Major Military Exercises of India - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Major Military Exercises of India
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
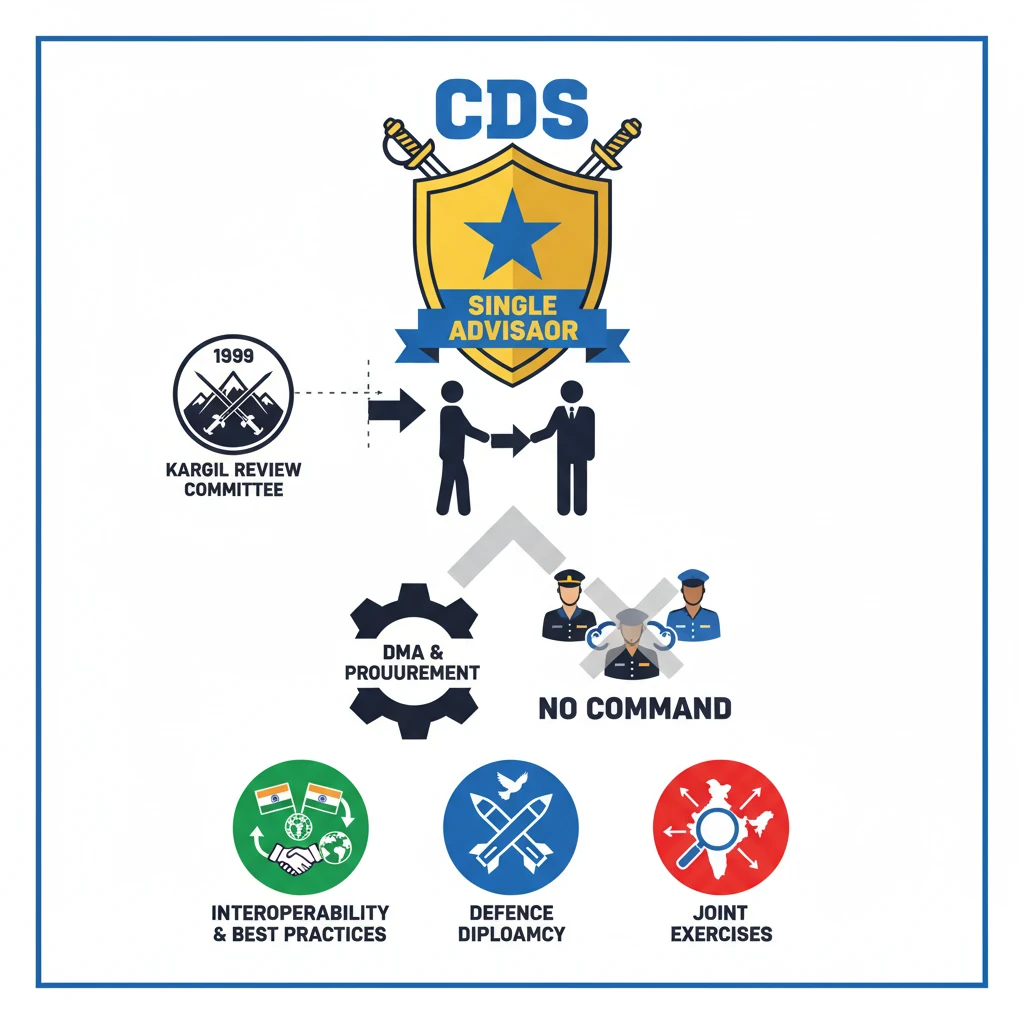
<h4>Understanding the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)</h4><p>The <strong>Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)</strong> is a pivotal position in India's defence architecture, designed to bring greater synergy and integration among the three armed services: the <strong>Indian Army</strong>, <strong>Indian Navy</strong>, and <strong>Indian Air Force</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary role of the <strong>CDS</strong> is to serve as the <strong>single-point military adviser</strong> to the <strong>Defence Minister</strong>, streamlining military counsel and decision-making.</p></div><h4>Historical Evolution of the CDS Post</h4><p>The recommendation for creating the <strong>CDS</strong> post first emerged in <strong>2001</strong>. This was a direct outcome of the <strong>Group of Ministers (GoM)</strong> report, which was tasked with reviewing the findings of the <strong>Kargil Review Committee (1999)</strong>.</p><p>Following the <strong>GoM's</strong> recommendations, the government established the <strong>Integrated Defence Staff (IDS)</strong> in <strong>2002</strong>. The <strong>IDS</strong> was envisioned to eventually function as the secretariat for the future <strong>CDS</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>In <strong>2012</strong>, the <strong>Naresh Chandra Committee</strong> proposed an alternative: the appointment of a <strong>Permanent Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee</strong>. This was suggested as a compromise to address initial apprehensions regarding the <strong>CDS</strong> role.</p></div><p>The post of <strong>CDS</strong> was finally created in <strong>2019</strong>, based on the recommendations of a committee of defence experts led by <strong>Lt General DB Shekatkar</strong>. This marked a significant reform in India's higher defence management.</p><p><strong>General Bipin Rawat</strong> became the <strong>first CDS</strong> of India, appointed on <strong>December 31, 2019</strong>. His appointment underscored the government's commitment to military integration.</p><h4>Roles and Responsibilities of the CDS</h4><p>The <strong>CDS</strong> holds several critical responsibilities aimed at enhancing operational efficiency and inter-service cooperation. He heads the newly established <strong>Department of Military Affairs (DMA)</strong> within the <strong>Ministry of Defence</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>As the <strong>single-point military adviser</strong>, the <strong>CDS</strong> provides comprehensive counsel to the <strong>Defence Minister</strong> on matters concerning all three services. The individual service chiefs are expected to advise only on issues specific to their respective forces.</p></div><p>The <strong>CDS</strong>, as the head of the <strong>DMA</strong> and <strong>Permanent Chairman-Chiefs of Staff Committee</strong>, is empowered to prioritize <strong>inter-service procurement decisions</strong>. This ensures optimal allocation of resources across the armed forces.</p><p>While the <strong>CDS</strong> can issue directives to the three service chiefs, it is crucial to note that he <strong>does not possess any command authority</strong> over the forces themselves. This distinction maintains the operational autonomy of the individual services.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>CDS</strong> is considered <strong>'first among equals'</strong> among the service chiefs. He holds the rank of <strong>Secretary</strong> within the <strong>Department of Defence (DoD)</strong>, and his financial powers are primarily confined to the <strong>revenue budget</strong>.</p></div><p>Additionally, the <strong>CDS</strong> plays an important <strong>advisory role</strong> within the <strong>Nuclear Command Authority (NCA)</strong>, contributing to strategic decision-making regarding India's nuclear arsenal.</p><h4>Major Joint Military Exercises of India</h4><p><strong>Joint Military Exercises</strong> are crucial components of India's defence cooperation strategy. These exercises serve as flagship events that showcase the <strong>Indian Army's professional competence</strong> across various operational scenarios.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>These exercises provide invaluable opportunities for participating forces to <strong>learn best practices</strong>, enhance interoperability, and build mutual understanding with partner nations.</p></div><h4>Scope and Evolution of Joint Exercises</h4><p>The scope of these joint exercises is both <strong>realistic and highly diversified</strong>. They cover a wide array of operational environments and challenges.</p><ul><li><strong>Counter Terrorist Operations:</strong> Training for combating insurgency and terrorism.</li><li><strong>Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR):</strong> Preparing for rapid response during natural calamities or crises.</li><li><strong>UN Peacekeeping:</strong> Practicing protocols and procedures for international peacekeeping missions.</li><li><strong>High Altitude Operations:</strong> Specialised training for warfare in mountainous and extreme cold conditions.</li><li><strong>Desert Warfare:</strong> Exercises conducted in arid and semi-arid environments.</li><li><strong>Urban Warfare:</strong> Training for combat operations in densely populated urban areas.</li><li><strong>Jungle Warfare:</strong> Developing tactics and skills for operations in dense forest regions.</li></ul><p>The complexity of these exercises is continually increased to incorporate the latest advancements in warfighting. This includes integrating scenarios like <strong>Drone Warfare</strong> and understanding tactics related to <strong>Grey Zone Warfare</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC aspirants should pay close attention to the <strong>purpose and specific focus</strong> of different exercises, as well as the <strong>participating countries</strong>. Questions often test understanding of these aspects.</p></div><h4>Key Joint Exercises of the Indian Army with Partner Nations</h4><p>India conducts numerous bilateral and multilateral exercises with various countries to bolster defence ties and operational readiness. Below is a list of major joint exercises involving the <strong>Indian Army</strong>:</p><table class='info-table'><tr><th>Country</th><th>Exercise Name</th></tr><tr><td><strong>Australia</strong></td><td><strong>Ex AUSTRA HIND</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Bangladesh</strong></td><td><strong>Ex SAMPRITI</strong></td></tr><tr><td><td><strong>China</strong></td><td><strong>Ex HAND IN HAND</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>France</strong></td><td><strong>Ex SHAKTI</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Indonesia</strong></td><td><strong>Ex GARUDA SHAKTI</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Kazakhstan</strong></td><td><strong>Ex PRABAL DOSTYK</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Kyrgyzstan</strong></td><td><strong>Ex KHANJAR</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Maldives</strong></td><td><strong>Ex EKUVERIN</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Mongolia</strong></td><td><strong>Ex NOMADIC ELEPHANT</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Myanmar</strong></td><td><strong>IMBEX</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Nepal</strong></td><td><strong>Ex SURYA KIRAN</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Oman</strong></td><td><strong>AL NAGAH</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Russia</strong></td><td><strong>Ex INDRA</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Seychelles</strong></td><td><strong>Ex LAMITYE</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Sri Lanka</strong></td><td><strong>Ex MITRA SHAKTI</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>Thailand</strong></td><td><strong>Ex MAITREE</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>UK</strong></td><td><strong>Ex AJEYA WARRIOR</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>USA</strong></td><td><strong>Ex YUDHABHAYAS</strong></td></tr><tr><td><strong>USA</strong></td><td><strong>Ex VAJRA PRAHAR</strong></td></tr></table><p>Recently, the <strong>16th edition</strong> of the <strong>India-Mongolia Joint Military Exercise NOMADIC ELEPHANT</strong> commenced at the <strong>Foreign Training Node, Umroi (Meghalaya)</strong>. This highlights the ongoing nature and importance of these engagements.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •CDS is India's single-point military advisor to the Defence Minister, fostering inter-service synergy.
- •The CDS post was created in 2019, following recommendations from the Kargil Review Committee (1999) and subsequent expert panels.
- •CDS heads the Department of Military Affairs (DMA) and prioritizes inter-service procurement but lacks command authority over forces.
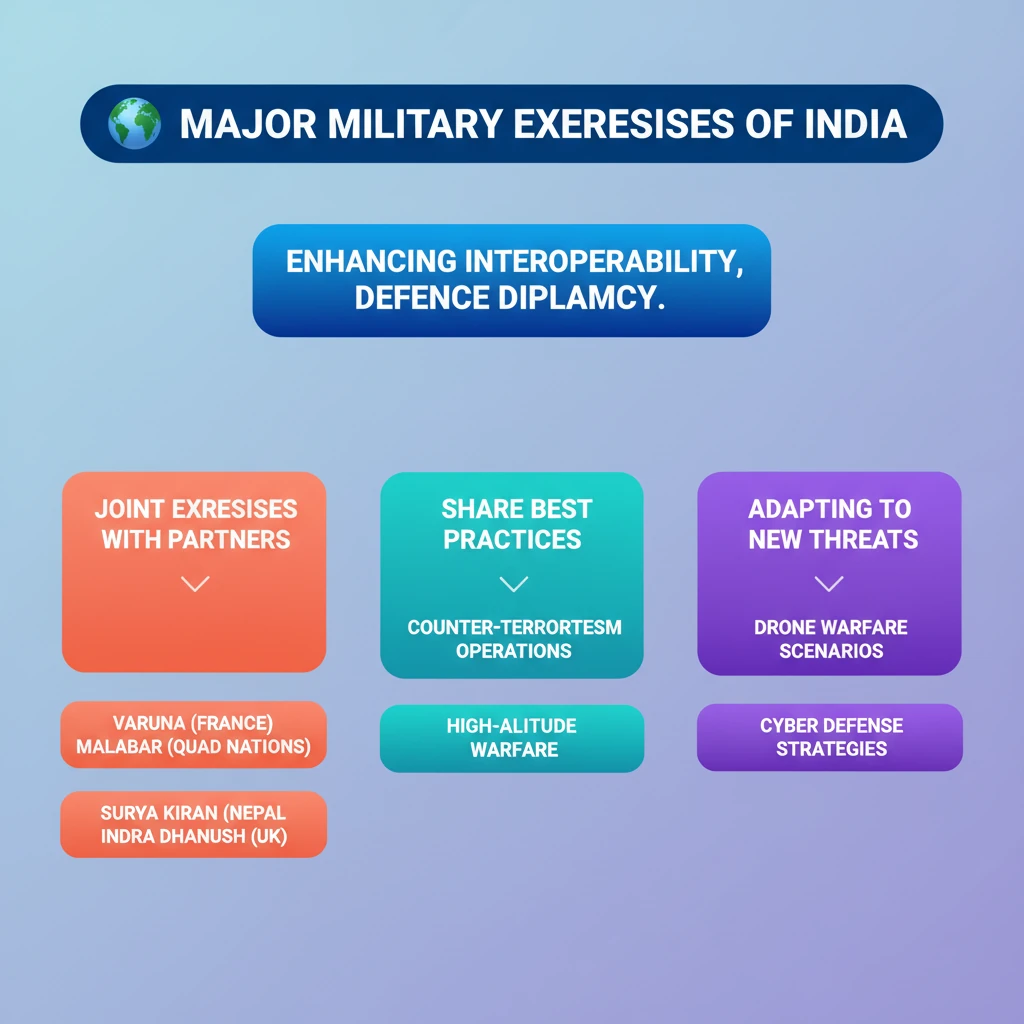
- •Joint Military Exercises enhance interoperability, share best practices, and strengthen defence diplomacy with partner nations.
- •Exercises cover diverse scenarios from counter-terrorism to high-altitude warfare, adapting to new threats like drone warfare.
- •Key exercises include NOMADIC ELEPHANT (Mongolia), YUDHABHAYAS/VAJRA PRAHAR (USA), SAMPRITI (Bangladesh), and SHAKTI (France).
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official Government of India (Ministry of Defence) releases (general knowledge base)
•Reputable defence news outlets and strategic think tanks (general knowledge base)