What is Capital Expenditure? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Capital Expenditure?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
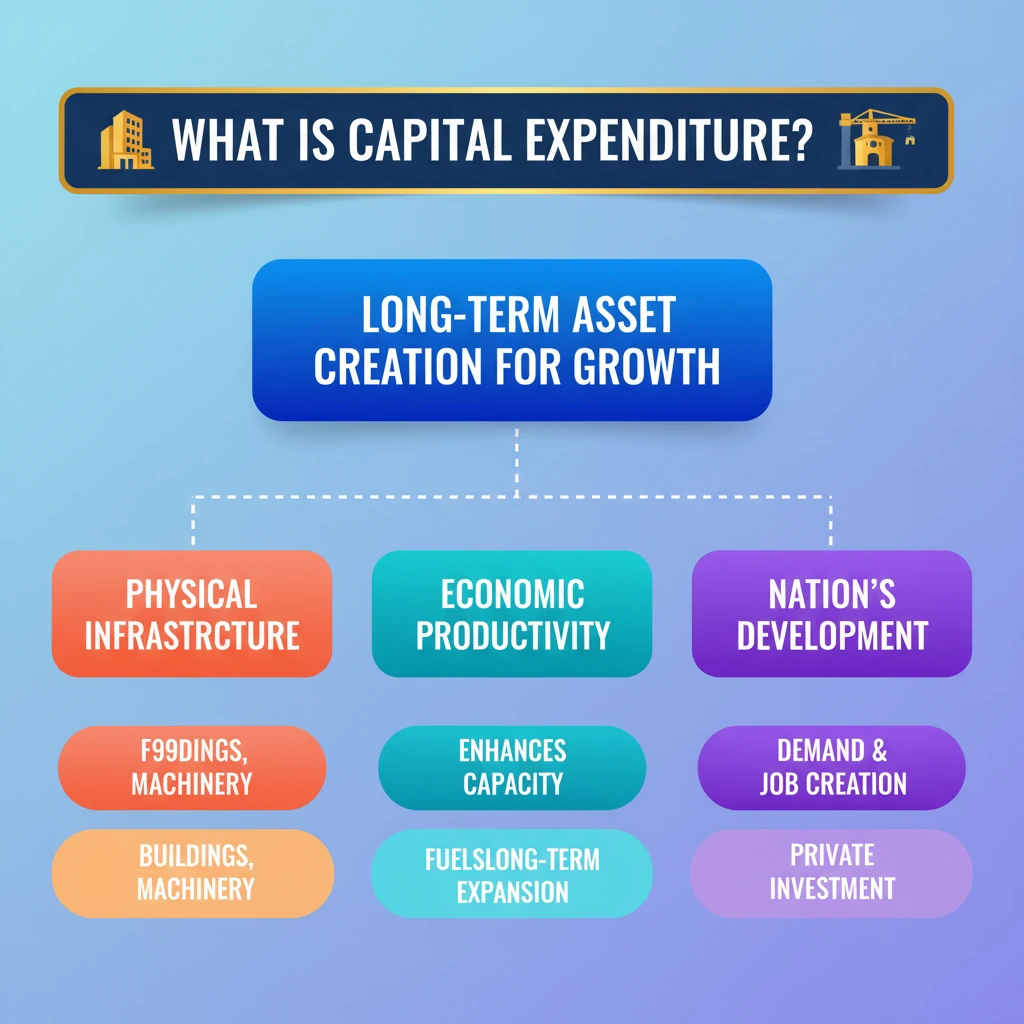
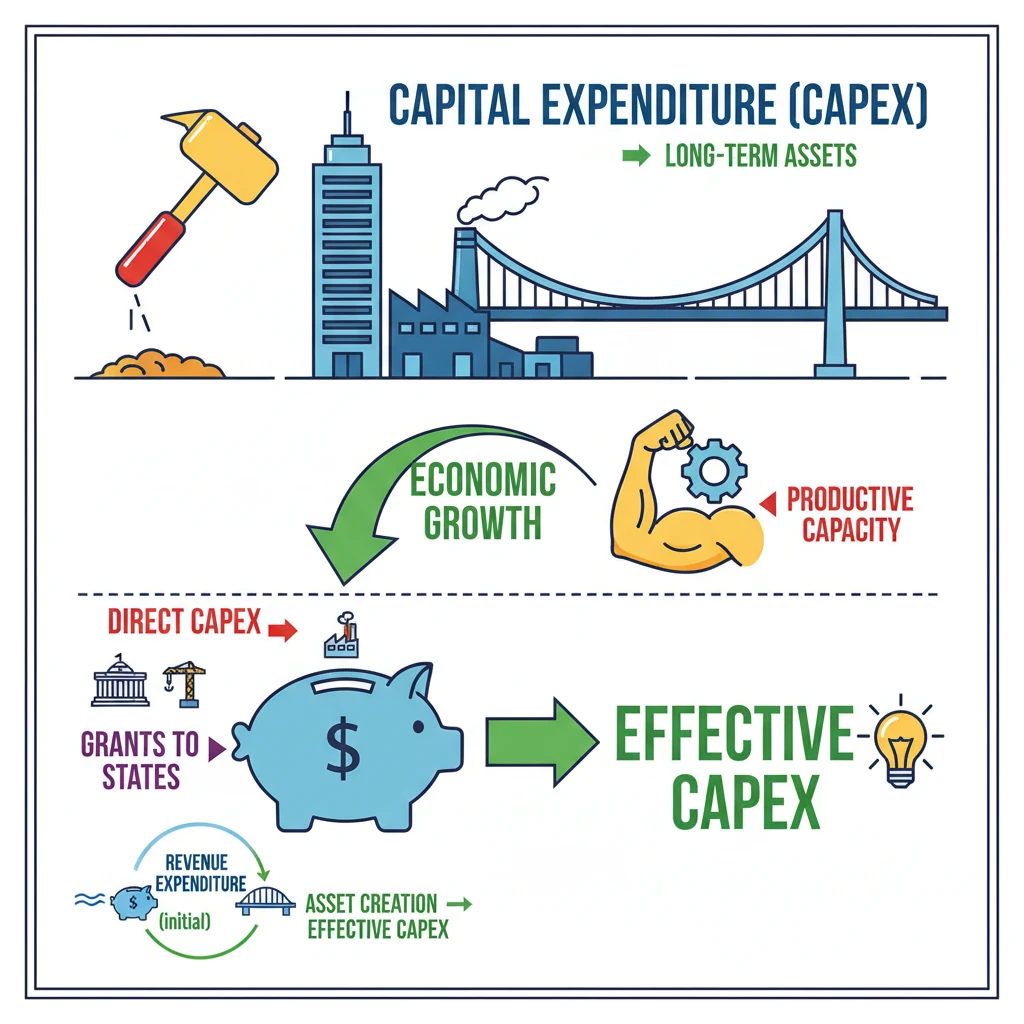
<h4>Understanding Capital Expenditure (Capex)</h4><p><strong>Capital Expenditure (Capex)</strong> refers to the funds allocated by the government for the acquisition, construction, or improvement of <strong>physical assets</strong>. These assets are typically long-term and are expected to provide benefits over many years.</p><p>This type of expenditure is crucial for a nation's long-term economic growth and development. It directly contributes to building the productive capacity of the economy.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of Capital Expenditure:</strong></p><ul><li>Creates or acquires <strong>assets</strong> (e.g., roads, bridges, hospitals, schools).</li><li>Results in a reduction of <strong>liabilities</strong> (e.g., repayment of loans).</li><li>Often involves a large, one-time investment.</li><li>Benefits accrue over an extended period.</li></ul></div><h4>Components of Capital Expenditure</h4><p>Capex primarily involves spending on tangible assets. These can range from large-scale infrastructure projects to essential machinery and equipment for government operations.</p><p>Examples include investments in <strong>infrastructure</strong> like highways and railways, construction of <strong>buildings</strong> such as government offices or public housing, and procurement of <strong>machinery and equipment</strong> for various public services.</p><h4>Introducing Effective Capital Expenditure</h4><p>The concept of <strong>Effective Capital Expenditure</strong> was introduced to provide a more comprehensive picture of the government’s true public investment. It accounts for both direct and indirect capital formation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>While <strong>grants-in-aid for creating assets</strong> (like roads and schools) are initially classified as <strong>revenue expenditure</strong> in government accounts, they undeniably contribute to the creation of <strong>capital assets</strong>. This new concept captures that vital indirect investment.</p></div><p>This reclassification helps in better assessing the overall impact of government spending on asset creation, even when the funds are routed through states or other agencies.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition: Effective Capital Expenditure</strong></p><p>Effective Capital Expenditure is defined as the sum of:</p><ul><li><strong>Capital Expenditure</strong> (direct asset creation by the central government)</li><li><strong>Grants for Creation of Capital Assets</strong> (funds given to states/UTs/other bodies specifically for asset creation)</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the distinction between <strong>Capital Expenditure</strong> and <strong>Effective Capital Expenditure</strong> is crucial for analyzing government budgets. Questions often test your ability to differentiate between various types of government spending and their implications for economic growth (<strong>GS Paper 3: Economy</strong>).</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Capital Expenditure (Capex) creates long-term physical assets like infrastructure, buildings, and machinery.
- •It is crucial for a nation's long-term economic growth and enhances productive capacity.
- •Effective Capital Expenditure includes direct Capex plus grants to states for capital asset creation.
- •Grants-in-aid for asset creation are initially revenue expenditure but contribute to effective Capex.
- •Higher Capex stimulates demand, creates jobs, and crowds in private investment, boosting overall economic activity.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Union Budget Documents (various years)
•Economic Survey of India (various years)
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Publications on Public Finance