Concerns Regarding Opium Stockpiles in Afghanistan - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Concerns Regarding Opium Stockpiles in Afghanistan
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
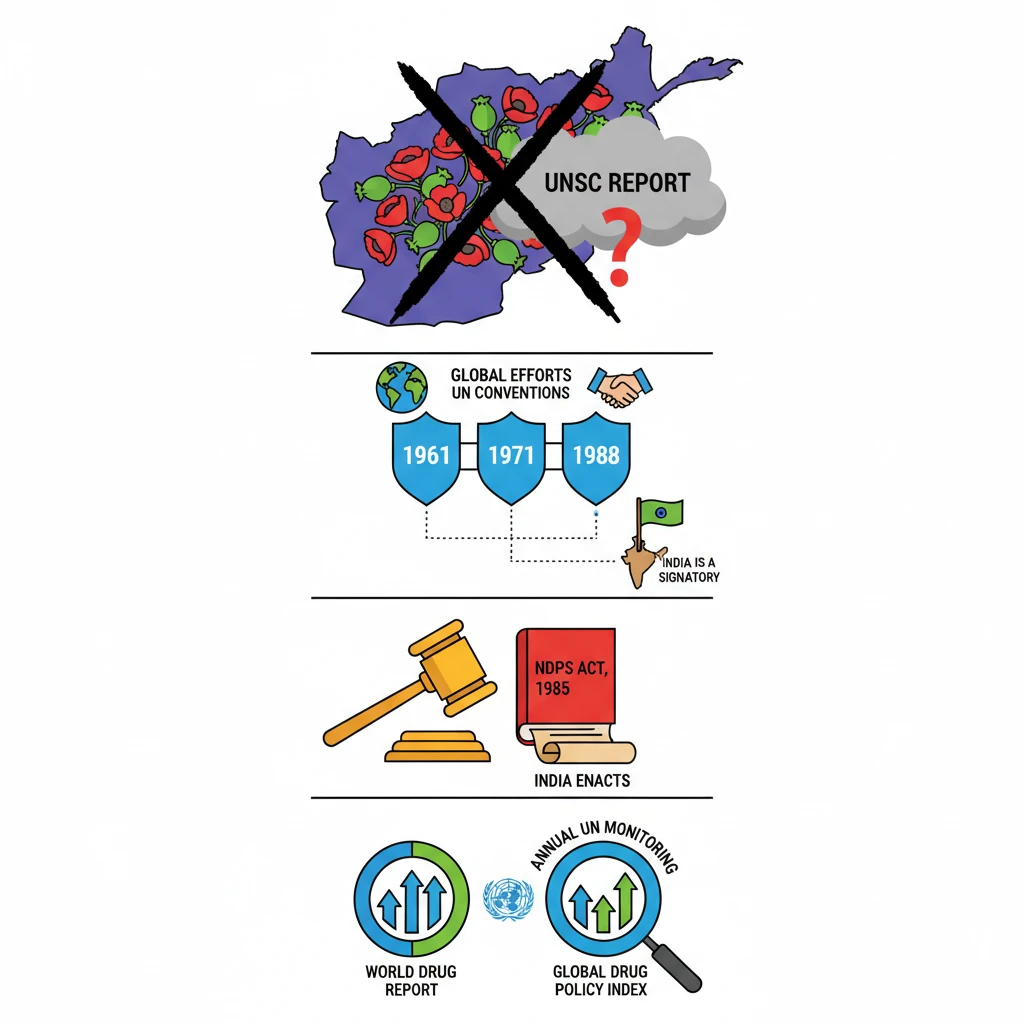
<h4>Introduction: Opium Concerns in Afghanistan</h4><p>A recent report published by the <strong>United Nations Security Council (UNSC)</strong> has raised significant concerns regarding Afghanistan’s extensive <strong>opium stockpiles</strong>.</p><p>This concern persists despite the <strong>Taliban's ban</strong> on <strong>poppy cultivation</strong>, highlighting a complex challenge in the region.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>UNSC report</strong> serves as a critical indicator of the ongoing illicit drug trade and its potential implications for regional and global security.</p></div><h4>Global Frameworks Against Drug Abuse</h4><p>The international community has established several key conventions to combat drug abuse and illicit trafficking. These frameworks provide a legal and operational basis for global cooperation.</p><ul><li><strong>Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961</strong>: Focuses on controlling narcotic drugs.</li><li><strong>The Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971</strong>: Aims to control psychotropic substances.</li><li><strong>The UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988</strong>: Targets illicit trafficking, money laundering, and precursor chemicals.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>These three conventions form the bedrock of the <strong>international drug control system</strong>, promoting coordinated efforts among member states.</p></div><h4>India's Commitment to Drug Control</h4><p><strong>India</strong> is a committed signatory to all three major <strong>UN conventions</strong> on drug control. This commitment underscores its dedication to combating drug abuse and trafficking both domestically and internationally.</p><p>To implement these international obligations and address internal drug challenges, India enacted the <strong>Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight (GS-2, GS-3)</strong>: India's role as a signatory and its domestic legislation like the <strong>NDPS Act</strong> are crucial points for demonstrating its commitment to international law and internal security challenges.</p></div><h4>International Reporting on Drug Policy</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations</strong> regularly monitors and reports on global drug trends and policies to inform international efforts and policy-making.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li>Every year, the <strong>UN</strong> publishes the <strong>World Drug Report</strong>, which provides comprehensive statistics and analysis on global drug markets.</li><li>The <strong>Global Drug Policy Index</strong> is another key publication, assessing national drug policies against international standards.</li></ul></div>
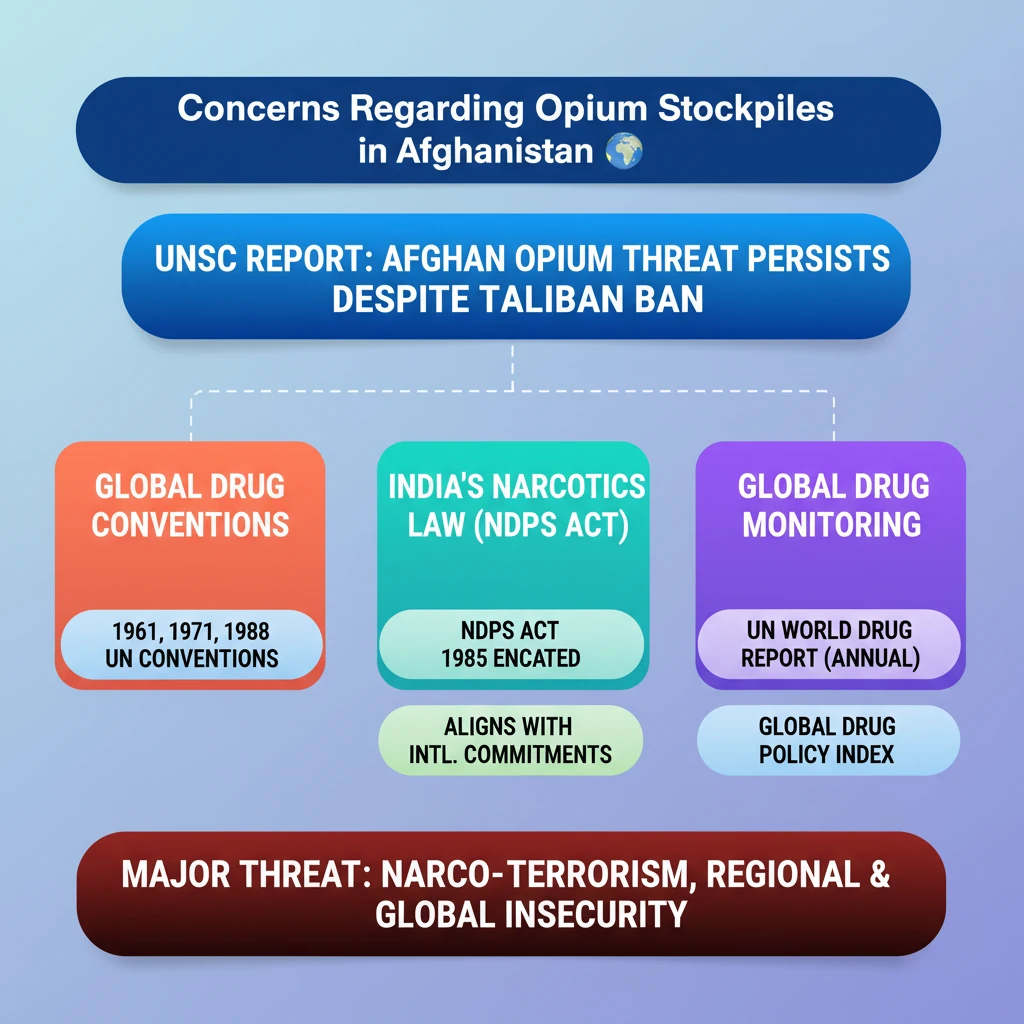
💡 Key Takeaways
- •UNSC report highlights significant concerns over Afghanistan's opium stockpiles despite the Taliban's ban on poppy cultivation.
- •Global efforts to tackle drug abuse are guided by three key UN conventions (1961, 1971, 1988), to which India is a signatory.
- •India has enacted the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985, to align with international commitments.
- •The UN annually publishes the World Drug Report and Global Drug Policy Index to monitor global drug trends.
- •Afghan opium stockpiles pose a significant threat, fueling narco-terrorism and impacting regional and international security.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Reports on Afghanistan
•United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) World Drug Reports
•The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985