Initiatives to Tackle Drug Abuse - Defence And Security | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Initiatives to Tackle Drug Abuse
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
defence and security
📖 Introduction
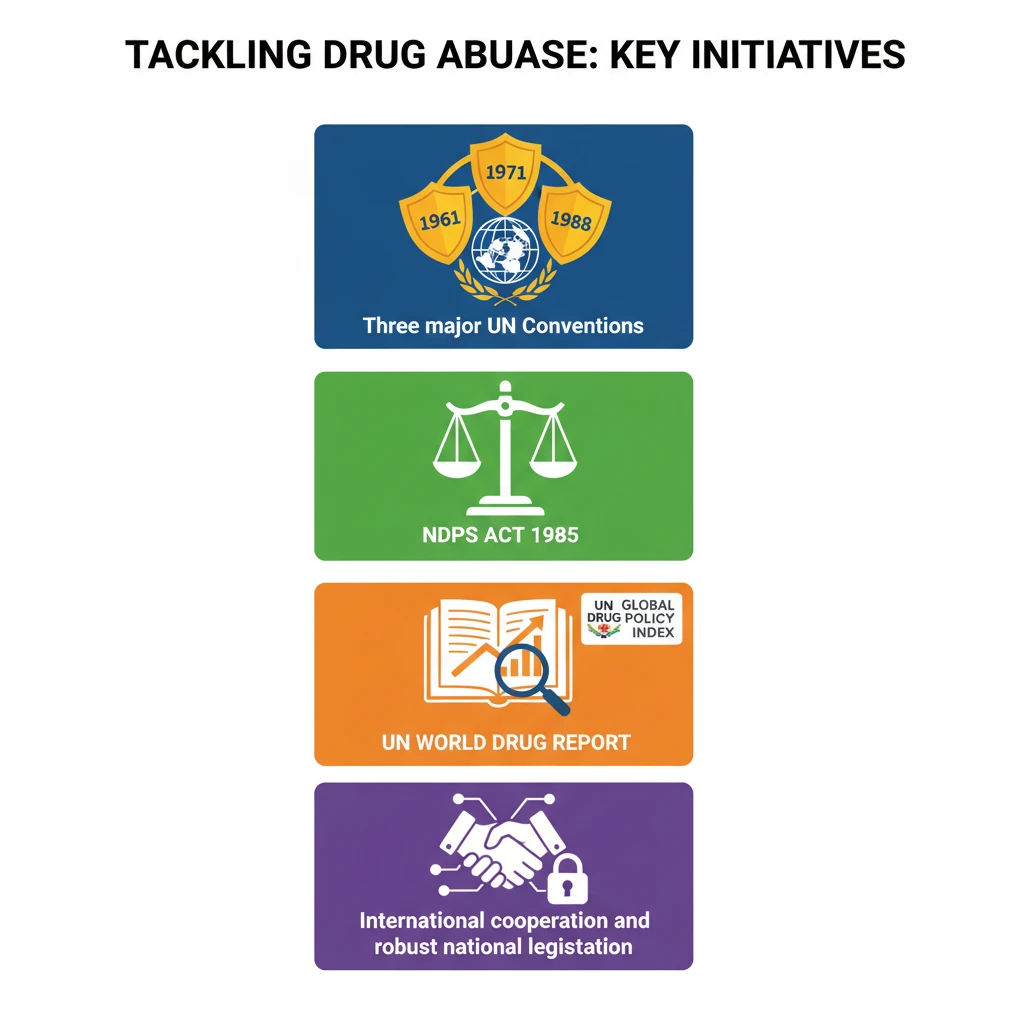
<h4>Global Framework for Drug Control</h4><p>The global community has established a robust framework to combat <strong>drug abuse</strong> and <strong>illicit trafficking</strong>. These initiatives are crucial for international cooperation and harmonized efforts across nations.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>India is a proud <strong>signatory</strong> to all major international conventions addressing narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, demonstrating its commitment to global drug control efforts.</p></div><h4>Key International Conventions</h4><p>Three principal <strong>United Nations Conventions</strong> form the bedrock of international drug control law. These treaties guide national legislation and foster multilateral collaboration.</p><ul><li><strong>Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961</strong>: This convention aims to limit the production and distribution of narcotic drugs exclusively for medical and scientific purposes, while preventing illicit cultivation and trafficking.</li><li><strong>The Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971</strong>: This treaty extends control to a wider range of psychoactive substances that are not covered by the 1961 Convention, focusing on substances with abuse potential.</li><li><strong>The UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988</strong>: This convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking, including provisions for money laundering, asset forfeiture, and extradition.</li></ul><h4>India's National Legislation</h4><p>In consonance with its international commitments, India enacted the <strong>Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985</strong>. This Act provides for the penalty, control, and regulation of operations relating to narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>NDPS Act, 1985</strong> is the primary legislation in India that prohibits the production, possession, sale, purchase, transport, storage, and consumption of any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance, except for medical or scientific purposes.</p></div><h4>Global Monitoring and Reporting</h4><p>To monitor the global drug situation and inform policy, the <strong>United Nations</strong> publishes key reports annually. These documents provide critical data and analysis on drug trends worldwide.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>World Drug Report</strong>: Published annually by the <strong>UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime)</strong>, this report offers a comprehensive overview of the international drug situation.</li><li><strong>Global Drug Policy Index</strong>: This index assesses and ranks countries' drug policies based on various criteria, promoting evidence-based and human rights-centered approaches.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding these global and national initiatives is vital for questions on <strong>Internal Security (GS Paper III)</strong> and <strong>International Relations (GS Paper II)</strong>, especially concerning global governance and India's role.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Three major UN Conventions (1961, 1971, 1988) form the global legal framework against drug abuse.
- •India is a signatory to all UN drug conventions and enacted the NDPS Act, 1985, as its primary domestic law.
- •The UN World Drug Report and Global Drug Policy Index monitor global drug trends and inform policy.
- •International cooperation and robust national legislation are crucial for tackling the complex issue of drug abuse and trafficking.
- •Drug control initiatives address both supply and demand reduction, alongside harm reduction strategies.
🧠 Memory Techniques
100% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC)
•Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India