Indian Coast Guard - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Indian Coast Guard
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
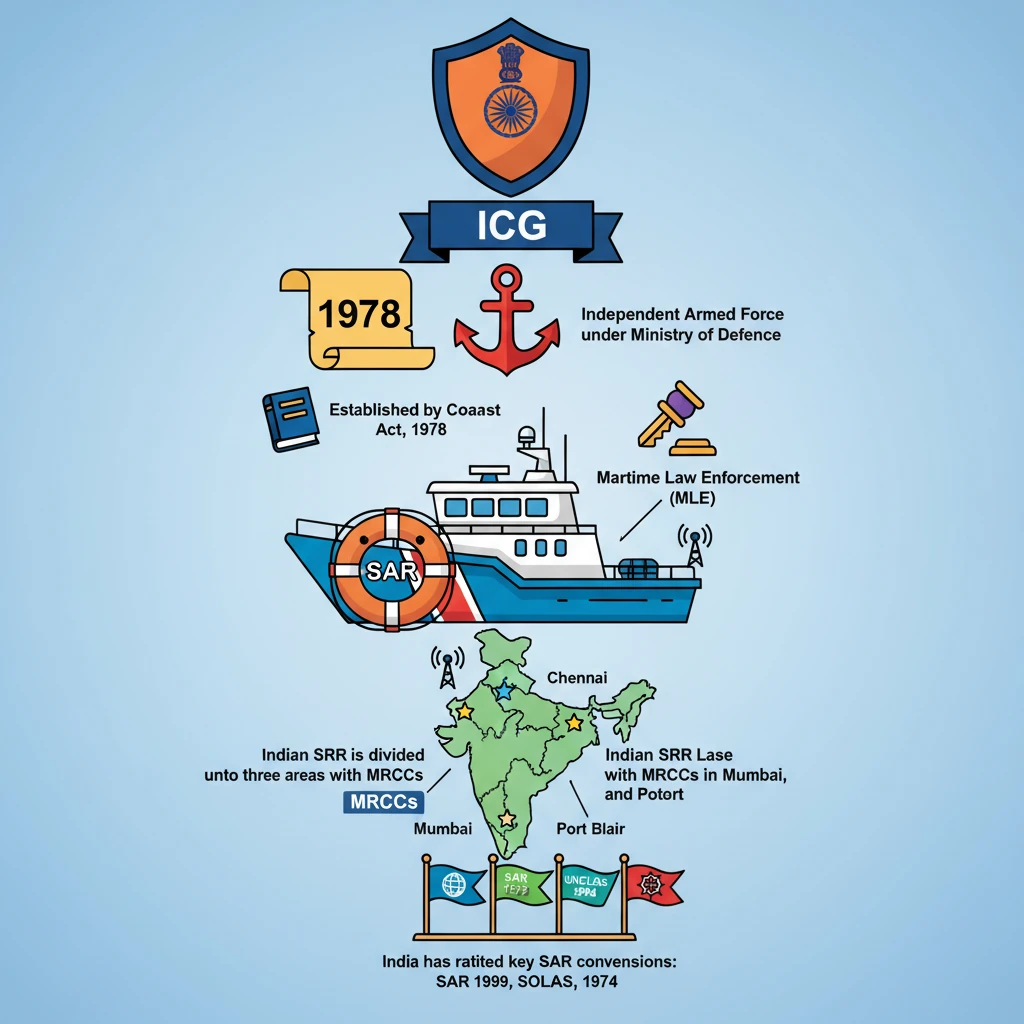
<h4>Introduction to the Indian Coast Guard (ICG)</h4><p>The <strong>Indian Coast Guard (ICG)</strong> plays a pivotal role in ensuring maritime safety and security along India's vast coastline. It operates as an <strong>independent Armed Force</strong> of India.</p><p>The ICG is also designated as the primary agency for <strong>Search and Rescue (SAR)</strong> operations and <strong>Maritime Law Enforcement</strong> in India's maritime zones.</p><h4>Maritime Rescue Coordination Centres (MRCCs)</h4><p><strong>Maritime Rescue Coordination Centres (MRCCs)</strong> in India are specialized operational units within the <strong>Indian Coast Guard</strong>. These centres are crucial for coordinating effective SAR missions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>MRCC Function:</strong> MRCCs are responsible for receiving distress alerts, coordinating rescue efforts, and deploying resources to assist vessels and personnel in distress at sea.</p></div><h4>Search and Rescue Region (SRR)</h4><p>A <strong>Search and Rescue Region (SRR)</strong> is a precisely defined geographical area. Within this area, specific SAR services are provided and coordinated by an associated <strong>MRCC</strong>.</p><p>The <strong>Indian Coast Guard</strong> is tasked with coordinating all <strong>SAR missions</strong> within the <strong>Indian Maritime Search and Rescue Region (ISRR)</strong>, ensuring comprehensive coverage.</p><h4>Structure of the Indian SRR</h4><p>The extensive <strong>Indian SRR</strong> is strategically divided into three distinct operational areas. Each of these areas is overseen by a dedicated <strong>MRCC</strong>.</p><ul><li><strong>Mumbai:</strong> Covers the western maritime region.</li><li><strong>Chennai:</strong> Manages the eastern maritime region.</li><li><strong>Port Blair:</strong> Oversees the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and surrounding waters.</li></ul><h4>International SAR Cooperation: Key Conventions</h4><p>India actively participates in international efforts to enhance maritime safety and SAR capabilities. It has ratified several crucial international conventions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Ratified Conventions:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>International Convention on Maritime Search and Rescue (SAR) 1979:</strong> Establishes a global framework for SAR operations.</li><li><strong>United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) 1982:</strong> Defines the rights and responsibilities of nations in their use of the world's oceans, including SAR.</li><li><strong>International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) 1974:</strong> Sets minimum safety standards in the construction, equipment, and operation of merchant ships.</li></ul></div><h4>Other Initiatives for SAR and Maritime Cooperation</h4><p>Beyond formal conventions, India engages in various initiatives to bolster maritime security and SAR cooperation with regional and global partners.</p><ul><li><strong>India’s SAGAR Vision:</strong> This initiative, standing for <strong>"Security and Growth for All in the Region,"</strong> emphasizes cooperative measures for sustainable development and security in the Indian Ocean.</li><li><strong>Djibouti Code of Conduct (DCoC):</strong> This framework is specifically designed to enhance capacity building and cooperation to combat <strong>piracy and armed robbery against ships</strong> in the <strong>Western Indian Ocean</strong> and the <strong>Gulf of Aden</strong>.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>DCoC Observer Status:</strong> India holds <strong>observer status</strong> in the <strong>Djibouti Code of Conduct</strong>, alongside Japan, Norway, the UK, and the USA. This signifies its commitment to regional maritime security.</p></div><h4>Establishment and Mandate of the ICG</h4><p>The <strong>Indian Coast Guard</strong> was formally established by the <strong>Coast Guard Act, 1978</strong>. This act provided the legal framework for its creation as a distinct armed force.</p><p>The ICG functions under the administrative control of the <strong>Ministry of Defence</strong>, aligning its operations with national defence strategies.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>ICG's Triple Mandate:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Armed Force:</strong> Capable of defending national interests.</li><li><strong>Search and Rescue (SAR) Agency:</strong> Primary coordinator for maritime distress.</li><li><strong>Maritime Law Enforcement Agency:</strong> Enforces laws in India's maritime zones.</li></ul></div><p>The <strong>headquarters</strong> of the <strong>Indian Coast Guard</strong> is located in <strong>New Delhi</strong>, from where it directs its nationwide operations.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Remember the <strong>Coast Guard Act, 1978</strong> and its placement under the <strong>Ministry of Defence</strong>. This distinguishes it from the Navy while highlighting its armed force status. Its multi-faceted role (Armed Force, SAR, MLE) is a crucial point for Mains answers.</p></div>
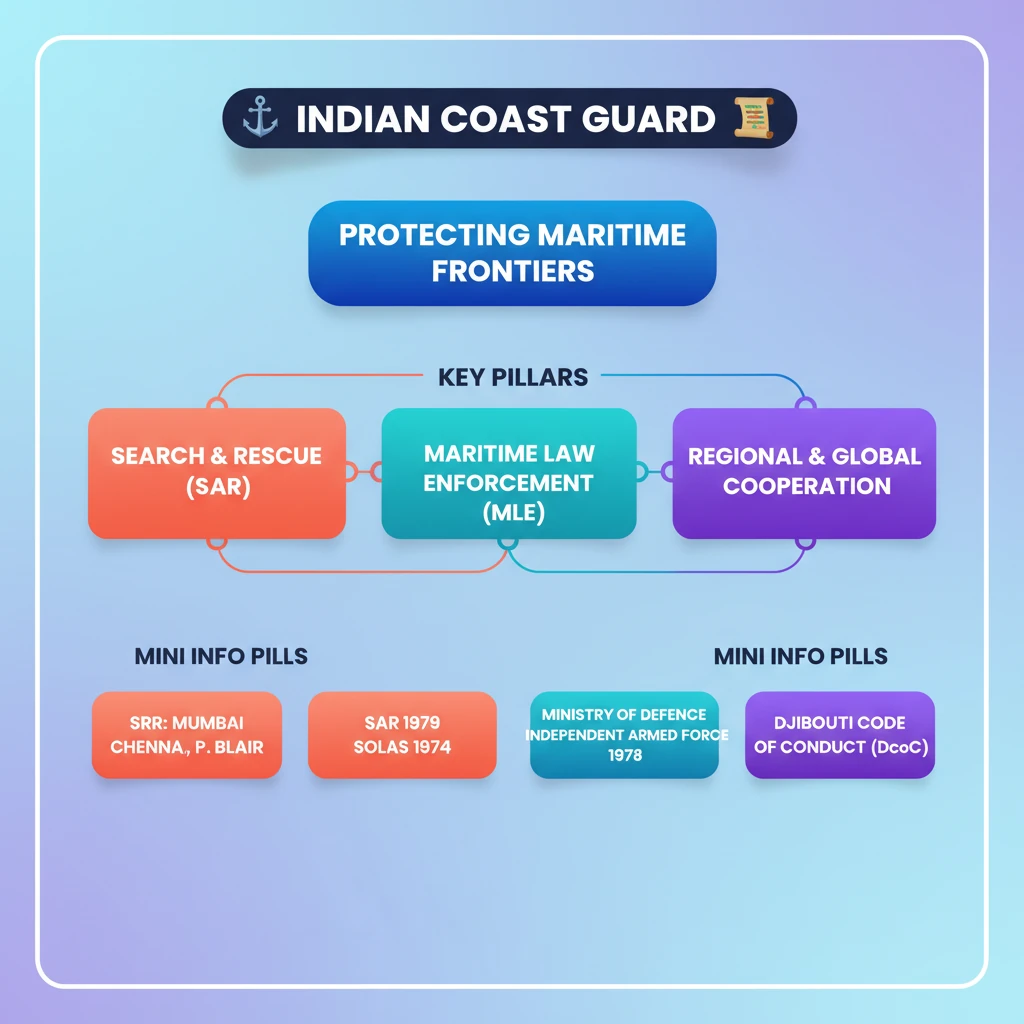
💡 Key Takeaways
- •ICG is an independent Armed Force under Ministry of Defence, established by Coast Guard Act, 1978.
- •It serves as India's primary Search and Rescue (SAR) and Maritime Law Enforcement (MLE) agency.
- •Indian SRR is divided into three areas with MRCCs in Mumbai, Chennai, and Port Blair.
- •India has ratified key SAR conventions: SAR 1979, UNCLOS 1982, SOLAS 1974.
- •ICG contributes to India's SAGAR Vision and holds observer status in the Djibouti Code of Conduct (DCoC).
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content