What Differentiates Floating Exchange Rate Dynamics from Stabilized Arrangement? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What Differentiates Floating Exchange Rate Dynamics from Stabilized Arrangement?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
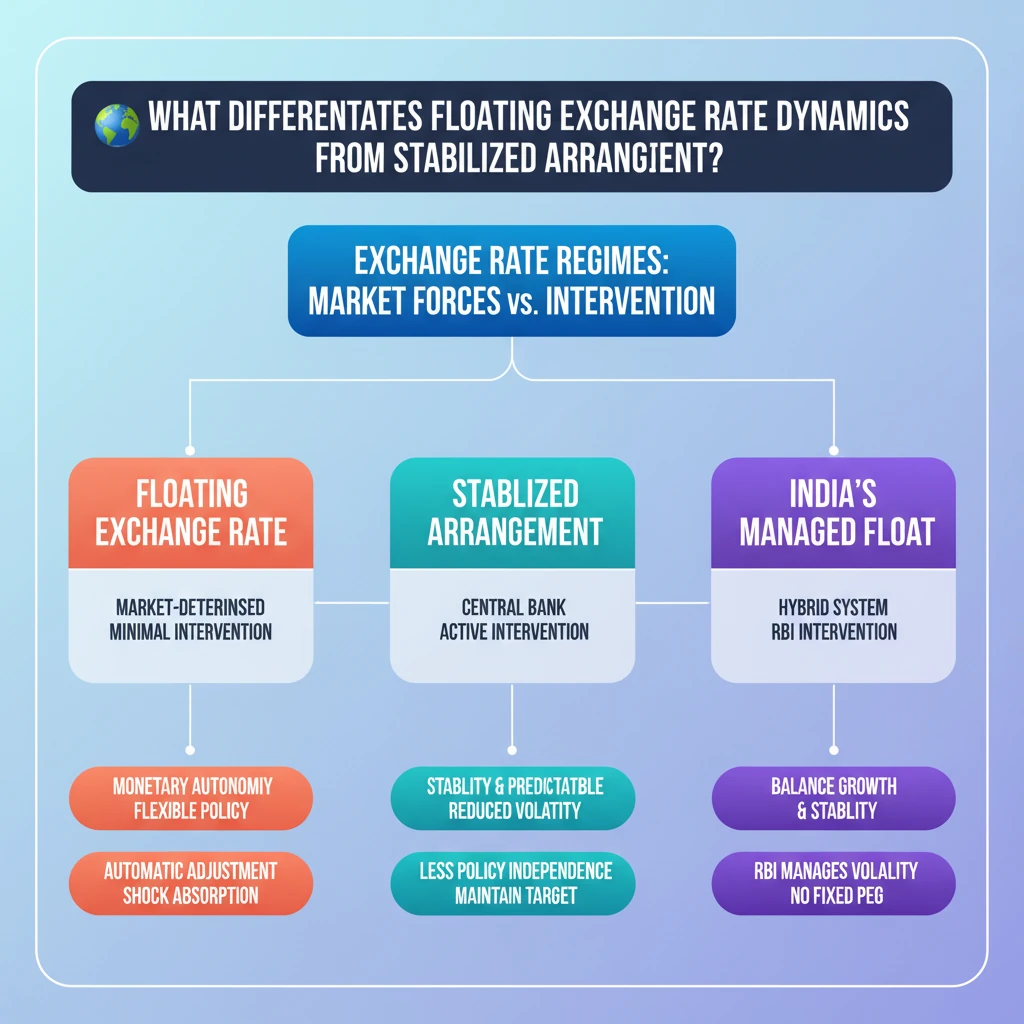
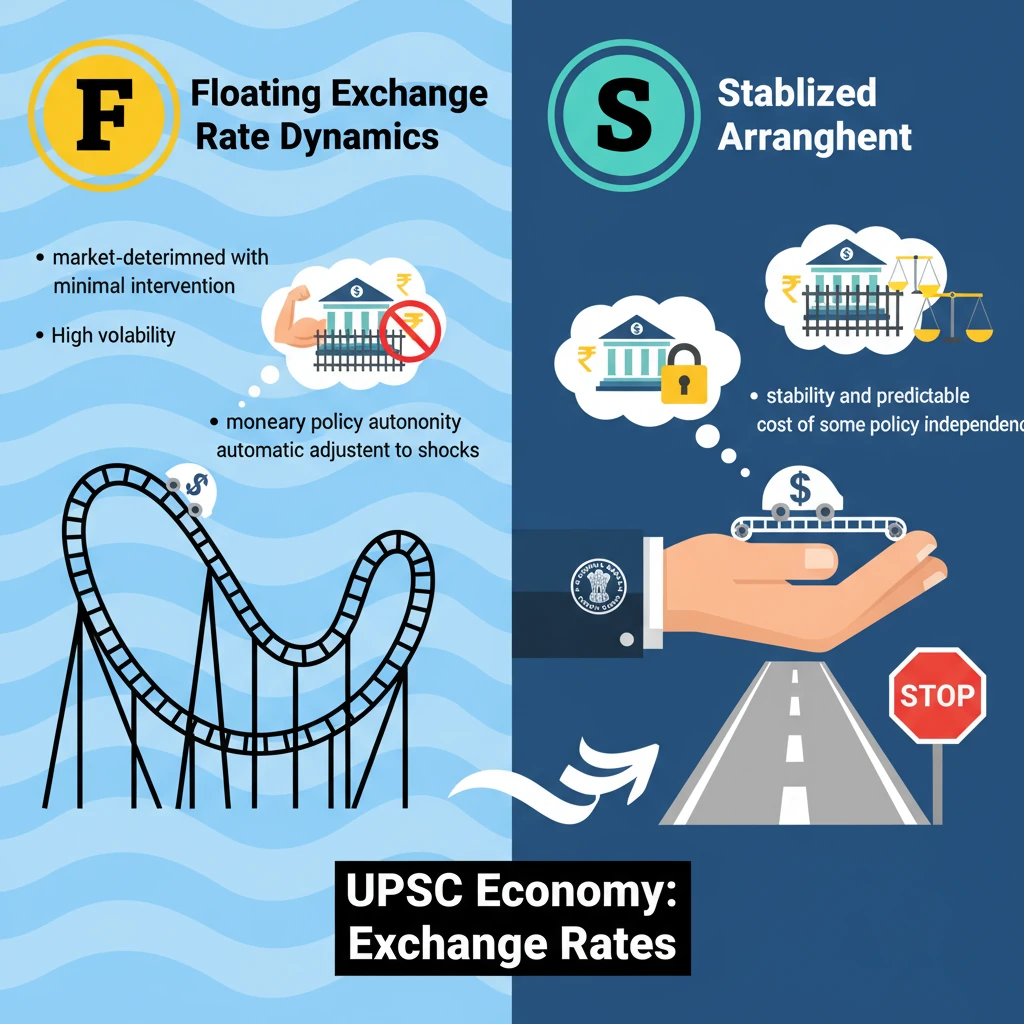
<h4>Understanding Exchange Rate Regimes</h4><p>The value of a nation's currency relative to others is a critical aspect of its economic health. This value is determined by different mechanisms, broadly categorized into <strong>floating exchange rates</strong> and <strong>stabilized arrangements</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>These arrangements dictate the degree of <strong>government intervention</strong> or <strong>central bank involvement</strong> in managing the currency's value in the global foreign exchange market.</p></div><h4>Floating Exchange Rate Dynamics</h4><p>A <strong>floating exchange rate</strong> system is characterized by the currency's value being determined almost entirely by the forces of <strong>supply and demand</strong> in the foreign exchange market. Government or central bank intervention is minimal, if any.</p><p>In this system, the exchange rate can experience significant and frequent fluctuations. These changes are typically in response to various factors such as <strong>economic news</strong>, major global or domestic events, or shifts in <strong>market sentiment</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of Floating Exchange Rates:</strong><ul><li><strong>Market-determined:</strong> Value set by supply and demand.</li><li><strong>High Volatility:</strong> Frequent and often significant fluctuations.</li><li><strong>Automatic Adjustment:</strong> Helps economies adjust to external shocks.</li><li><strong>Minimal Intervention:</strong> Central bank typically does not interfere to fix the rate.</li></ul></p></div><p>Businesses and individuals operating under a floating regime must constantly adjust to these changing economic conditions. The market itself acts as the primary mechanism for price discovery and adjustment.</p><h4>Stabilized Arrangement Explained</h4><p>A <strong>stabilized arrangement</strong> represents a middle ground between a pure floating rate and a fixed exchange rate. In this system, the government or <strong>central bank</strong> actively intervenes in the <strong>foreign exchange market</strong>.</p><p>The primary goal of such intervention is to <strong>smooth out excessive volatility</strong> in the currency's value. While it allows for some degree of fluctuation, it aims to keep the exchange rate within a predefined <strong>target range</strong> or to prevent sharp, disruptive movements.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of Stabilized Arrangements:</strong><ul><li><strong>Managed Fluctuations:</strong> Allows some movement but with limits.</li><li><strong>Central Bank Intervention:</strong> Active buying or selling of foreign currency.</li><li><strong>Greater Stability:</strong> Aims for more predictability than a pure float.</li><li><strong>Target Range:</strong> Often seeks to maintain the rate within a specific band.</li></ul></p></div><p>This approach seeks to combine the flexibility of a floating rate with the stability benefits of a fixed rate, providing a more predictable environment for trade and investment while still allowing for some market adjustment.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For UPSC, understanding the <strong>trade-offs</strong> between flexibility and stability is crucial. Analyze how each system impacts a country's <strong>monetary policy autonomy</strong>, <strong>inflation control</strong>, and <strong>external competitiveness</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Floating rates are market-determined with minimal intervention, leading to high volatility.
- •Stabilized arrangements involve central bank intervention to smooth volatility or maintain a target range.
- •Floating rates offer monetary policy autonomy and automatic adjustment to shocks.
- •Stabilized arrangements prioritize stability and predictability, often at the cost of some policy independence.
- •India operates a managed float, a form of stabilized arrangement, with active RBI intervention.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•International Monetary Fund (IMF) publications on exchange rate regimes
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) official statements and reports
•NCERT Economics Textbooks (Macroeconomics)