What are Key Facts About Pali Language? - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Key Facts About Pali Language?
Easy⏱️ 6 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
<h4>Origin and Linguistic Classification</h4><p>The <strong>Pali language</strong> is an ancient Middle Indo-Aryan language that belongs to the larger <strong>Indo-European language family</strong>. Its roots are deeply embedded in the linguistic landscape of ancient India.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Language Family:</strong> Indo-European<br><strong>Classification:</strong> Middle Indo-Aryan</div><p>Initially, scholars believed <strong>Pali</strong> was identical to <strong>Magadhi</strong>, the language spoken in the ancient kingdom of <strong>Magadha</strong> (modern-day Bihar). However, recent linguistic studies suggest a stronger resemblance to the <strong>Prakrits of Western India</strong>.</p><h4>Classical Language Status</h4><p>The <strong>Union Cabinet</strong> has officially approved the recognition of <strong>Pali</strong> as a <strong>Classical Language</strong> in India. This prestigious status is shared with other significant Indian languages such as <strong>Prakrit</strong>, <strong>Marathi</strong>, <strong>Assamese</strong>, and <strong>Bengali</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Classical Language Status:</strong> Approved by Union Cabinet<br><strong>Significance:</strong> Recognizes its rich heritage and literary tradition.</div><h4>Historical Connection with Emperor Ashoka</h4><p><strong>Emperor Ashoka's inscriptions</strong>, particularly those found in modern-day <strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong>, were often written in <strong>Pali</strong>. This highlights the language's prevalence and importance during the Mauryan period.</p><h4>Religious Significance: Buddhism</h4><p><strong>Pali</strong> holds immense religious significance as the sacred language of <strong>Theravada Buddhism</strong>. It is the language in which the entire <strong>Theravada Buddhist canon</strong> is preserved.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Theravada Buddhist Canon (Tipitaka):</strong><ul><li><strong>Vinaya Pitaka:</strong> Rules for monastic discipline</li><li><strong>Sutta Pitaka:</strong> Discourses of the Buddha</li><li><strong>Abhidhamma Pitaka:</strong> Further teachings and philosophy</li></ul></div><h4>Evolution of Pali Scripts</h4><p>Originally, <strong>Pali</strong> was written using ancient Indian scripts such as <strong>Brahmi</strong> and <strong>Kharosthi</strong>. As <strong>Buddhism</strong> spread across Asia, <strong>Pali</strong> adapted to local scripts.</p><ul><li>In <strong>Sri Lanka</strong>, it was written in <strong>Sinhalese script</strong>.</li><li>In <strong>Myanmar</strong>, it adopted the <strong>Burmese script</strong>.</li><li>In <strong>Thailand</strong>, the <strong>Thai script</strong> was used.</li><li>In <strong>Cambodia</strong>, it was transcribed into the <strong>Khmer script</strong>.</li></ul><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the linguistic evolution and geographical spread of Pali helps in comprehending the cultural diffusion of Buddhism in Southeast Asia. This can be relevant for GS Paper 1 (Art & Culture) and Prelims.</div>
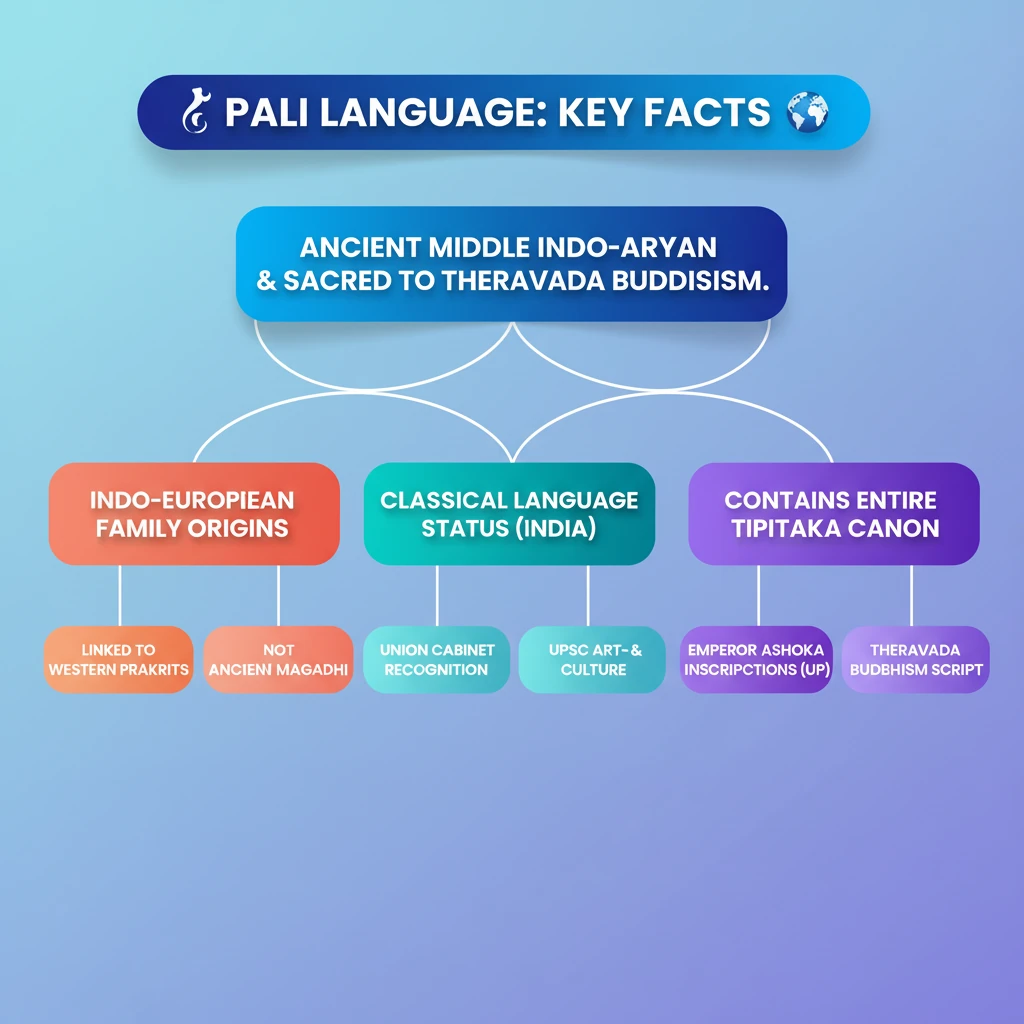
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Pali is an ancient Middle Indo-Aryan language from the Indo-European family.
- •It was once thought to be Magadhi but is now linked more closely to Western Indian Prakrits.
- •The Union Cabinet has recognized Pali as a Classical Language.
- •Emperor Ashoka used Pali for some of his inscriptions, especially in Uttar Pradesh.
- •Pali is the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism and contains its entire canon (Tipitaka).
- •It was originally written in Brahmi and Kharosthi, later adapting to local scripts like Sinhalese and Burmese.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge sources on Indian languages and Buddhism