GDP Base Year Revision - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

GDP Base Year Revision
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
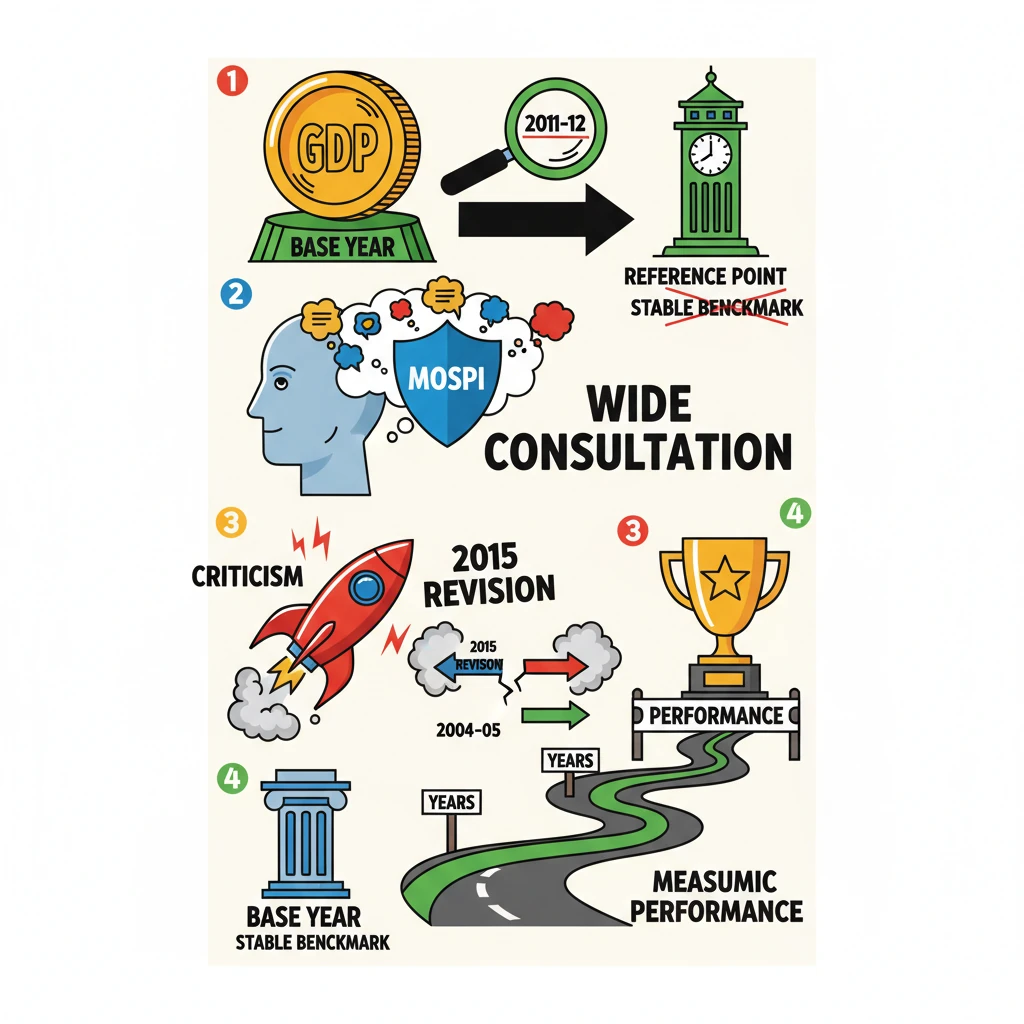
<h4>Introduction to GDP Base Year Revision</h4><p>The <strong>Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)</strong> recently initiated discussions with economists and forecasters regarding the revision of India's <strong>Gross Domestic Product (GDP) base year</strong>.</p><p>This move highlights <strong>MoSPI's</strong> commitment to extensive consultation. Such broad engagement is crucial, especially given the significant debates and criticisms that arose from previous base year revisions.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The last <strong>base year revision</strong> occurred in <strong>2015</strong>. It changed the base year from <strong>2004-05</strong> to <strong>2011-12</strong>. This revision, however, faced considerable criticism due to perceived flaws in the accompanying methodological changes.</p></div><h4>What is a Base Year?</h4><p>A <strong>base year</strong> serves as a fundamental reference point in economic calculations. It is a specific year against which the <strong>GDP figures</strong> for all subsequent and prior years are measured and compared.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> A <strong>base year</strong> is a fixed reference period used for calculating various economic indices, including <strong>GDP</strong>, to remove the effect of price changes and reflect real economic growth.</p></div><h4>Need for a Base Year</h4><p>The primary purpose of a <strong>base year</strong> is to establish a stable and consistent benchmark. This allows for accurate measurement of a nation's <strong>economic performance</strong> over time.</p><p>By pegging <strong>GDP figures</strong> to a specific reference year, economists and analysts can effectively interpret long-term trends and significant shifts in the country's economic landscape.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A <strong>base year</strong> is essential for:<ul><li>Providing a <strong>stable reference point</strong> for economic data.</li><li>Enabling <strong>accurate comparisons</strong> of economic performance across different periods.</li><li>Allowing for the interpretation of <strong>real economic growth</strong> by isolating price effects.</li></ul></p></div><h4>Features of an Ideal Base Year</h4><p>An ideal <strong>base year</strong> should represent a 'normal' economic period. This means it must be free from any major economic or natural disruptions that could skew data.</p><p>Such disruptions include significant events like widespread <strong>droughts</strong>, devastating <strong>floods</strong>, major <strong>earthquakes</strong>, or large-scale <strong>pandemics</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> When discussing <strong>GDP calculations</strong> or <strong>economic data reliability</strong> in <strong>GS-III</strong>, understanding the criteria for an ideal <strong>base year</strong> is crucial for critical analysis.</p></div><p>Furthermore, an effective <strong>base year</strong> should not be too far removed in the past. Using an outdated base year can lead to inaccurate reflections of the current economic structure and activity.</p>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •GDP base year is a reference point for calculating economic figures.
- •MoSPI is discussing the next base year revision, emphasizing wide consultation.
- •The 2015 revision changed the base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12 but faced criticism.
- •A base year provides a stable benchmark for measuring economic performance over time.
- •An ideal base year should be a 'normal' year, free from major disruptions, and not too old.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content