What is Sundarbans? - environment-and-ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Sundarbans?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
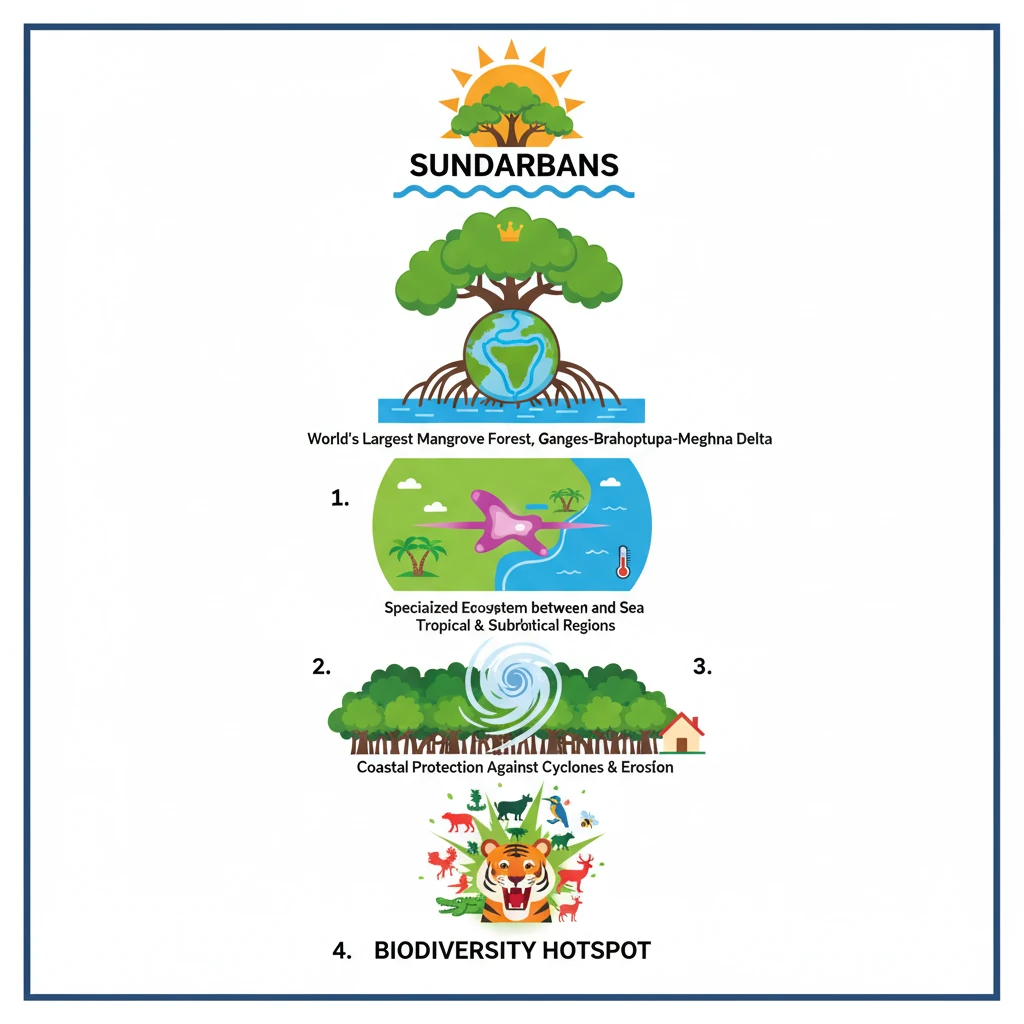
<h4>Introduction to the Sundarbans</h4><p>The <strong>Sundarbans</strong> represents the <strong>largest contiguous mangrove forest</strong> in the world. It is a vast region characterized by an intricate network of tidal waterways, mudflats, and small islands covered by salt-tolerant mangrove forests.</p><h4>Geographical Location and Formation</h4><p>This unique ecosystem is situated on the expansive <strong>delta</strong> formed by the confluence of three major rivers: the <strong>Ganges</strong>, <strong>Brahmaputra</strong>, and <strong>Meghna</strong>.</p><p>Its geographical spread lies across the <strong>Bay of Bengal</strong>, shared between India (West Bengal) and Bangladesh.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Location:</strong> Delta of <strong>Ganges</strong>, <strong>Brahmaputra</strong>, and <strong>Meghna</strong> rivers.</p><p><strong>Region:</strong> <strong>Bay of Bengal</strong>, spanning India and Bangladesh.</p></div><h4>The Mangrove Ecosystem</h4><p>The <strong>Sundarbans</strong> is globally renowned for hosting the <strong>largest mangrove forests</strong>, which are crucial for ecological balance and biodiversity.</p><p>A <strong>mangrove ecosystem</strong> is a highly specialized type of environment that thrives in specific conditions.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Definition:</strong> It exists as an interface, or transitional zone, precisely <strong>between the land and the sea</strong>.</p></div><p>These ecosystems are predominantly found in particular climatic zones, adapting to unique environmental stressors.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Climatic Zones:</strong> Primarily located in <strong>tropical</strong> and <strong>subtropical regions</strong> worldwide.</p></div><div class="exam-tip-box"><p>Understanding the <strong>unique geographical setting</strong> and the <strong>specialized nature of mangrove ecosystems</strong> is vital for questions on coastal ecology and biodiversity in <strong>UPSC Prelims (GS Paper I)</strong> and <strong>Mains (GS Paper III)</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
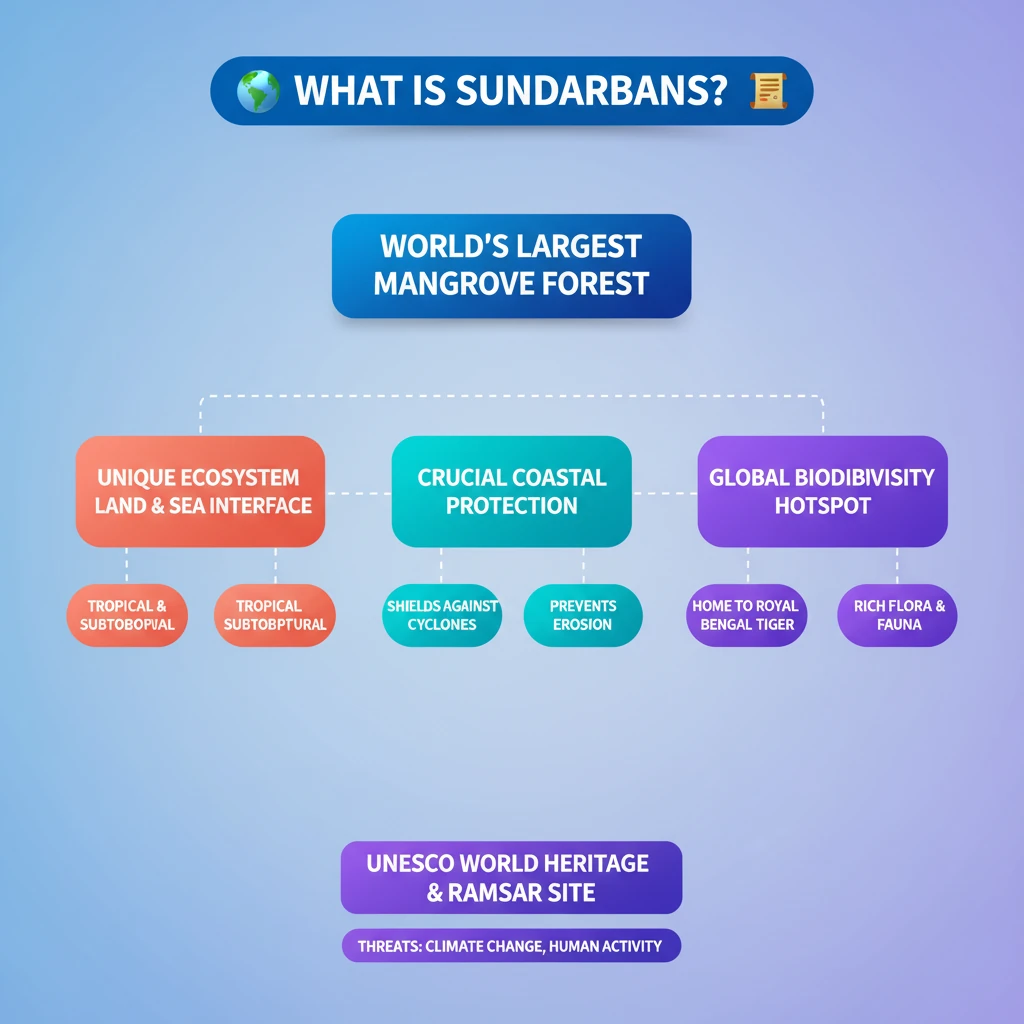
- •Sundarbans is the world's largest mangrove forest, located on the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta.
- •It is a specialized ecosystem between land and sea, found in tropical and subtropical regions.
- •Mangroves provide crucial ecosystem services, including coastal protection against cyclones and erosion.
- •It is a global biodiversity hotspot, home to the Royal Bengal Tiger and numerous other species.
- •The Sundarbans is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a Ramsar Site, facing severe threats from climate change and human activities.
- •Its conservation is vital for both ecological balance and the livelihoods of local communities.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•UNESCO World Heritage Centre official website
•Ramsar Convention on Wetlands official website
•WWF India publications on Sundarbans
•National Geographic articles on mangrove ecosystems