Regional Cooperation) Countries for the period 2024 to 2027. - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Regional Cooperation) Countries for the period 2024 to 2027.
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
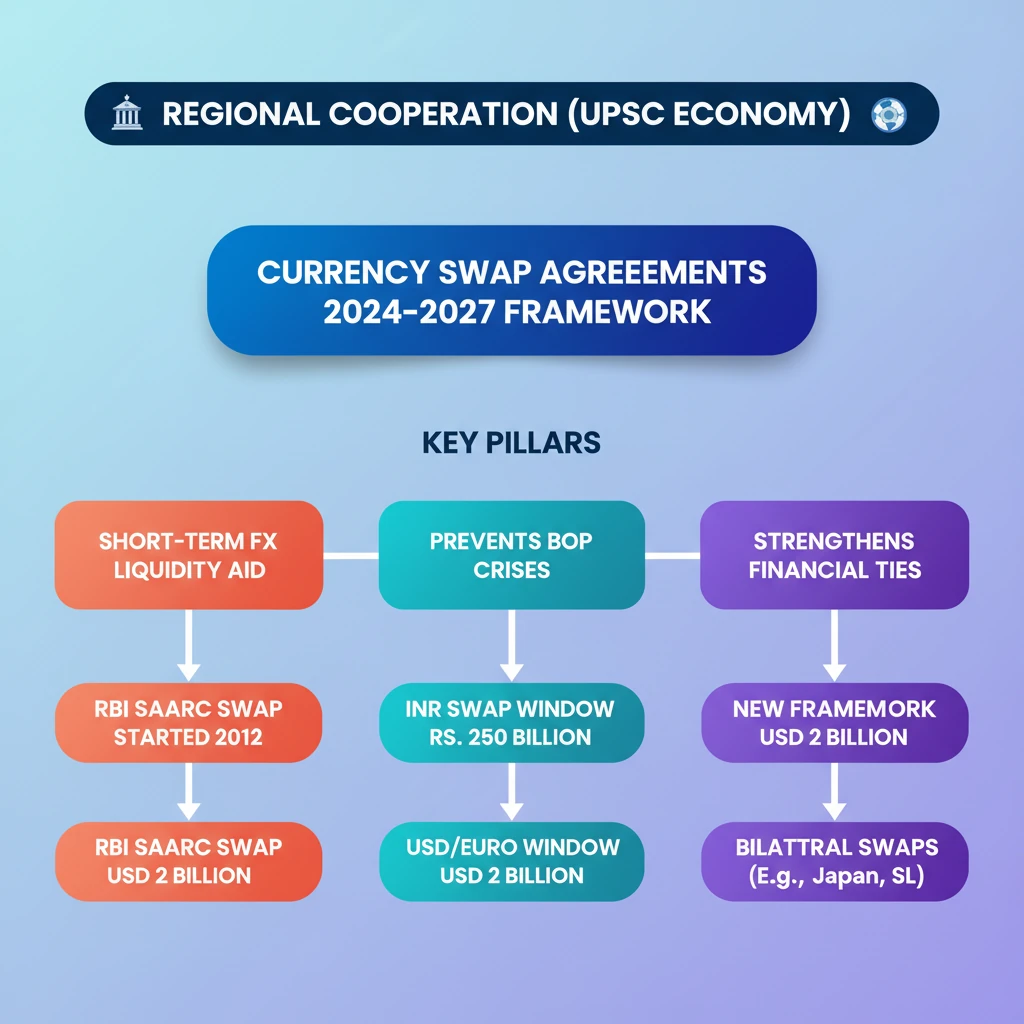
<h4>Understanding Currency Swap Agreements</h4><p>A <strong>Currency Swap Agreement</strong> is a crucial financial contract established between two countries.</p><p>It involves the exchange of currencies under <strong>predetermined terms and conditions</strong>, primarily to provide <strong>liquidity support</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>These agreements are vital tools for central banks and governments to manage <strong>foreign exchange liquidity</strong> effectively.</p></div><h4>Purpose of Currency Swaps</h4><p>The primary aim of these agreements is to meet <strong>short-term foreign exchange liquidity requirements</strong>.</p><p>They also serve to ensure adequate foreign currency to avert a <strong>Balance of Payments (BOP) crisis</strong> until more permanent arrangements can be established.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Risk Mitigation:</strong> These swap operations inherently carry <strong>no exchange rate or other market risks</strong> because all transaction terms are explicitly set in advance.</p></div><h4>RBI's SAARC Currency Swap Facility (Original Framework)</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> formally initiated its <strong>SAARC currency swap facility</strong> on <strong>15th November 2012</strong>.</p><p>This framework was designed to offer a <strong>backstop line of funding</strong> for SAARC member countries.</p><ul><li>It addresses <strong>short-term foreign exchange liquidity requirements</strong>.</li><li>It helps mitigate potential <strong>Balance of Payments crises</strong> within the region.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Overall Corpus:</strong> Under the original framework, the RBI could offer swap arrangements within an overall corpus of <strong>USD 2 billion</strong>.</p></div><p>Swaps could be executed in <strong>US dollars</strong>, <strong>Euro</strong>, or <strong>Indian Rupees</strong>, with specific concessions provided for transactions in INR.</p><p>The facility was made available to all <strong>SAARC member countries</strong>, contingent upon them signing bilateral swap agreements with India.</p><h4>New Framework for 2024-2027: Key Changes</h4><p>The RBI has introduced significant modifications to the framework for the period <strong>2024 to 2027</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A notable change is the introduction of a <strong>separate INR (Indian Rupee) swap window</strong>.</p></div><p>This new window comes with various <strong>concessions</strong> specifically tailored for swap support in the <strong>Indian Rupee</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>INR Swap Corpus:</strong> The total corpus allocated for the Rupee support under this new window is <strong>Rs. 250 billion</strong>.</p></div><p>The existing arrangement for swaps in <strong>USD and Euro</strong> will continue under a separate <strong>US Dollar/Euro swap window</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>USD/Euro Corpus:</strong> This separate window maintains its overall corpus of <strong>USD 2 billion</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> The introduction of a dedicated INR swap window highlights India's growing economic influence and its efforts to promote the <strong>internationalization of the Indian Rupee</strong>. This is crucial for <strong>GS Paper 3 (Economy)</strong> and <strong>International Relations</strong>.</p></div><h4>India's Other Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements</h4><p>Beyond the SAARC framework, India also maintains bilateral currency swap agreements with other nations.</p><ul><li><strong>India-Japan:</strong> A long-standing agreement enhancing financial stability.</li><li><strong>India-Sri Lanka:</strong> Critical for supporting Sri Lanka's economy during periods of financial stress.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Currency swap agreements provide short-term foreign exchange liquidity and prevent BoP crises.
- •RBI's SAARC Currency Swap Facility began in 2012, with an initial corpus of USD 2 billion.
- •The new 2024-27 framework introduces a dedicated INR swap window with a corpus of Rs. 250 billion.
- •The USD/Euro swap window continues with USD 2 billion corpus.
- •India also has bilateral swap agreements with countries like Japan and Sri Lanka.
- •These agreements are crucial for regional financial stability and India's economic diplomacy.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) official press releases/notifications on Currency Swap Agreements
•Ministry of Finance documents related to bilateral agreements