RBI Imposes Restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

RBI Imposes Restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to RBI's Action on Paytm Payments Bank</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> has imposed stringent regulatory restrictions on <strong>Paytm Payments Bank Ltd (PPBL)</strong>. These actions highlight the RBI's commitment to maintaining the stability and integrity of the financial system.</p><p>The restrictions were initiated due to persistent non-compliance and supervisory concerns identified by the central bank. This move underscores the importance of robust compliance frameworks for all financial institutions.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>RBI's regulatory powers</strong> and the functioning of <strong>Payments Banks</strong> are common in <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>. Understanding such actions provides practical context to theoretical concepts.</p></div><h4>Key Restrictions Imposed on PPBL</h4><p>The RBI's directive outlines several critical restrictions impacting PPBL's operations and its ability to serve customers. These measures are designed to safeguard consumer interests and ensure adherence to banking regulations.</p><h4>Deposit and Top-Up Bar</h4><p>Effective <strong>February 29, 2024</strong>, <strong>PPBL</strong> is prohibited from accepting new deposits or credit transactions. This includes any form of top-ups into customer accounts or wallets.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This restriction also extends to <strong>prepaid instruments</strong> such as <strong>FASTag</strong> and <strong>National Common Mobility Cards (NCMC)</strong> issued by <strong>Paytm Payments Bank</strong>.</p></div><h4>Service Limitations</h4><p>The ban encompasses a range of banking services provided by <strong>PPBL</strong>. This significantly curtails its operational scope for customers.</p><ul><li><strong>Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS)</strong> transactions are halted.</li><li><strong>Immediate Payment Service (IMPS)</strong> is no longer permitted.</li><li>Services related to <strong>bill payments</strong> and <strong>UPI transactions</strong> are also restricted.</li></ul><p>All pending transactions in pipeline and nodal accounts must be settled by <strong>March 29, 2024</strong>, with no further transactions allowed thereafter.</p><h4>Closure of Nodal Accounts</h4><p><strong>PPBL</strong> has been instructed to terminate the <strong>nodal accounts</strong> of its parent company, <strong>One97 Communications Ltd.</strong>, and <strong>Paytm Payments Services Ltd.</strong> This termination must be completed before <strong>February 29, 2024</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The closure of nodal accounts is a significant step, impacting the flow of funds between the bank and its associated entities, particularly affecting the broader <strong>Paytm ecosystem</strong>.</p></div><h4>Related Financial Instruments and RBI Operations</h4><p>The original source material also touched upon various financial instruments and RBI operations, which are fundamental to understanding India's financial market. While seemingly distinct from the Paytm issue, these concepts are crucial for a holistic understanding of the economy.</p><h4>Cash Management Bills (CMBs)</h4><p><strong>CMBs</strong> are a new <strong>short-term instrument</strong> introduced by the government. Their primary purpose is to address temporary mismatches in the <strong>cash flow</strong> of the <strong>Government of India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>CMBs</strong> are typically issued for maturities of less than 91 days, making them a flexible tool for short-term liquidity management.</p></div><h4>Dated Government Securities (G-Secs)</h4><p><strong>Dated G-Secs</strong> are long-term debt instruments issued by the central government. They represent a significant component of government borrowing.</p><p>These securities carry either a <strong>fixed or floating coupon rate (interest rate)</strong>, which is paid on their face value on a <strong>half-yearly basis</strong>. Their tenor generally ranges from <strong>5 years to 40 years</strong>.</p><h4>State Development Loans (SDLs)</h4><p>Similar to central government securities, <strong>State Development Loans (SDLs)</strong> are market borrowings undertaken by <strong>State Governments</strong>. These funds are raised to finance their developmental projects and budgetary needs.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Both <strong>G-Secs</strong> and <strong>SDLs</strong> are crucial for government financing and are traded in the <strong>debt market</strong>, influencing bond yields and interest rates.</p></div><h4>Open Market Operations (OMOs)</h4><p>The <strong>RBI</strong> utilizes <strong>Open Market Operations (OMOs)</strong> as a key tool of <strong>monetary policy</strong>. OMOs involve the sale or purchase of <strong>G-Secs</strong> in the open market.</p><ul><li>When the <strong>RBI sells G-Secs</strong>, it aims to <strong>remove liquidity</strong> from the market, thereby tightening money supply.</li><li>Conversely, when the <strong>RBI buys back G-Secs</strong>, it seeks to <strong>infuse liquidity</strong> into the market, expanding money supply.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding <strong>OMOs</strong> is vital for <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>, especially for questions on <strong>monetary policy tools</strong> and their impact on <strong>inflation</strong> and <strong>economic growth</strong>.</p></div>
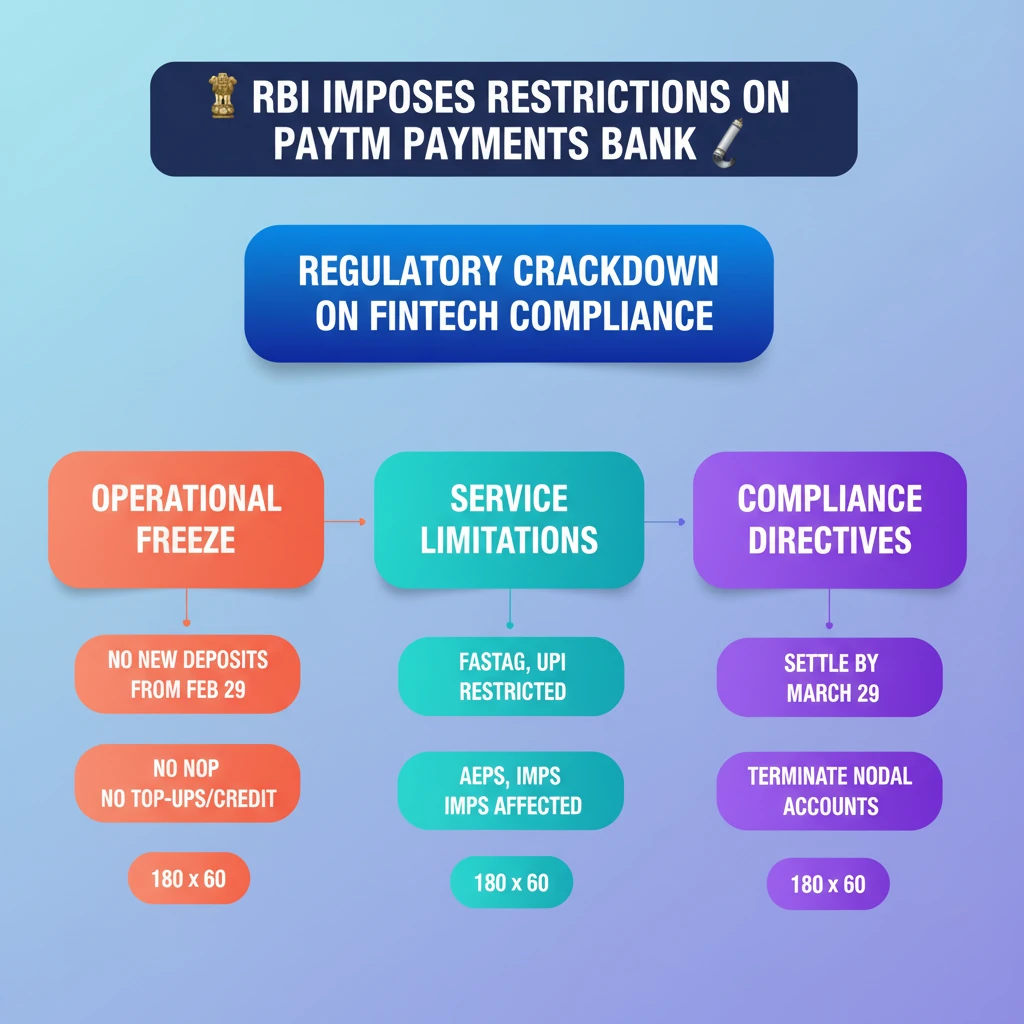
💡 Key Takeaways
- •RBI imposed strict restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank (PPBL) due to non-compliance and supervisory concerns.
- •PPBL is barred from accepting new deposits, top-ups, or credit transactions from Feb 29, 2024.
- •Restrictions extend to services like FASTag, NCMC, AePS, IMPS, bill payments, and UPI transactions.
- •PPBL must settle all pipeline transactions by March 29, 2024, and terminate nodal accounts by Feb 29, 2024.
- •The action highlights RBI's vigilant regulatory role and the importance of compliance in the fintech sector.
- •Concepts like CMBs, G-Secs, SDLs, and OMOs are fundamental to understanding government finance and RBI's monetary policy tools.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•The Economic Times - Reports on Paytm Payments Bank
•Livemint - Analysis of RBI's actions
•Drishti IAS - Economy Notes