What is the Global Minimum Tax (GMT)? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is the Global Minimum Tax (GMT)?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>What is the Global Minimum Tax (GMT)?</h4><p>The <strong>Global Minimum Tax (GMT)</strong> is a globally agreed minimum tax rate designed to address tax challenges arising from the digitalization of the economy. Its primary aim is to mitigate <strong>tax base erosion</strong> and prevent <strong>profit shifting</strong> by multinational corporations.</p><p>This initiative seeks to ensure that large multinational enterprises pay a fair share of tax, regardless of where they operate or where they declare their profits.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The currently suggested <strong>minimum tax rate</strong> under the GMT framework is <strong>15%</strong>. This rate is intended to reduce the incentive for companies to move their profits to low-tax jurisdictions.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core objective of <strong>GMT</strong> is to curb the practice of <strong>multinationals</strong> moving profits to <strong>low-tax jurisdictions</strong>, irrespective of where their actual sales or economic activities occur. This prevents companies from gaining a financial advantage by exploiting tax differentials between countries.</p></div><h4>Challenges of Profit Shifting</h4><p>There is a significant trend of companies shifting income derived from <strong>intangibles</strong>, such as <strong>patents</strong>, <strong>software</strong>, and <strong>Intellectual Property (IP) royalties</strong>, to designated <strong>tax havens</strong>. This strategy allows them to sidestep higher tax obligations in their home countries, leading to revenue loss for governments.</p><h4>India's Current Debt Scenario (as per IMF Article IV Consultation Report)</h4><p>The <strong>International Monetary Fund (IMF)</strong> released its annual <strong>Article IV consultation report</strong> on <strong>India</strong>, providing an assessment of the country's economic health, including its debt sustainability and exchange rate management.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Government Current Debt Levels:</strong></p><ul><li>The <strong>central government’s debt</strong> stood at <strong>₹155.6 trillion</strong>, approximately <strong>57.1% of GDP</strong> by <strong>March 2023</strong>.</li><li><strong>State governments</strong> carried a debt of about <strong>28% of GDP</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>As stated by the <strong>Finance Ministry</strong>, <strong>India’s public debt-to-GDP ratio</strong> was <strong>81%</strong> in <strong>2022-23</strong>. These figures are crucial for assessing the nation's fiscal health and its capacity for future economic growth and stability.</p>
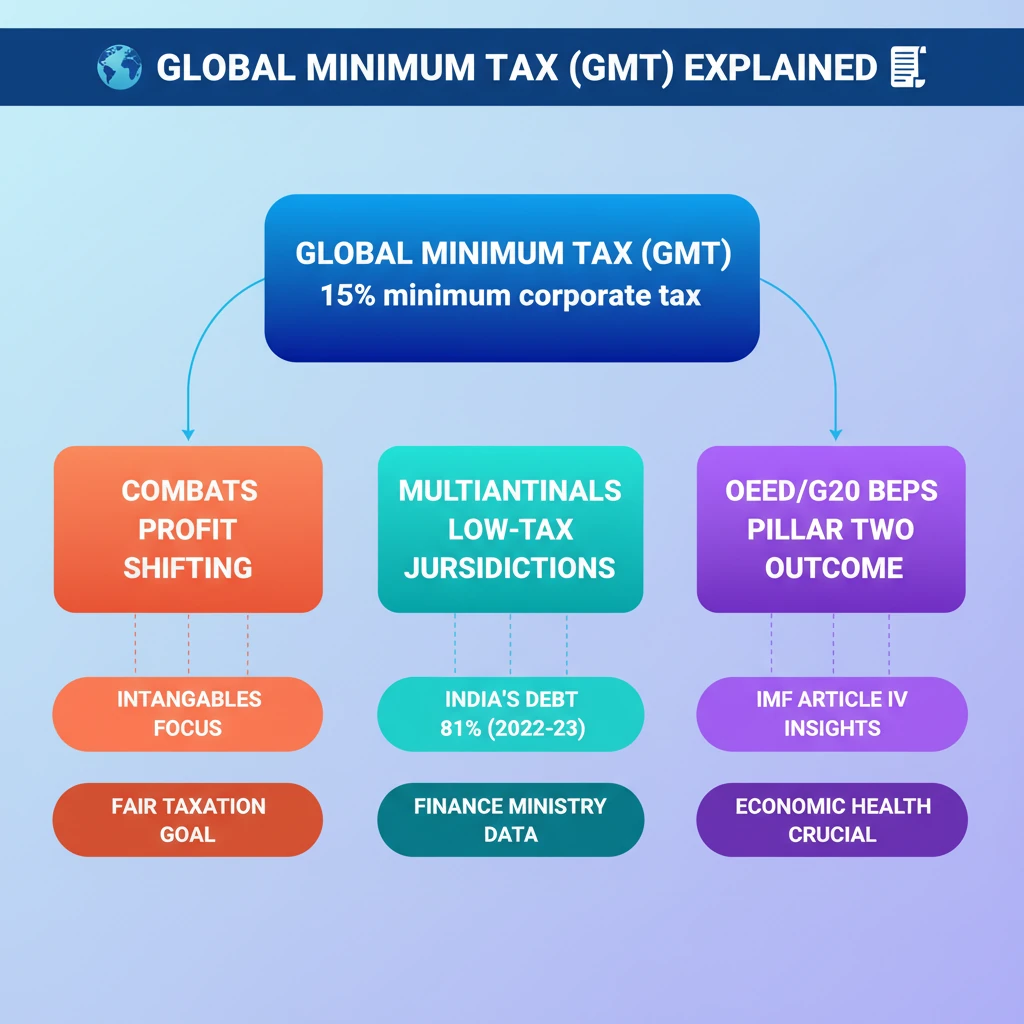
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Global Minimum Tax (GMT) aims to set a 15% minimum corporate tax rate globally.
- •GMT combats profit shifting by multinationals to low-tax jurisdictions, especially for intangibles.
- •It is a key outcome of the OECD/G20 BEPS project (Pillar Two).
- •India's public debt-to-GDP ratio was 81% in 2022-23, as per the Finance Ministry.
- •IMF's Article IV report provides crucial insights into India's debt and economic health.
- •GMT seeks to ensure fairer taxation and global economic stability.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•International Monetary Fund (IMF) - Article IV Consultation Reports
•Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) - Inclusive Framework on BEPS