Sundarbans: Environmental Challenges and Sustainable Solutions - environment-and-ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Sundarbans: Environmental Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Sundarbans</h4><p>The <strong>Sundarbans</strong>, a vast tract of <strong>mangrove forest</strong>, is a critical ecological zone shared by <strong>India</strong> and <strong>Bangladesh</strong>. It is the <strong>largest single block of tidal halophytic mangrove forest</strong> in the world and a <strong>UNESCO World Heritage Site</strong>.</p><p>This unique ecosystem is vital for its <strong>biodiversity</strong>, including the iconic <strong>Royal Bengal Tiger</strong>, and provides essential ecosystem services to millions of people.</p><div class='info-box'><p>📍 The <strong>Sundarbans</strong> is located at the mouth of the <strong>Ganges</strong>, <strong>Brahmaputra</strong>, and <strong>Meghna</strong> rivers in the <strong>Bay of Bengal</strong>.</p><p>🌳 It is recognized as a <strong>Ramsar Site</strong> (Wetland of International Importance) and a <strong>Biosphere Reserve</strong>.</p></div><h4>Current Environmental Challenges</h4><p>The <strong>Sundarbans</strong> is currently grappling with a multitude of severe <strong>environmental challenges</strong>. These threats jeopardize its ecological integrity, biodiversity, and the livelihoods of its inhabitants, necessitating urgent and <strong>sustainable solutions</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>⚠️ Key challenges include <strong>freshwater scarcity</strong>, various forms of <strong>pollution</strong>, and accelerating <strong>coastal erosion</strong>.</p></div><h4>Freshwater Scarcity</h4><p>One of the most pressing issues is the acute <strong>freshwater scarcity</strong>. This problem stems largely from upstream river diversions and reduced flow, leading to increased <strong>salinity intrusion</strong> into the delta.</p><p>The lack of adequate freshwater affects the delicate balance of the mangrove ecosystem, impacting species that rely on specific salinity levels for survival. It also severely affects local agriculture and drinking water availability.</p><h4>Pollution Threats</h4><p>The <strong>Sundarbans</strong> faces significant threats from various forms of <strong>pollution</strong>, which degrade its pristine environment and harm its diverse flora and fauna.</p><h5>Microplastic Pollution</h5><p><strong>Microplastics</strong> are a growing concern, originating from plastic waste carried by rivers from inland areas and marine debris from the Bay of Bengal. These tiny plastic particles are ingested by marine organisms, entering the food chain and posing risks to the entire ecosystem.</p><h5>Chemical Pollution</h5><p>The region is also exposed to <strong>chemical pollution</strong> from agricultural runoff, industrial effluents, and urban waste discharged into the rivers. These chemicals can be toxic to aquatic life, accumulate in sediments, and disrupt the natural biological processes of the mangrove ecosystem.</p><h4>Coastal Erosion</h4><p><strong>Coastal erosion</strong> is another major challenge, exacerbated by rising sea levels due to <strong>climate change</strong> and increased frequency of severe cyclones. The erosion leads to loss of land, displacement of communities, and destruction of mangrove habitats that act as natural barriers against storms.</p><p>The protective function of the mangroves is crucial for the mainland, and their degradation makes the coast more vulnerable to natural disasters.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>💡 For UPSC, understand the <strong>interconnectedness</strong> of these challenges. For example, freshwater scarcity can weaken mangroves, making them more susceptible to coastal erosion and pollution impacts. Focus on both <strong>natural and anthropogenic causes</strong>.</p></div><h4>Importance of Sustainable Solutions</h4><p>Given the multifaceted nature of these threats, finding and implementing <strong>sustainable solutions</strong> is paramount. These solutions must address the root causes of environmental degradation while ensuring the well-being of the local communities.</p><p>Effective conservation strategies require a holistic approach, integrating ecological protection with socio-economic development.</p>
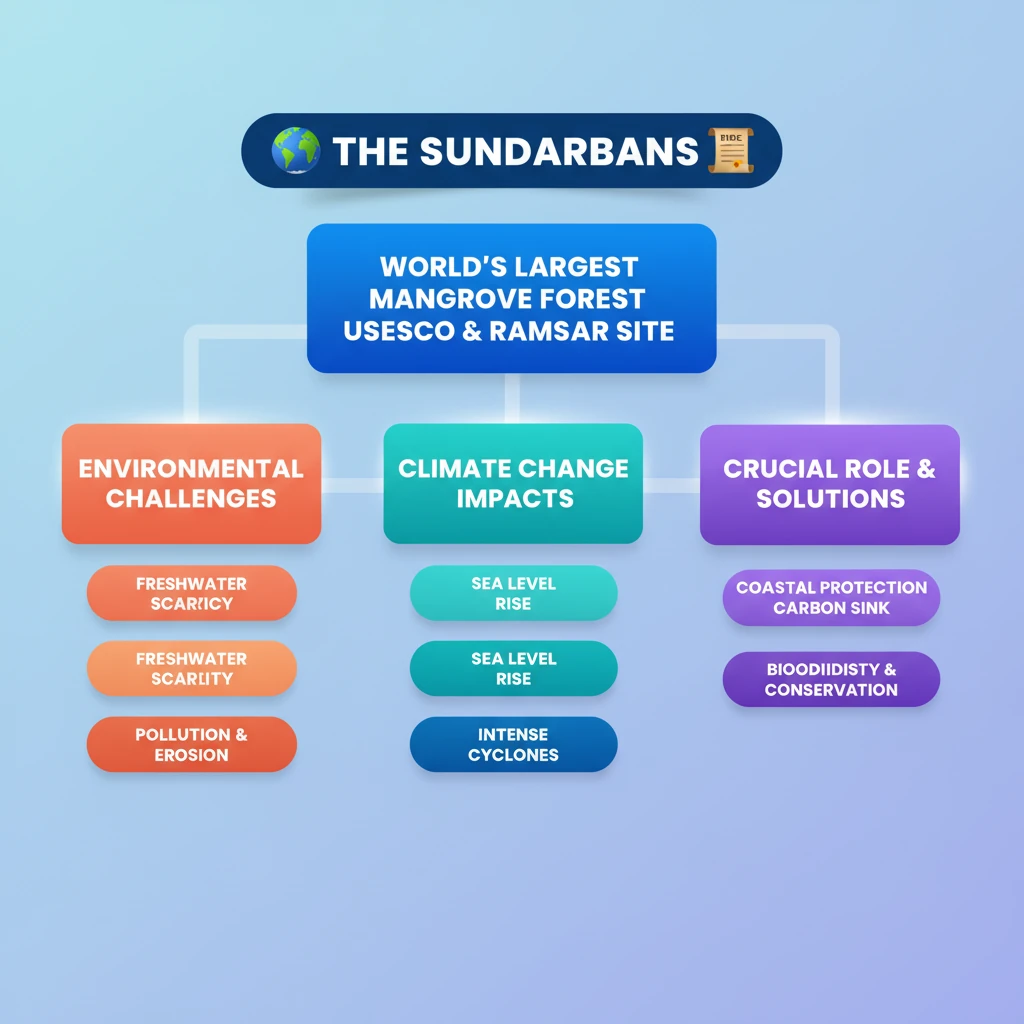
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Sundarbans is the world's largest mangrove forest, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and Ramsar Site, shared by India and Bangladesh.
- •It faces severe environmental challenges: freshwater scarcity (due to upstream diversions), microplastic and chemical pollution, and accelerated coastal erosion.
- •These threats are exacerbated by climate change, leading to rising sea levels and more intense cyclones, impacting biodiversity and local livelihoods.
- •Mangroves are crucial for coastal protection, carbon sequestration, and supporting unique biodiversity, including the Royal Bengal Tiger.
- •Sustainable solutions require integrated approaches, including conservation programs, pollution control, community engagement, and international cooperation.
- •The Sundarbans serves as a critical case study for climate change adaptation and sustainable development in deltaic regions.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•UNESCO World Heritage Centre - Sundarbans National Park
•Ramsar Sites Information Service - Sundarbans Wetland
•Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) reports on Mangrove Conservation
•Scientific publications on microplastic pollution and coastal erosion in the Sundarbans
•Reports from IUCN and WWF on Sundarbans conservation