What is Effective Exchange Rate (EER)? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Effective Exchange Rate (EER)?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
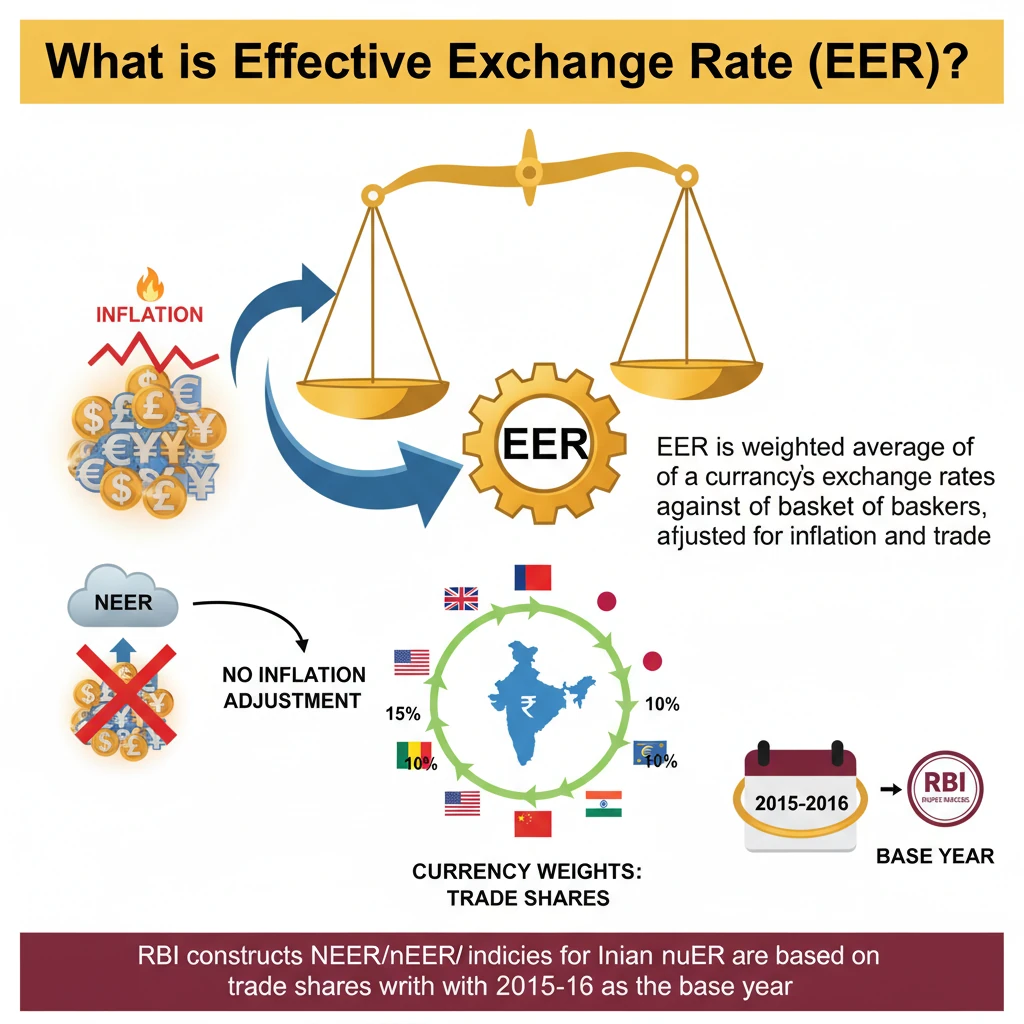
<h4>Understanding Effective Exchange Rate (EER)</h4><p>The <strong>Effective Exchange Rate (EER)</strong> of a currency, such as the Indian Rupee, is a crucial economic indicator. It represents a <strong>weighted average</strong> of its exchange rates against a basket of other major currencies.</p><p>This calculation is typically <strong>adjusted for inflation</strong> and also considers the country's overall <strong>trade competitiveness</strong>. It provides a more holistic view than a simple bilateral exchange rate.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Principle:</strong> The <strong>currency weights</strong> used in EER calculation are derived from the <strong>share of individual countries</strong> in India’s total foreign trade. This ensures the index reflects actual trade patterns.</p></div><h4>Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER)</h4><p>The <strong>Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER)</strong> is a specific type of EER. It is calculated as a simple average of <strong>bilateral exchange rates</strong> between the domestic currency and the currencies of its major trading partners.</p><p>These bilateral rates are also <strong>weighted by their respective trade shares</strong>. A critical distinction is that <strong>NEER measures the overall strength or weakness of a currency without adjusting for inflation</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>NEER vs. EER:</strong> While EER generally implies inflation adjustment, <strong>NEER specifically excludes inflation adjustment</strong>, focusing solely on nominal exchange rate movements against a basket of currencies.</p></div><h4>NEER Indices and Base Values</h4><p>NEER indices are typically presented with reference to a <strong>base value of 100</strong>. This allows for easy comparison of currency movements over time.</p><div class='info-box'><p>For India, the <strong>base year for NEER indices is 2015-16</strong>. This provides a consistent benchmark for evaluating the rupee's performance.</p></div><h4>RBI's NEER Indices for the Rupee</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> is responsible for constructing and publishing NEER indices for the Indian Rupee. These indices are calculated against different baskets of currencies.</p><p>The RBI has constructed NEER indices of the rupee against <strong>two different baskets of currencies</strong>, though the source specifically details one prominent basket.</p><h4>The 6-Currency Basket</h4><p>One of the key baskets used by the RBI for NEER calculation is the <strong>6-Currency Basket</strong>. This is a <strong>trade-weighted average rate</strong> at which the rupee is exchangeable with these specific currencies.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Currencies in the 6-Currency Basket:</strong><ul><li><strong>US dollar</strong></li><li><strong>Euro</strong></li><li><strong>Chinese yuan</strong></li><li><strong>British pound</strong></li><li><strong>Japanese yen</strong></li><li><strong>Hong Kong dollar</strong></li></ul></p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding <strong>NEER</strong> and its components is vital for <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>. Questions often relate to its impact on trade, inflation, and RBI policy. Be prepared to explain the difference between nominal and real effective exchange rates.</p></div>
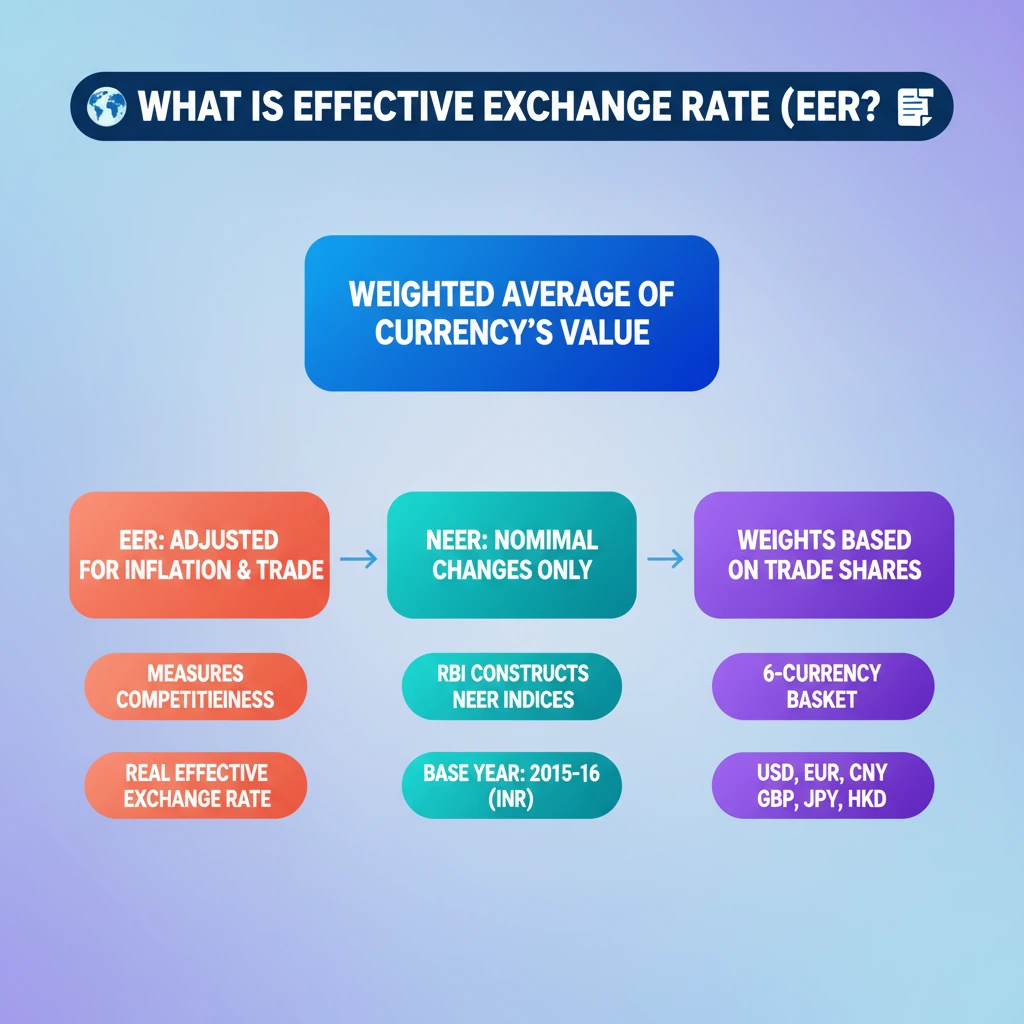
💡 Key Takeaways
- •EER is a weighted average of a currency's exchange rates against a basket of others, adjusted for inflation and trade.
- •NEER is a type of EER that does NOT adjust for inflation, measuring only nominal changes.
- •Currency weights for EER/NEER are based on trade shares with partner countries.
- •RBI constructs NEER indices for the Indian Rupee, with 2015-16 as the base year.
- •The 6-currency basket for RBI's NEER includes USD, Euro, CNY, GBP, JPY, and HKD.
- •EER/NEER is crucial for assessing trade competitiveness, imported inflation, and guiding monetary policy.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on Exchange Rate Management