Steel Sector Decarbonization - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Steel Sector Decarbonization
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Steel Sector Decarbonization</h4><p>The <strong>Ministry of Steel</strong> in India is actively evaluating various <strong>funding strategies</strong> to bolster initiatives aimed at <strong>decarbonizing</strong> the domestic steel sector. This proactive approach is a direct response to mounting <strong>environmental concerns</strong> and the global imperative for more <strong>sustainable industrial practices</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Decarbonization</strong> refers to the process of reducing <strong>carbon emissions</strong>, particularly <strong>carbon dioxide (CO2)</strong>, resulting from human economic activity. For the steel sector, this means significantly lowering the carbon footprint associated with steel production.</p></div><h4>Why Decarbonize the Steel Sector?</h4><p>The steel industry is one of the largest industrial emitters of <strong>greenhouse gases (GHGs)</strong> globally. Traditional steelmaking processes, primarily using <strong>blast furnaces</strong> and <strong>basic oxygen furnaces (BF-BOF)</strong>, are highly energy-intensive and rely heavily on <strong>coking coal</strong>, leading to substantial CO2 emissions.</p><p>Addressing these emissions is crucial for India to meet its <strong>climate change commitments</strong> under international agreements like the <strong>Paris Agreement</strong> and to achieve its <strong>Net Zero targets</strong> by 2070.</p><h4>Role of the Ministry of Steel</h4><p>The <strong>Ministry of Steel</strong> plays a pivotal role in guiding the industry towards a greener future. Its consideration of <strong>funding mechanisms</strong> underscores the government's commitment to facilitating the transition to low-carbon steel production technologies.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> Understanding the government's role in industrial decarbonization is vital for <strong>GS Paper III (Economy and Environment)</strong>. Questions may focus on policy interventions, technological shifts, and India's climate strategy.</p></div><h4>Key Drivers for Sustainable Practices</h4><ul><li><strong>Environmental Regulations:</strong> Stricter national and international norms on emissions.</li><li><strong>Global Market Demand:</strong> Increasing preference for 'green steel' from consumers and industries.</li><li><strong>Technological Advancements:</strong> Development of new, cleaner steelmaking technologies.</li><li><strong>Energy Security:</strong> Reducing reliance on fossil fuels by exploring alternative energy sources.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Ministry of Steel is actively exploring funding for steel sector decarbonization.
- •Decarbonization is crucial due to environmental concerns and global push for sustainable industrial practices.
- •Steel industry is a major emitter; transition to cleaner production is vital for India's climate goals.
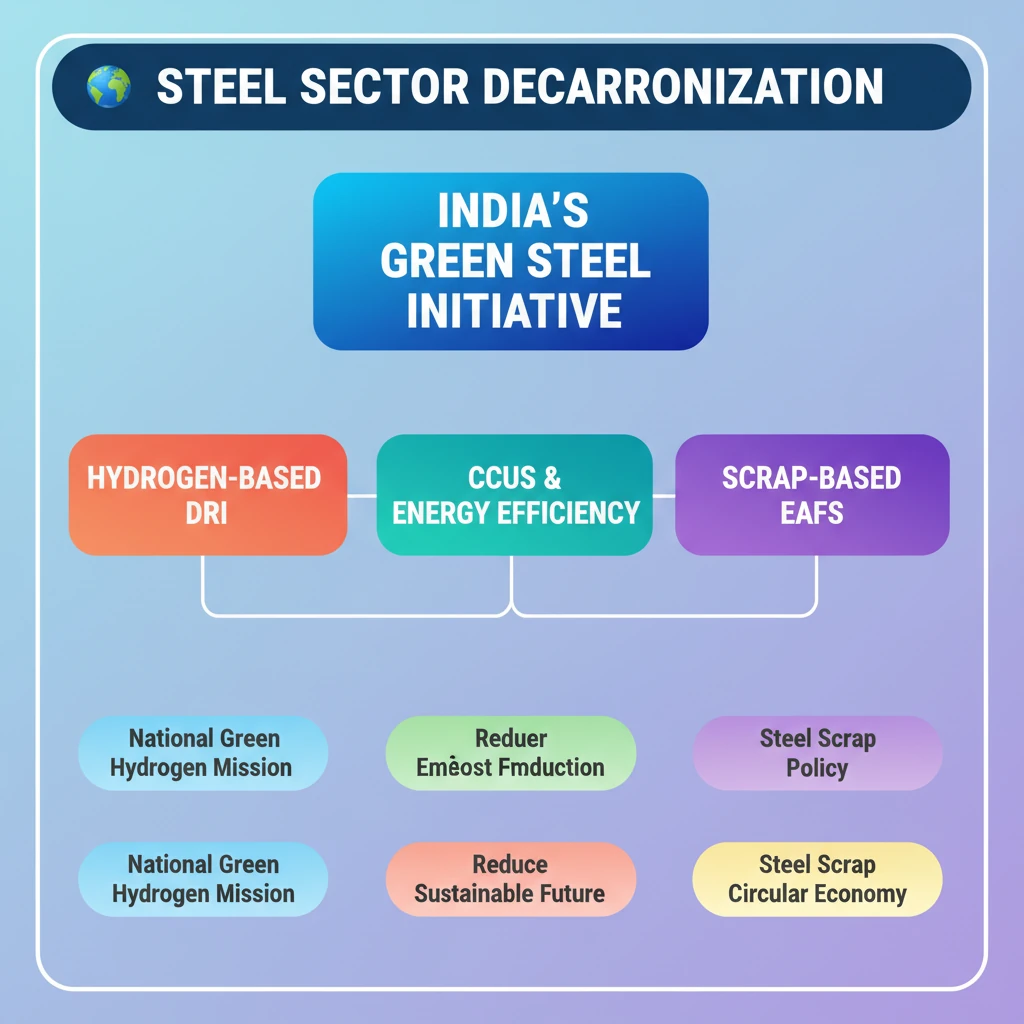
- •Key technologies include hydrogen-based DRI, CCUS, and increased scrap-based EAFs.
- •India's National Green Hydrogen Mission and National Steel Scrap Recycling Policy support decarbonization.
- •Efforts enhance India's global competitiveness and energy security.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Steel, Government of India Annual Reports
•NITI Aayog reports on Green Hydrogen and Decarbonization
•International Energy Agency (IEA) reports on Iron & Steel Technology Roadmaps
•UNFCCC reports on India's climate commitments