What is Duty Drawback? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Duty Drawback?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Duty Drawback</h4><p>The concept of <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> is a crucial mechanism in India's export promotion strategy. It essentially provides a refund of duties paid on imported or excisable materials that are subsequently used in the manufacture of goods for export.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Core Principle:</strong> Duty drawback aims to prevent the taxation of exported goods, ensuring they remain competitive in the international market by neutralizing the impact of domestic duties and taxes.</p></div><h4>Legal Framework of Duty Drawback</h4><p>In India, the provision for <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> is enshrined under <strong>Section 75</strong> of the <strong>Customs Act, 1962</strong>. This legal backing ensures that exporters can claim rebates on specific duties.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Section 75, Customs Act, 1962:</strong> This section specifically deals with the rebate of <strong>customs duty</strong> chargeable on any imported materials or <strong>excisable materials</strong> used in the manufacture of goods that are subsequently exported.</p></div><h4>Purpose and Benefits for Exporters</h4><p>The primary objective of the <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> system is to assist exporters in mitigating various costs incurred during the export process. These costs are particularly significant within the complex supply or value chain of manufactured goods.</p><ul><li>It helps reduce the overall cost of production for export-oriented units.</li><li>It enhances the price competitiveness of Indian goods in global markets.</li><li>It prevents the 'export of taxes', ensuring that only the value of the goods, not the embedded taxes, is reflected in the export price.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> is vital for questions related to India's <strong>Foreign Trade Policy</strong>, <strong>export promotion schemes</strong>, and the government's efforts to boost manufacturing and trade. It directly impacts India's <strong>Balance of Payments</strong>.</p></div><h4>Distinction: Duty Drawback vs. DTAA (Context from Source)</h4><p>While the source material mentioned <strong>Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)</strong>, it is important to note that <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> and <strong>DTAA</strong> are distinct concepts. <strong>Duty Drawback</strong> deals with duties on materials for exports, whereas <strong>DTAA</strong> addresses income tax for residents earning income across borders.</p>
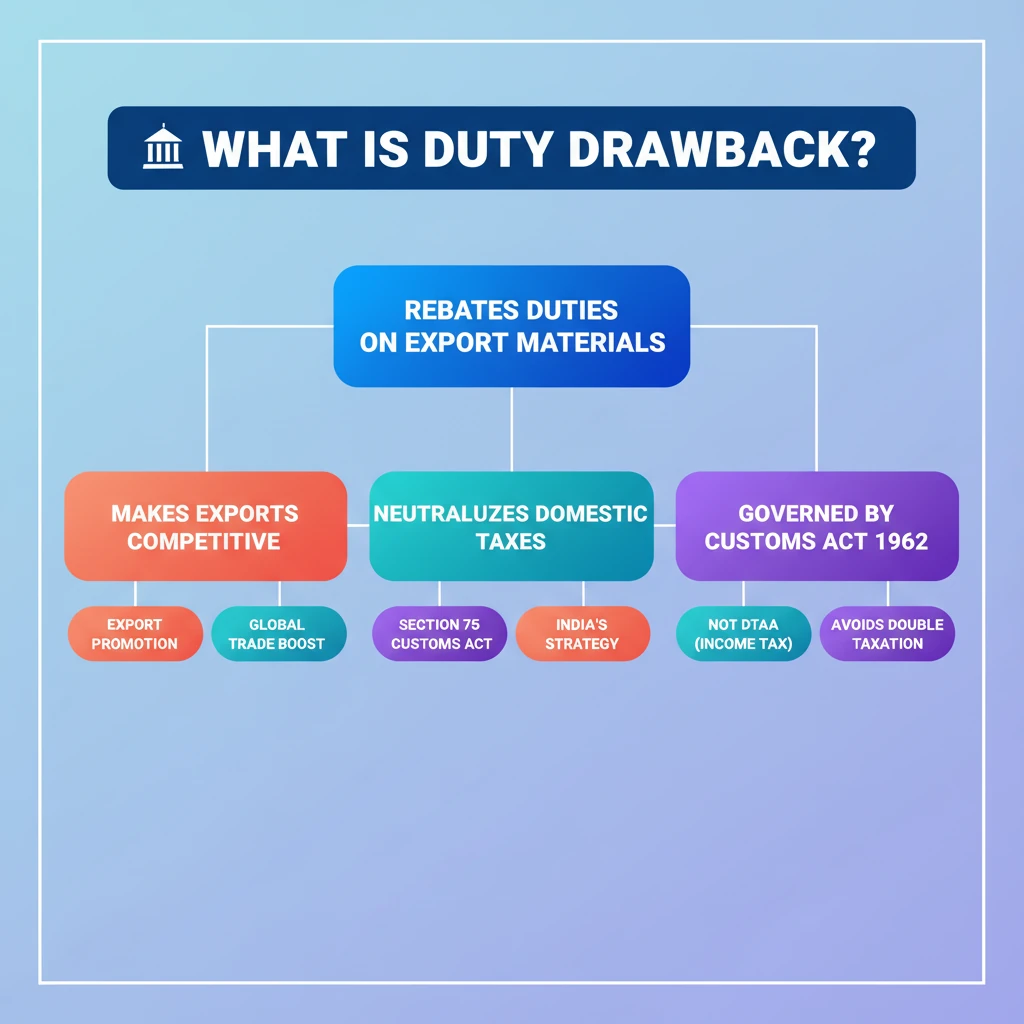
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Duty Drawback rebates customs/excise duties on materials used in export goods.
- •Its purpose is to make exports competitive by neutralizing domestic taxes.
- •It is governed by Section 75 of the Customs Act, 1962.
- •DTAA is a separate agreement to avoid double taxation on income between countries.
- •Both are crucial for India's export promotion and international investment strategy.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Customs Act, 1962 (Section 75)
•General knowledge of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) and India-Mauritius DTAA