National Flag of India: History, Design, and Significance - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

National Flag of India: History, Design, and Significance
Easy⏱️ 5 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the National Flag</h4><p>The <strong>National Flag of India</strong>, also known as the <strong>Tiranga</strong> (meaning 'tricolour'), is a symbol of national pride, unity, and sovereignty. Its design holds significant historical and constitutional importance for every Indian citizen.</p><h4>Architect of the Design</h4><p>The primary credit for the design of the <strong>Indian ensign</strong> is widely attributed to <strong>Pingali Venkayya</strong>, a distinguished Indian freedom fighter. His vision contributed significantly to the flag we recognize today.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Designer:</strong> <strong>Pingali Venkayya</strong></p></div><h4>First Hoisting of an Indian National Flag</h4><p>The earliest known instance of a national flag for India being hoisted occurred on <strong>7th August 1906</strong>. This historic event took place in <strong>Kolkata</strong>, specifically at <strong>Parsee Bagan Square</strong> (also known as <strong>Green Park</strong>).</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Date of First Hoisting:</strong> <strong>7th August 1906</strong></p><p><strong>Location:</strong> <strong>Parsee Bagan Square</strong> (Green Park), <strong>Kolkata</strong></p></div><h4>Physical Specifications of the National Flag</h4><p>The <strong>National Flag</strong> is designed in a rectangular shape. A specific ratio governs its dimensions, ensuring uniformity and respect for its design.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Shape:</strong> Rectangular</p><p><strong>Length-to-Width Ratio:</strong> <strong>3:2</strong></p></div><h4>Constitutional Mandate and Citizen's Duty</h4><p>Respect for the <strong>National Flag</strong> is not merely a custom but a constitutional obligation for every citizen of India. This duty is enshrined within the fundamental duties listed in the Constitution.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>According to <strong>Article 51A (a)</strong> of the <strong>Indian Constitution</strong>, it is the fundamental duty of every citizen to <strong>abide by the Constitution</strong> and to <strong>respect its ideals and institutions</strong>, including the <strong>National Flag</strong> and the <strong>National Anthem</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>Fundamental Duties</strong> (<strong>Article 51A</strong>) are common in <strong>GS-II Polity</strong>. Understanding the specific components, like respecting the <strong>National Flag</strong>, is crucial for both Prelims and Mains.</p></div>
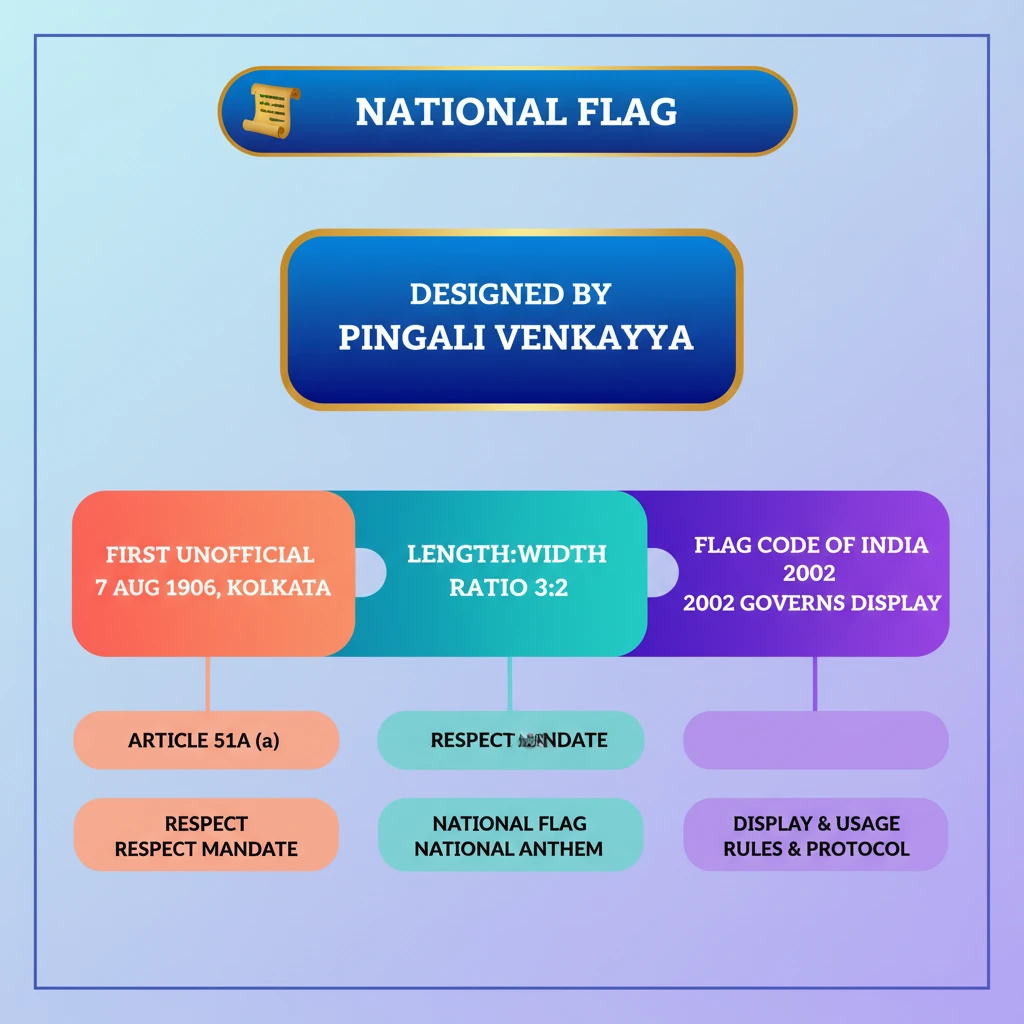
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The National Flag design is largely attributed to Pingali Venkayya.
- •The first unofficial national flag was hoisted on 7th August 1906 in Kolkata.
- •The flag is rectangular with a length-to-width ratio of 3:2.
- •Article 51A (a) mandates every citizen to respect the National Flag and National Anthem.
- •The Flag Code of India, 2002, governs its display and usage.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•The Constitution of India (Article 51A)
•Flag Code of India, 2002