India-Indonesia Relations - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India-Indonesia Relations
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
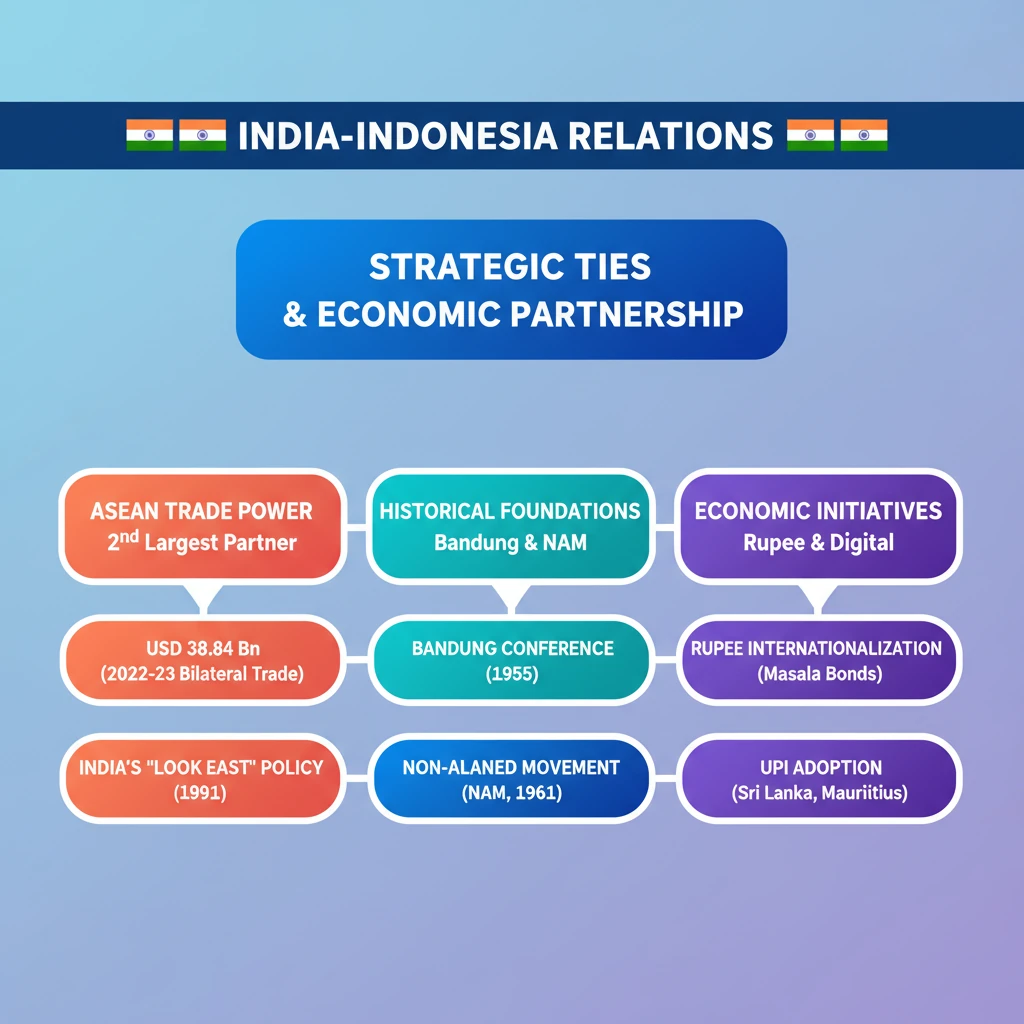
<h4>India-Indonesia Bilateral Relations: A Strategic Partnership</h4><p>India and <strong>Indonesia</strong> share a deep historical and cultural bond, evolving into a robust strategic partnership. This relationship is crucial for regional stability and economic prosperity in the <strong>Indo-Pacific</strong>.</p><h4>Commercial Ties and Economic Growth</h4><p><strong>Indonesia</strong> has emerged as a pivotal economic partner for India within the <strong>ASEAN</strong> region. It stands as India's <strong>second-largest trading partner</strong> in this vital bloc, underscoring the strength of their commercial engagement.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Bilateral Trade Growth:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>2005-06:</strong> USD <strong>4.3 billion</strong></li><li><strong>2022-23:</strong> USD <strong>38.84 billion</strong></li></ul><p>This significant increase reflects growing economic interdependence and opportunities.</p></div><h4>Political and Strategic Alignment</h4><p>Both nations historically championed the cause of independence for <strong>Asian</strong> and <strong>African</strong> countries. This shared vision laid the foundation for key international movements and policies.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Foundational Collaborations:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Bandung Conference (1955):</strong> A landmark event promoting Afro-Asian solidarity.</li><li><strong>Non-Aligned Movement (NAM, 1961):</strong> A crucial platform for newly independent states to assert autonomy during the Cold War.</li></ul></div><p>Since India's adoption of the <strong>‘Look East Policy’</strong> in <strong>1991</strong>, bilateral relations have witnessed rapid and comprehensive development. This policy shift prioritized engagement with Southeast Asian nations, including Indonesia.</p><h4>Internationalisation of the Indian Rupee</h4><p>India is actively pursuing strategies to enhance the global acceptance and usage of the <strong>Indian Rupee</strong>. This initiative aims to reduce reliance on foreign currencies for international transactions and boost India's financial influence.</p><h4>Capital Market Liberalisation</h4><p>A key effort involves liberalizing India's capital markets to make the <strong>Rupee</strong> more accessible and attractive internationally. This includes expanding the range of financial products available.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Rupee-Denominated Instruments:</strong></p><ul><li>India has increased the availability of financial instruments denominated in <strong>Rupees</strong>.</li><li>A prominent example is the <strong>Masala Bond</strong>, which allows Indian entities to raise capital from international markets in <strong>Rupees</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Promotion of Digital Payment Systems</h4><p>India is leveraging its advanced digital infrastructure to promote the <strong>Rupee</strong> globally. Digital payment systems are playing a significant role in facilitating cross-border transactions.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight: UPI's Global Footprint</strong></p><p>Initiatives like the <strong>Unified Payments Interface (UPI)</strong> have significantly facilitated digital transactions in <strong>Rupees</strong>. Notably, countries such as <strong>Sri Lanka</strong> and <strong>Mauritius</strong> have already adopted <strong>UPI</strong>, demonstrating its growing international acceptance and India's leadership in digital payments. This showcases India's <strong>soft power</strong> in the financial tech domain.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Indonesia is India's second-largest trading partner in the ASEAN region, with bilateral trade reaching USD 38.84 billion in 2022-23.
- •Both nations were key proponents of the Bandung Conference (1955) and founders of the Non-Aligned Movement (1961).
- •India's 'Look East Policy' (1991) significantly boosted bilateral relations with Indonesia.
- •Efforts to internationalize the Rupee include liberalizing capital markets (e.g., Masala Bonds) and promoting digital payment systems.
- •UPI has been adopted by countries like Sri Lanka and Mauritius, showcasing India's digital payment leadership.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India reports
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on financial market reforms