Cross-Border Remittances: Evolution from Traditional to Online Methods (NEFT) - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Cross-Border Remittances: Evolution from Traditional to Online Methods (NEFT)
Easy⏱️ 4 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
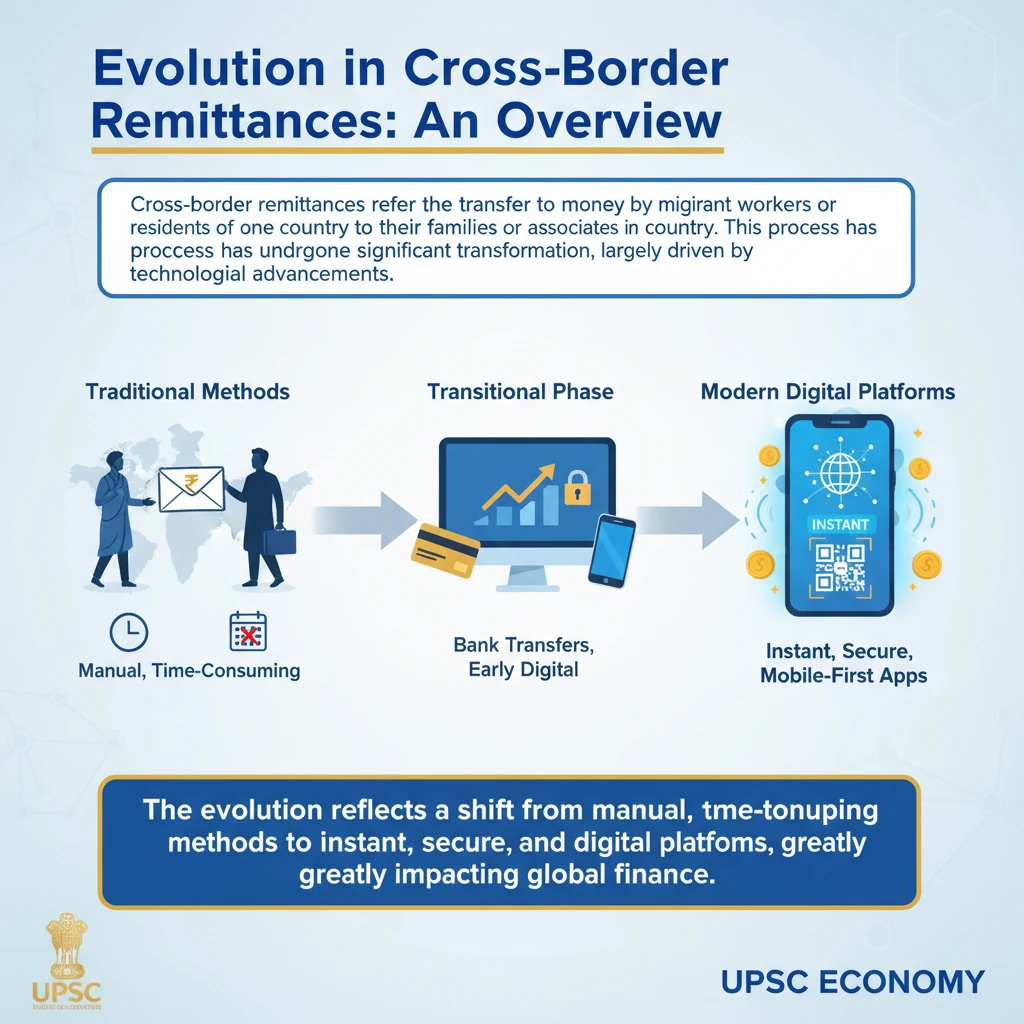
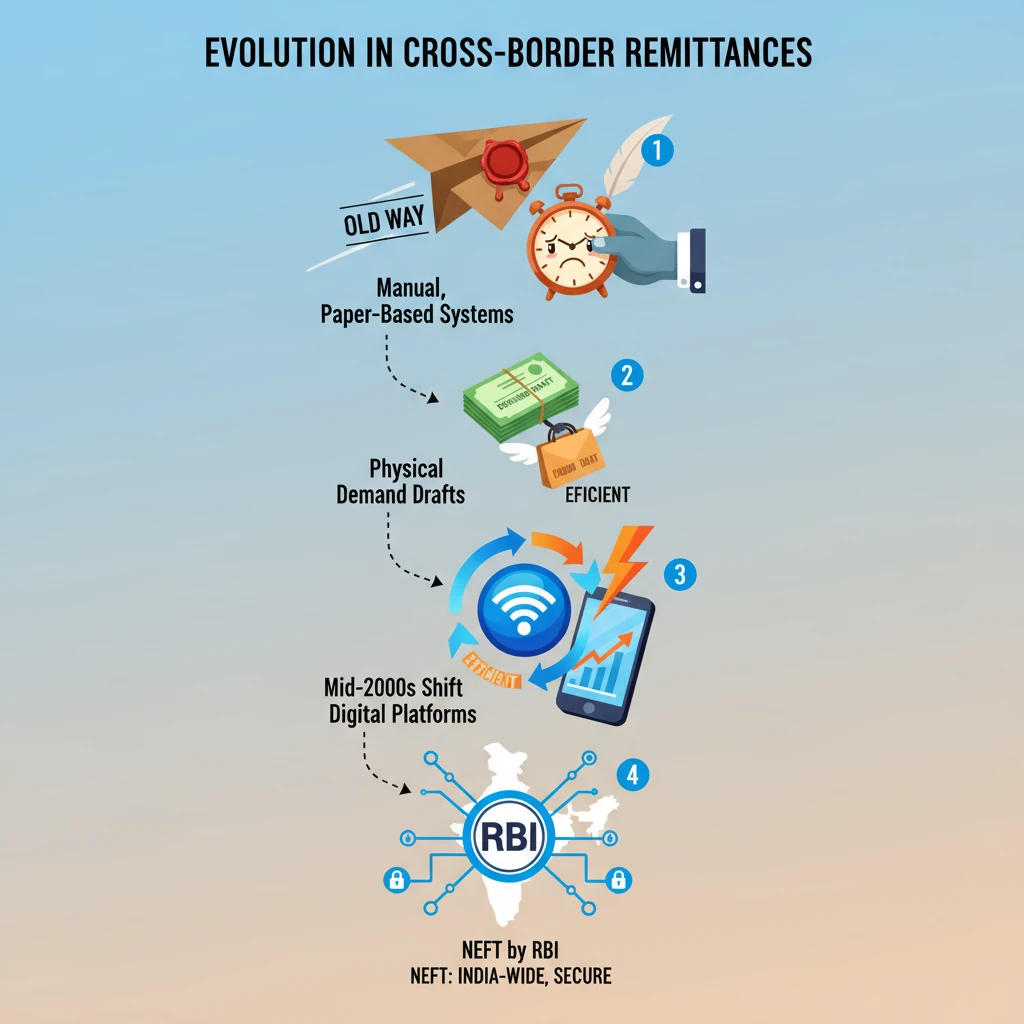
<h4>Evolution in Cross-Border Remittances: An Overview</h4><p><strong>Cross-border remittances</strong> refer to the transfer of money by migrant workers or residents of one country to their families or associates in another country. This process has undergone significant transformation, largely driven by technological advancements.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The evolution reflects a shift from manual, time-consuming methods to instant, secure, and digital platforms, greatly impacting global financial flows.</p></div><h4>Pre-Technology Era: Traditional Methods</h4><p>Before the advent of widespread digital technology, the process of sending money across borders was largely manual and involved several intermediaries.</p><p><strong>Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)</strong>, for instance, relied on traditional banking instruments for their remittances to India.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Method Used:</strong> NRIs typically used <strong>demand drafts</strong>. These were financial instruments drawn on <strong>federal banks</strong>, indicating a sum payable to a beneficiary.</p><p><strong>Process:</strong> The demand drafts were physically sent via <strong>courier</strong> to India. Upon receipt, the beneficiary would then present the draft to the designated bank for <strong>encashment</strong>.</p></div><p>This method, while secure, was often slow, incurring delays due to physical transportation and manual processing.</p><h4>Online Remittances: The Digital Shift</h4><p>The mid-2000s marked a significant turning point with the introduction of digital payment systems, revolutionizing cross-border remittances.</p><p>A key development in India was the launch of the <strong>National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT)</strong> system.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Launch:</strong> <strong>NEFT</strong> was launched in the <strong>mid-2000s</strong>, providing a robust digital platform for money transfers.</p><p><strong>Functionality:</strong> It enabled <strong>direct and secure transfers</strong> of funds to bank accounts across India, eliminating the need for physical instruments.</p><p><strong>Ownership & Operation:</strong> <strong>NEFT</strong> is a <strong>nation-wide centralised payment system</strong> that is <strong>owned and operated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong>.</p></div><p>The introduction of NEFT significantly reduced transaction times and costs, making remittances more efficient and accessible for NRIs.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the evolution of payment systems like NEFT is crucial for <strong>UPSC GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>, especially when discussing financial sector reforms and digital infrastructure.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
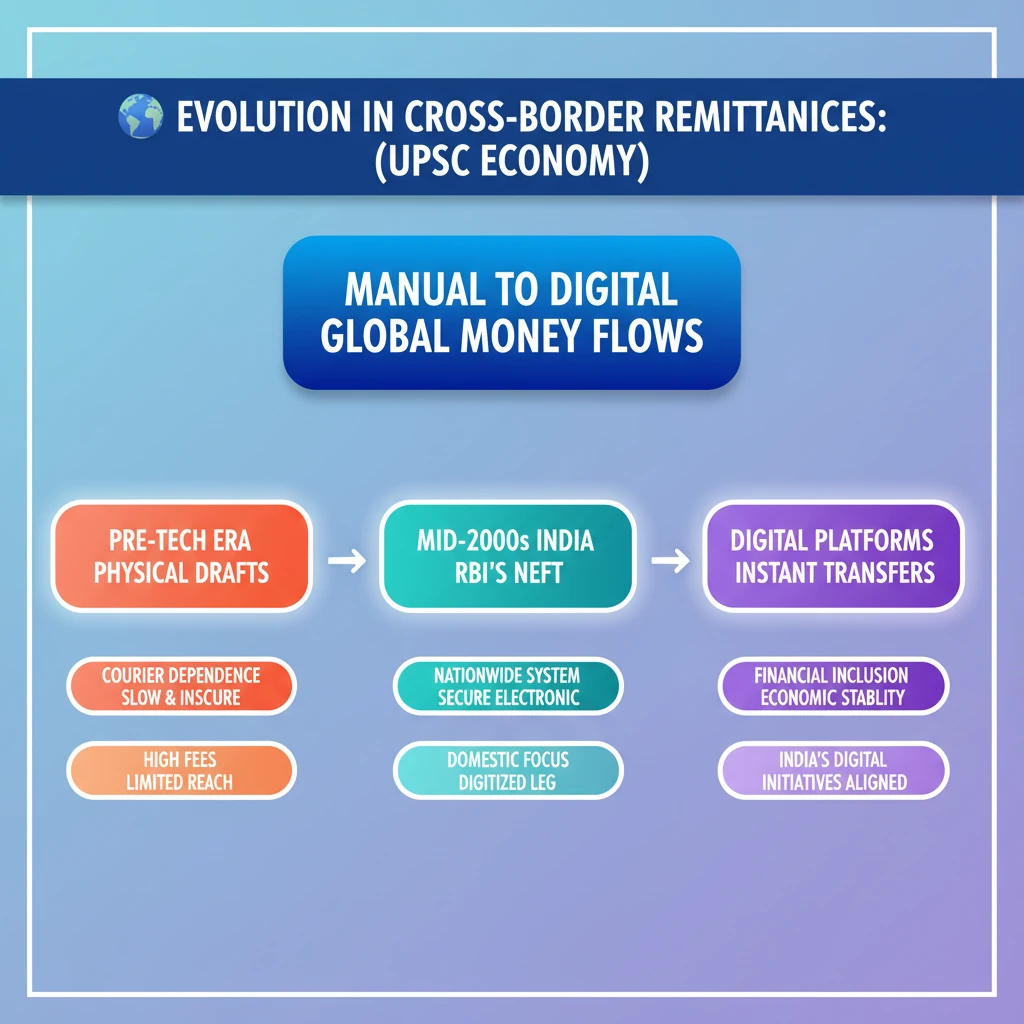
- •Cross-border remittances have evolved from manual, paper-based systems to highly efficient digital platforms.
- •Pre-technology era relied on physical demand drafts sent via courier, leading to delays.
- •The mid-2000s saw a significant shift with the launch of NEFT by RBI, enabling direct and secure electronic transfers within India.
- •NEFT is a nationwide centralized payment system, crucial for digitizing the domestic leg of remittances.
- •This evolution has improved financial inclusion, boosted economic stability, and aligned with India's digital initiatives.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) official website - Payment Systems data
•National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) documentation