship and significant influence over the management of the foreign enterprise.</p><div class='info-box'><strong>FDI Definition:</strong> An investment by a company or individual in one country into a business interest located in another country, establishing a <strong>controlling ownership</strong>.</div><h4>Beyond Capital: The Broader Impact of FDI</h4><p>FDI is not merely about the inflow of <strong>capital</strong>. It encompasses a much broader transfer of resources that are vital for economic development.</p><p>These additional contributions include essential <strong>expertise</strong>, advanced <strong>technology</strong>, and valuable <strong>skills</strong>. Such transfers significantly boost the capabilities of the host country's economy.</p><div class='key-point-box'><strong>Key Contributions of FDI:</strong> Beyond capital, FDI brings <strong>managerial expertise</strong>, <strong>cutting-edge technology</strong>, and <strong>specialized skills</strong>, fostering overall economic growth and development.</div><h4>Types of Foreign Direct Investment</h4><p>FDI can broadly be categorized into two primary types, each with distinct characteristics and implications for the host economy.</p><ul><li><strong>Greenfield Investment</strong>: This involves establishing completely <strong>new business operations</strong> from the ground up in a foreign country.</li><li><strong>Brownfield Investment</strong>: This type of investment occurs through <strong>mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures</strong>, utilizing existing facilities and infrastructure.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><strong>Greenfield Investment:</strong> Creating entirely <strong>new production facilities</strong> or operations. Offers <strong>high control</strong> and <strong>customization</strong>.<br><strong>Brownfield Investment:</strong> Expanding through <strong>M&A</strong> or <strong>JVs</strong> by acquiring or investing in <strong>existing assets</strong>. May offer less control than Greenfield but leverages existing structures.</div><h4>Governance and Regulation of FDI in India</h4><p>The regulatory framework for <strong>FDI in India</strong> is robust and well-defined. It ensures transparency and adherence to national economic objectives.</p><p><strong>FDI</strong> inflows in India are primarily governed by the provisions of the <strong>Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999</strong>. This act provides the legal framework for foreign exchange transactions.</p><p>The administration and promotion of <strong>FDI</strong> in the country fall under the purview of the <strong>Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)</strong>, part of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'>Remember that <strong>FEMA, 1999</strong>, is the key legislation governing foreign exchange, including <strong>FDI</strong>, while <strong>DPIIT</strong> is the nodal government agency responsible for its promotion and policy formulation in India.</div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •India has surpassed <strong>USD 1 Trillion in cumulative FDI inflows</strong> since <strong>2000</strong>, highlighting its global investment appeal.
- •<strong>FDI</strong> involves a <strong>controlling interest</strong> and brings <strong>capital, expertise, technology, and skills</strong> to the host country.
- •<strong>Greenfield FDI</strong> creates new operations; <strong>Brownfield FDI</strong> involves mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures of existing assets.
- •<strong>FDI in India</strong> is governed by the <strong>Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999</strong>, and administered by <strong>DPIIT</strong>.
- •FDI is crucial for India's <strong>economic growth, job creation, technology transfer</strong>, and achieving targets like becoming a <strong>USD 5 trillion economy</strong>.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on Foreign Direct Investment
•Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999