India-US Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India-US Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
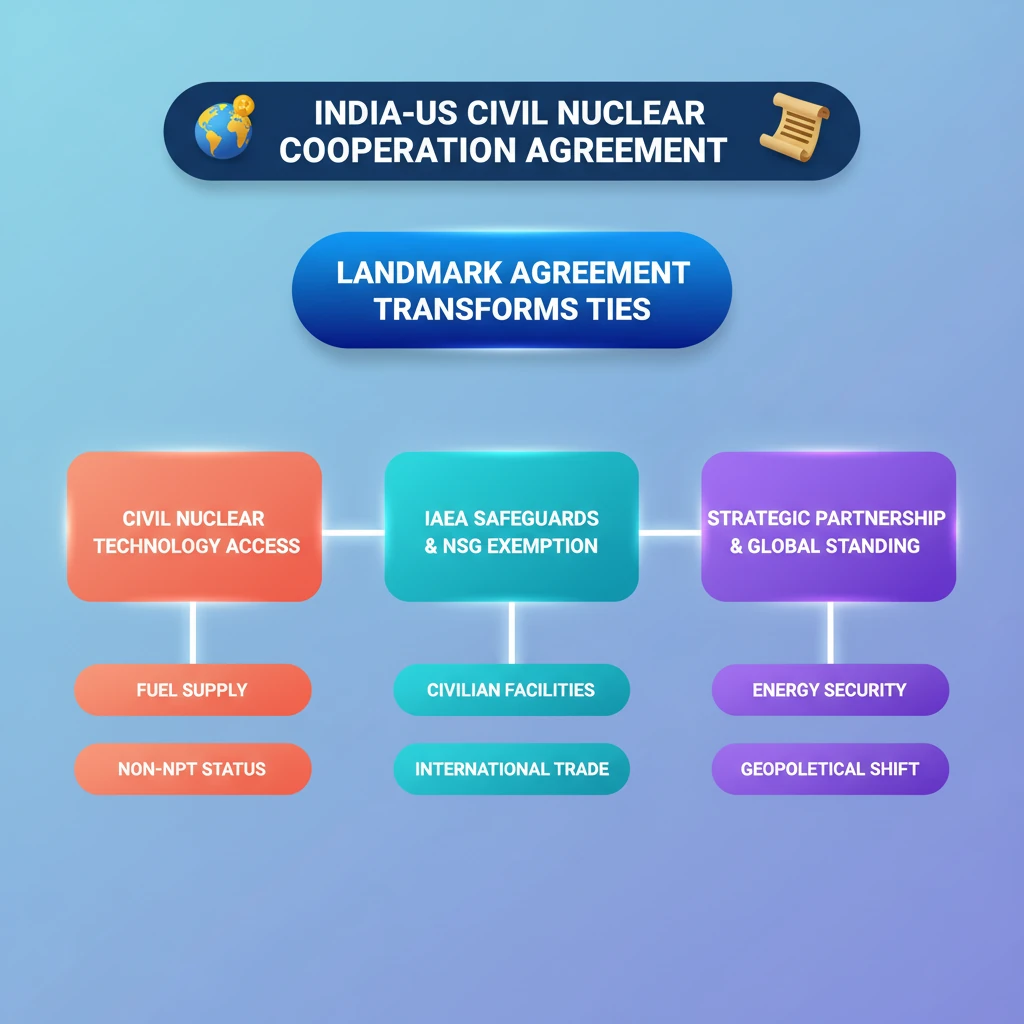
<h4>Introduction to the 123 Agreement</h4><p>The <strong>India-US Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement</strong>, often referred to as the <strong>123 Agreement</strong>, is a landmark bilateral accord between <strong>India</strong> and the <strong>United States</strong>. It was signed in <strong>2008</strong> and became operational in <strong>2008</strong>.</p><p>This agreement specifically permits <strong>India</strong> to access crucial <strong>nuclear fuel</strong>, advanced <strong>technology</strong>, and modern <strong>reactors</strong> from the global market. These resources are intended exclusively for <strong>peaceful purposes</strong>, primarily for <strong>energy generation</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A critical aspect of this agreement is that it allows such cooperation despite <strong>India</strong> not being a signatory to the <strong>Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)</strong>. This grants <strong>India</strong> a unique status in the global nuclear order.</p></div><h4>Key Components and India's Commitments</h4><p>As a core component of the agreement, <strong>India</strong> made a significant commitment. It agreed to place its <strong>civilian nuclear facilities</strong> under the comprehensive safeguards of the <strong>International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>These <strong>IAEA safeguards</strong> are crucial mechanisms. They ensure the <strong>peaceful use of nuclear material</strong> and technology transferred under the agreement, preventing diversion for military applications.</p></div><h4>US Role and NSG Exemption</h4><p>The <strong>United States</strong> played a pivotal role in facilitating this cooperation. It actively sought and secured an exemption for <strong>India</strong> from the <strong>Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>NSG exemption</strong> was essential. It enabled member states of the <strong>Nuclear Suppliers Group</strong> to engage in civil nuclear trade with <strong>India</strong>, recognizing <strong>India's</strong> expanding and responsible <strong>peaceful nuclear sector</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The 123 Agreement allows India access to civil nuclear technology and fuel despite its non-NPT status.
- •India committed to IAEA safeguards for its civilian nuclear facilities.
- •The US secured an NSG exemption for India to enable international nuclear trade.
- •It was a landmark agreement that transformed India's nuclear energy prospects and its global standing.
- •The agreement significantly strengthened the India-US strategic partnership.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) official website
•Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India documents
•US Department of State archives and press releases