Narasapur Lace: Challenges of Stagnant Market & Chinese Competition - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Narasapur Lace: Challenges of Stagnant Market & Chinese Competition
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
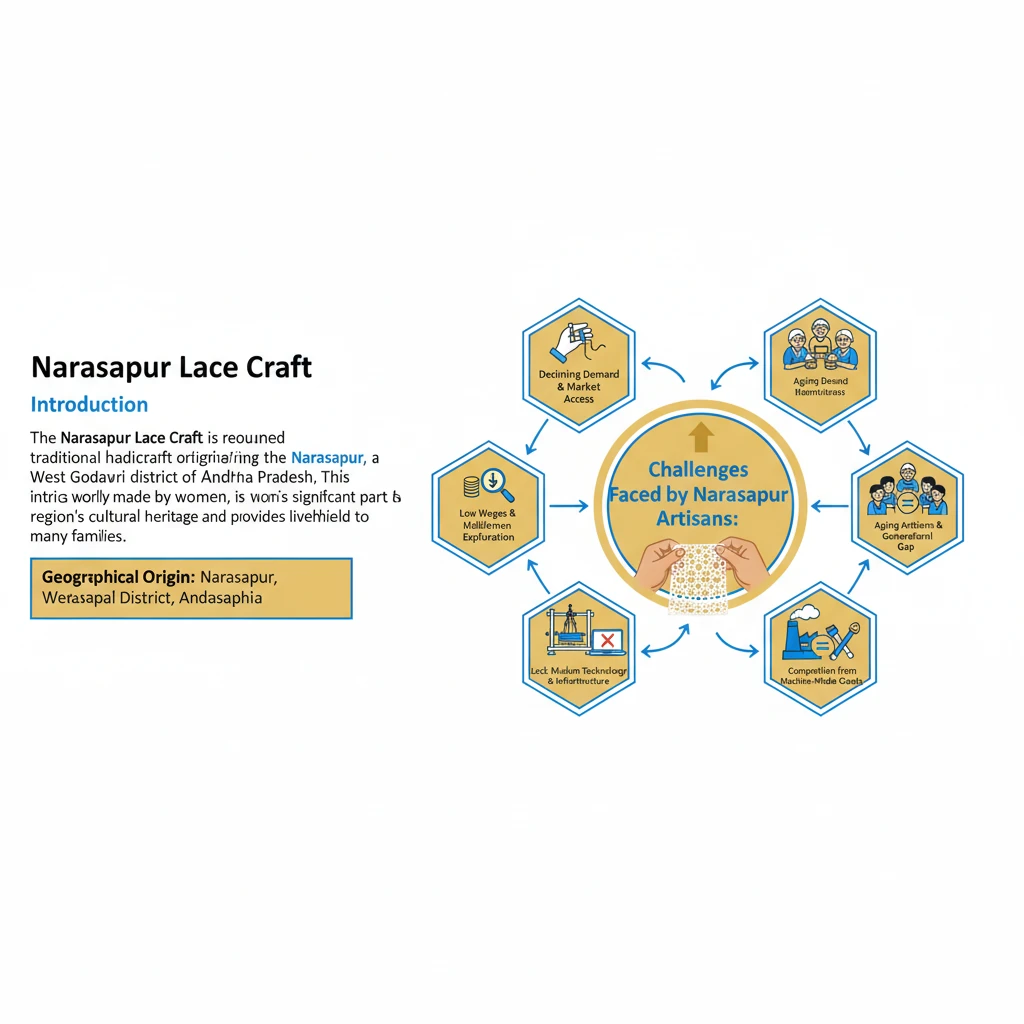
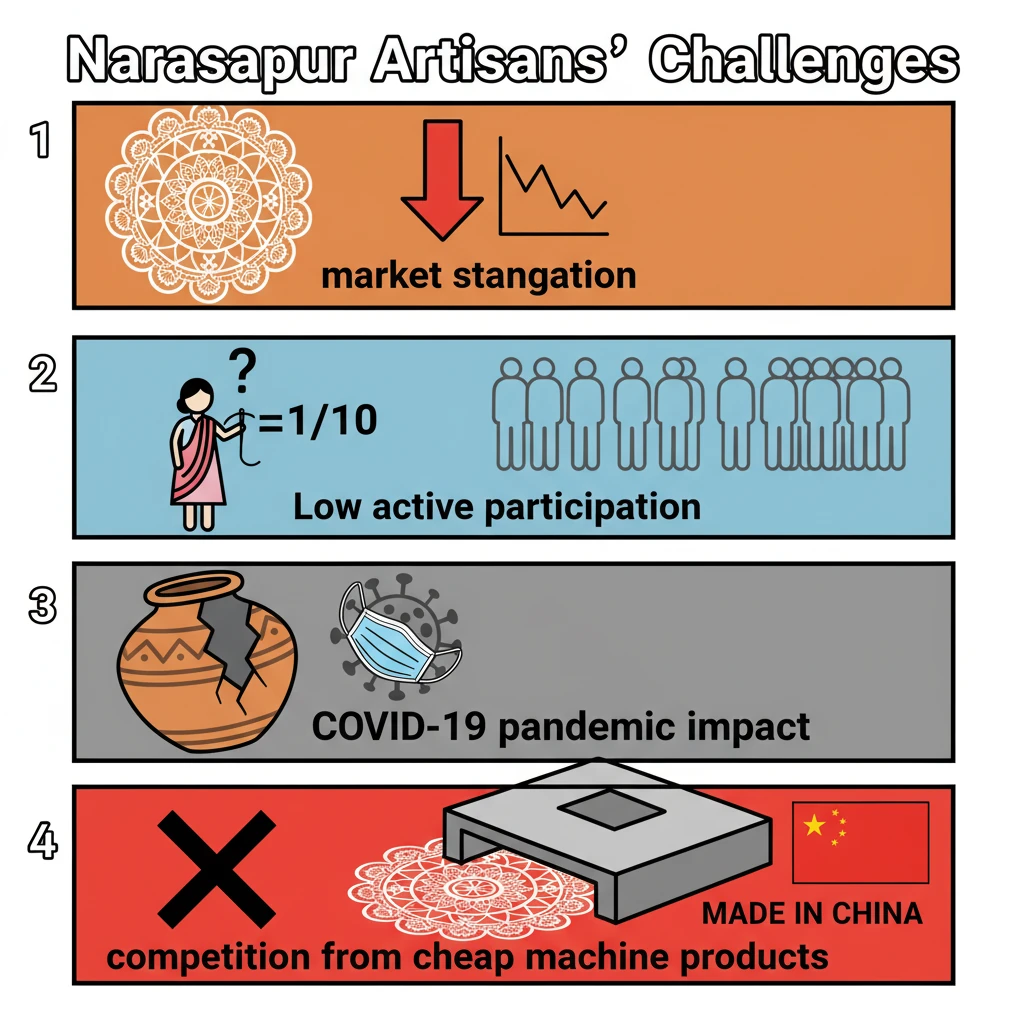
<h4>Introduction to Narasapur Lace Craft</h4><p>The <strong>Narasapur Lace Craft</strong> is a renowned traditional handicraft originating from <strong>Narasapur</strong>, a town in the <strong>West Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh</strong>. This intricate lace work, primarily made by women, is a significant part of the region's cultural heritage and provides livelihood to many families.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Geographical Origin:</strong> Narasapur, West Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh<br><strong>Primary Artisans:</strong> Women<br><strong>Craft Type:</strong> Hand-made lace products</div><h4>Challenge 1: Market Stagnation Post-Pandemic</h4><p>One of the most significant hurdles faced by <strong>Narasapur artisans</strong> is the persistent market stagnation. This issue has been particularly severe since the onset of the <strong>Covid-19 pandemic</strong>, disrupting established supply chains and consumer behavior.</p><p>The stagnation has directly led to a severe <strong>lack of new orders</strong> for their handcrafted lace products. Consequently, the overall <strong>production volume has significantly decreased</strong>, impacting the artisans' income and stability.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Impact:</strong> Reduced orders, decreased production, economic instability for artisans.</div><h4>Challenge 2: Low Active Artisan Involvement</h4><p>Despite a large number of individuals associated with the craft, active participation remains critically low. While over <strong>15,000 women</strong> are formally associated with the <strong>Narasapur lace craft</strong>, only a fraction are regularly involved in production.</p><p>Currently, only around <strong>200 women</strong> are actively engaged in consistent, regular production. This disparity highlights underlying issues such as inconsistent demand, inadequate training, or lack of sustained economic incentives.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Associated Artisans:</strong> Over 15,000 women<br><strong>Actively Producing Artisans:</strong> Approximately 200 women</div><h4>Challenge 3: Competition from Inexpensive Machine Products</h4><p>The traditional <strong>Narasapur lace products</strong> face immense competition from mass-produced, inexpensive alternatives. These machine-made goods often mimic the aesthetics of handcrafted items but are sold at significantly lower prices.</p><p>Specifically, <strong>inexpensive machine products from China</strong> have heavily infiltrated the market. This influx poses a substantial threat to the demand for authentic <strong>Narasapur lace products</strong>, as consumers often opt for cheaper options.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> This challenge is common across many traditional Indian handicrafts. When discussing solutions, consider policies for promoting authentic products, GI tags, and market linkages.</div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Narasapur lace artisans face market stagnation, low active participation, and competition from cheap machine products.
- •The Covid-19 pandemic severely impacted demand and production for traditional crafts.
- •Only a small fraction of associated women artisans are actively engaged in regular production.
- •Inexpensive machine-made products, particularly from China, pose a significant threat to market demand.
- •These challenges are common to many traditional Indian handicrafts.
- •Government support, market linkages, and skill development are crucial for craft revival.
🧠 Memory Techniques
90% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Textiles, Government of India reports on handicrafts
•Art & Culture books for UPSC preparation
•News articles and reports on Indian handicrafts