Advance Pricing Agreements and Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Advance Pricing Agreements and Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
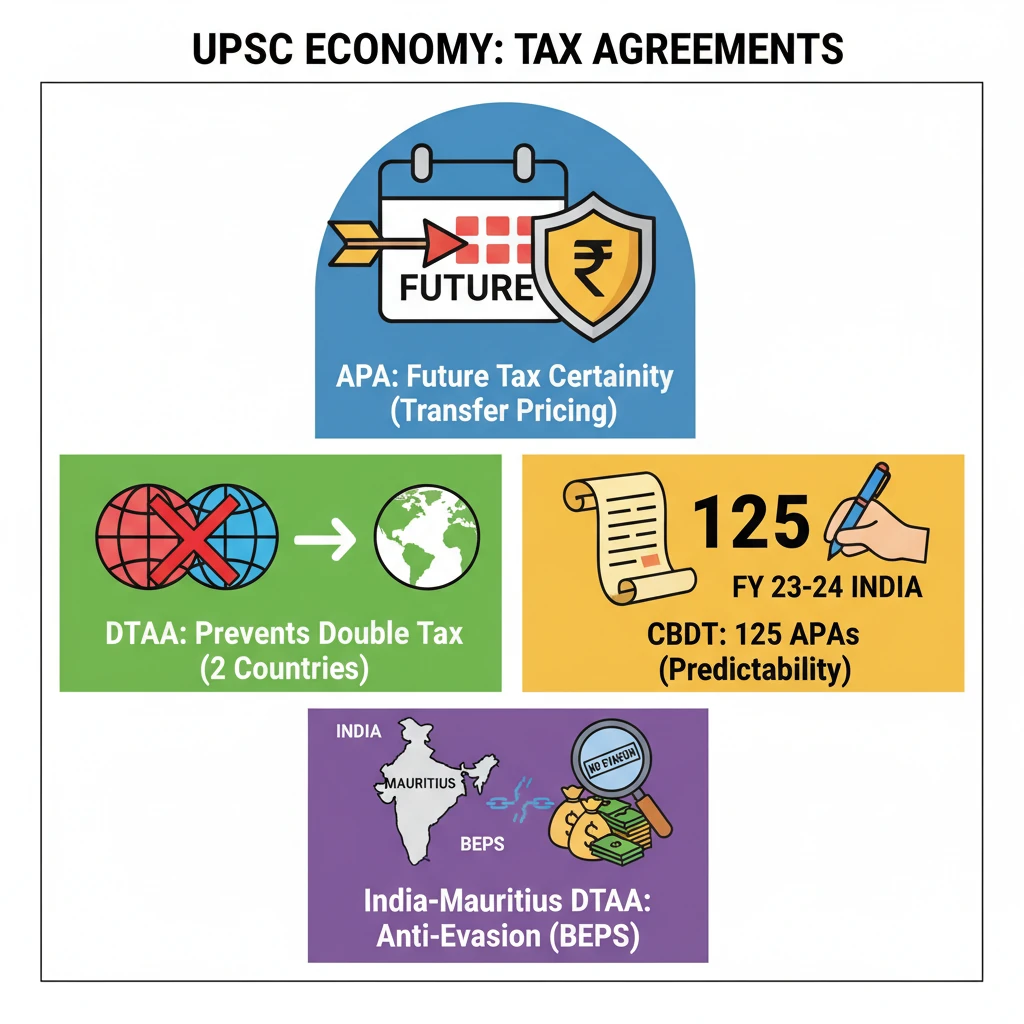
<h4>Introduction to International Tax Agreements</h4><p>International taxation is a complex area, often leading to challenges like <strong>double taxation</strong> or opportunities for <strong>tax evasion</strong>. To address these, countries enter into various agreements, notably <strong>Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs)</strong> and <strong>Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs)</strong>.</p><p>These mechanisms are crucial for fostering a stable and predictable tax environment, which in turn encourages <strong>cross-border trade</strong> and <strong>investment</strong>.</p><h4>Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs)</h4><p>An <strong>Advance Pricing Agreement (APA)</strong> is an agreement between a taxpayer and a tax authority. It determines the <strong>transfer pricing methodology</strong> for specified international transactions for a fixed period in advance.</p><p>The primary goal of an APA is to provide <strong>tax certainty</strong> to multinational corporations (MNCs) regarding their future transactions, thereby reducing litigation and compliance costs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Recent Milestone:</strong> The <strong>Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)</strong> in India signed a remarkable <strong>125 Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs)</strong> during the fiscal year <strong>2023-24</strong>. This achievement highlights India's commitment to tax certainty and ease of doing business.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Benefit of APAs:</strong> They offer <strong>predictability</strong> and <strong>transparency</strong> in transfer pricing matters, significantly mitigating potential disputes between taxpayers and tax authorities.</p></div><h4>Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs)</h4><p>A <strong>Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)</strong> is a tax treaty signed between two or more countries. Its main purpose is to prevent taxpayers from being taxed twice on the same income in two different countries.</p><p>DTAAs typically cover various types of income, including salaries, dividends, interest, royalties, and capital gains, specifying which country has the right to tax which income.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Recent Development:</strong> <strong>India</strong> and <strong>Mauritius</strong> have recently amended their <strong>Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)</strong>. This amendment aims to curb <strong>tax evasion</strong> and ensure more equitable and fair taxation practices between the two nations.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the distinction between <strong>APAs</strong> (forward-looking, specific to transfer pricing) and <strong>DTAAs</strong> (broader, covering various income types to prevent double taxation) is crucial for both Prelims and Mains. Focus on their objectives and recent amendments.</p></div>
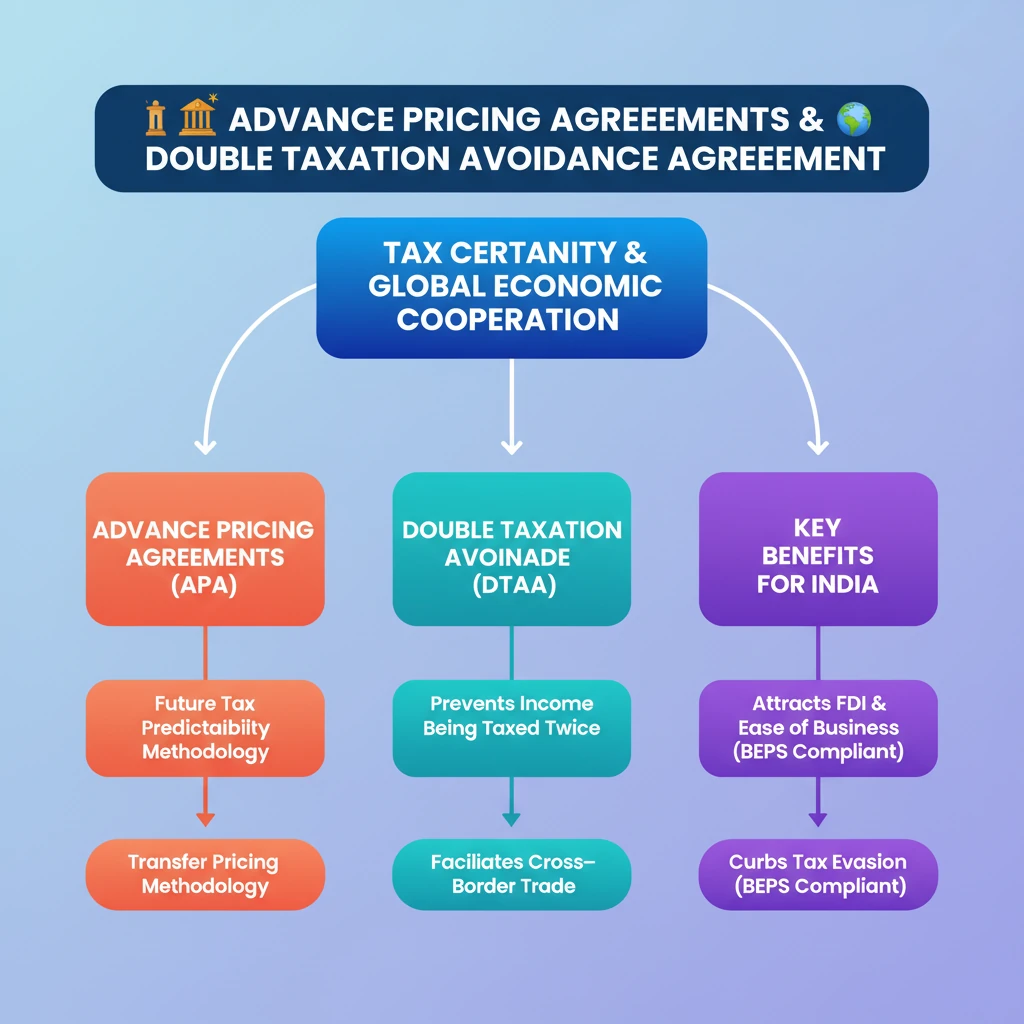
💡 Key Takeaways
- •APAs provide tax certainty for future international transactions, especially regarding transfer pricing.
- •DTAAs prevent income from being taxed twice by two different countries.
- •CBDT signed 125 APAs in FY 2023-24, indicating India's commitment to tax predictability.
- •India and Mauritius amended their DTAA to curb tax evasion, aligning with global BEPS efforts.
- •Both APAs and DTAAs are vital for attracting FDI, improving ease of doing business, and combating illicit financial flows.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) Annual Reports/Press Releases
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India Publications
•OECD Model Tax Convention and BEPS Action Plans