Corridor Projects for Vishnupad and Mahabodhi Temples - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Corridor Projects for Vishnupad and Mahabodhi Temples
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
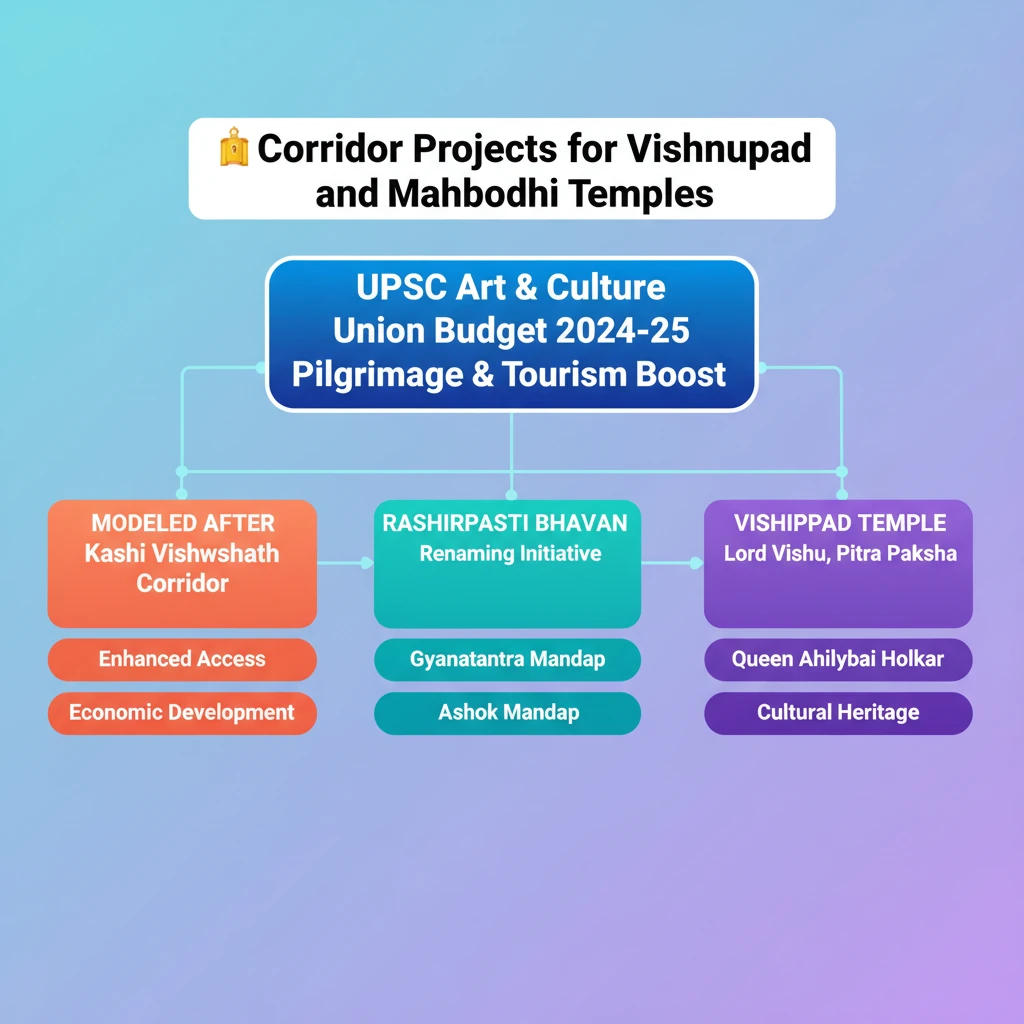
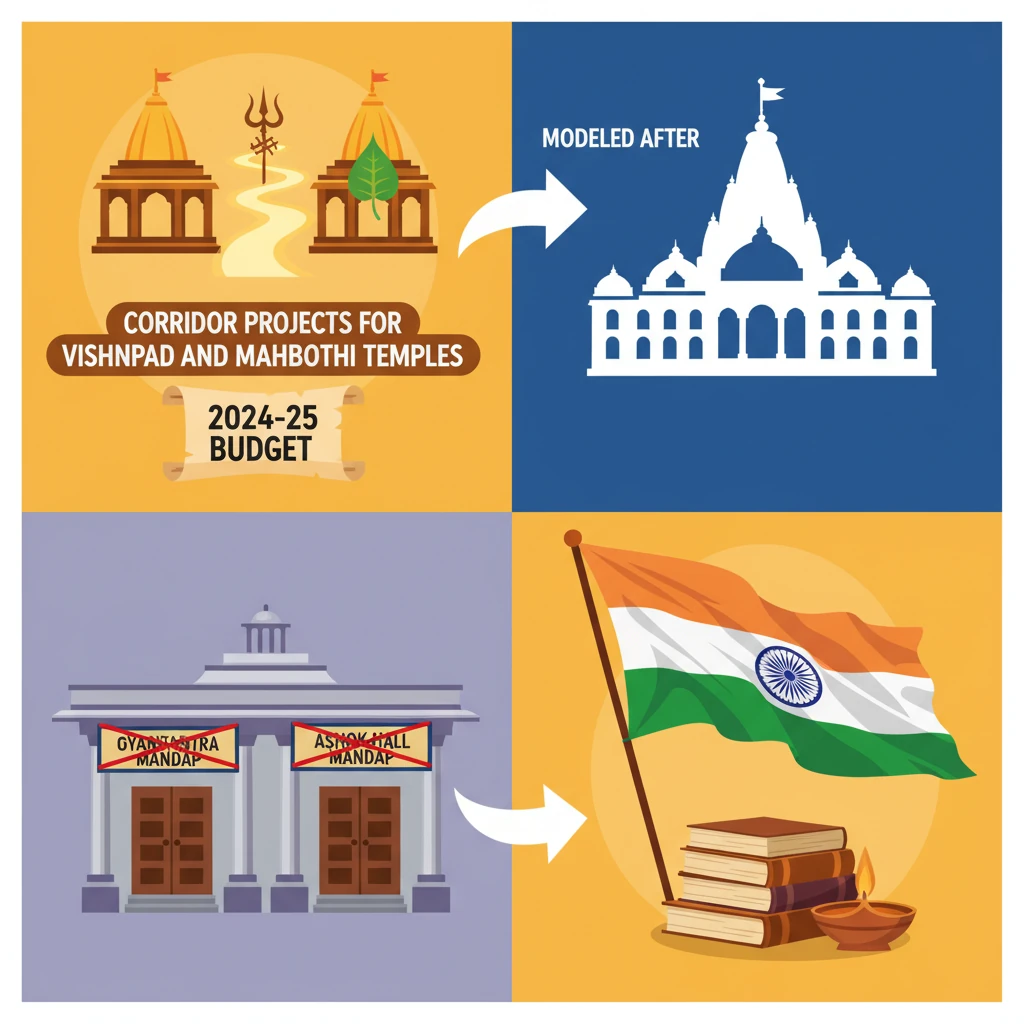
<h4>Understanding Sundial Functionality</h4><p>The <strong>Sundial Functionality</strong> described relates to the <strong>Konark wheels</strong>, which are ancient astronomical instruments. Two of the wheels are designed to accurately determine the time from <strong>sunrise to sunset</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Time Measurement:</strong> Two wheels determine time from sunrise to sunset.</div><p>The arrangement of spokes on these wheels is crucial for timekeeping. <strong>Wider spokes</strong> indicate <strong>3-hour intervals</strong>, while <strong>thinner spokes</strong> represent <strong>1.5-hour periods</strong>. Smaller <strong>beads between spokes</strong> mark even finer increments of <strong>3 minutes</strong>.</p><p>The sundial operates with a unique orientation. The <strong>top center wider spoke</strong> symbolizes <strong>midnight</strong>. From this point, the dial moves in an <strong>anti-clockwise direction</strong> to display the time.</p><h4>Rashtrapati Bhavan Renaming Initiatives</h4><p>In a significant move to align with <strong>Indian cultural values</strong> and diminish traces of <strong>colonial influence</strong>, <strong>Rashtrapati Bhavan</strong> has officially renamed two of its prominent halls.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Objective:</strong> Align with Indian cultural values, reduce colonial influence.</div><p>The former <strong>Durbar Hall</strong> has been renamed <strong>Gyanatantra Mandap</strong>. This new name reflects the concept of a <strong>republic</strong>, directly replacing the colonial term 'Durbar', which referred to courts and assemblies of Indian rulers and the British.</p><p>Similarly, <strong>Ashok Hall</strong> has been renamed <strong>Ashok Mandap</strong>. This change honors <strong>Emperor Ashoka</strong> and reinforces <strong>Indian cultural significance</strong>, aiming to remove anglicized influences associated with the original ballroom function.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Original Use of Ashok Hall:</strong> Ballroom<br><strong>Meaning of 'Ashok':</strong> Free from sufferings/sorrow; refers to <strong>Emperor Ashoka</strong> (symbol of unity, peaceful co-existence); also refers to the <strong>Ashok tree</strong> (deep significance in Indian traditions).</div><p>The <strong>Rashtrapati Bhavan</strong> in <strong>New Delhi</strong> is the largest residence of any Head of State globally. It was originally constructed as the <strong>'Viceroy House'</strong> for the <strong>British Viceroy of India</strong> and was renamed Rashtrapati Bhavan in <strong>1950</strong> when India became a Republic.</p><p>The architectural design was by <strong>Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens</strong>, a British architect, who blended <strong>Indian, Mughal, and European architectural styles</strong> in its construction.</p><h4>Vishnupad and Mahabodhi Temple Corridor Projects</h4><p>The <strong>Union Budget 2024-25</strong> announced plans for new <strong>corridor projects</strong> for the <strong>Vishnupad Temple</strong> at <strong>Gaya</strong> and the <strong>Mahabodhi Temple</strong> at <strong>Bodh Gaya</strong>, both located in <strong>Bihar</strong>.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> These projects reflect the government's focus on heritage tourism and infrastructure development, a recurring theme in <strong>GS-1 Art & Culture</strong> and <strong>GS-3 Economy/Infrastructure</strong>.</div><p>These projects are envisioned to be modeled after the successful <strong>Kashi Vishwanath Corridor</strong>. Their primary goal is to significantly enhance both temples, transforming them into major <strong>pilgrim and tourist destinations</strong>.</p><p>The two temples, <strong>Vishnupad</strong> and <strong>Mahabodhi</strong>, are approximately <strong>10 kilometers apart</strong> and hold immense <strong>cultural and religious significance</strong> for devotees and tourists alike.</p><h4>Vishnupad Temple at Gaya: Key Details</h4><p>The <strong>Vishnupad Temple</strong> is located on the banks of the <strong>Falgu/Falgun river</strong> in the <strong>Gaya district of Bihar</strong>. It is a revered shrine dedicated to <strong>Lord Vishnu</strong>.</p><p>Local mythology narrates the legend of a demon named <strong>Gayasur</strong>. He requested the gods to grant him the power to help others achieve <strong>moksha</strong> (liberation from the cycle of rebirth). However, upon misusing this power, <strong>Lord Vishnu</strong> subdued him, leaving a <strong>footprint</strong> within the temple, believed to be a mark of this event.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Architectural Features:</strong><br><strong>Height:</strong> Approximately 100 feet<br><strong>Pillars:</strong> 44, constructed from large <strong>gray granite blocks</strong> (Munger Black stone)<br><strong>Construction Method:</strong> Blocks joined with <strong>iron clamps</strong><br><strong>Shrine Orientation:</strong> Octagonal, oriented towards the <strong>east</strong></div><p>The temple's construction dates back to <strong>1787</strong>, commissioned by <strong>Queen Ahilyabai Holkar</strong>.</p><p>It holds particular significance during <strong>Pitra Paksha</strong>, a period dedicated to honoring ancestors, drawing numerous devotees. The <strong>Brahma Kalpit Brahmins</strong>, also known as <strong>Gayawal Brahmins</strong>, have served as the traditional priests of the temple since ancient times.</p><h4>Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya: Key Details</h4><p>The <strong>Mahabodhi Temple</strong>, situated at <strong>Bodh Gaya</strong>, is widely believed to be the sacred site where <strong>Gautam Buddha</strong> attained <strong>enlightenment</strong> under the legendary <strong>Mahabodhi Tree</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Historical Construction:</strong> The original temple was built by <strong>Emperor Ashoka</strong> in the <strong>3rd century BCE</strong>.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Union Budget 2024-25 includes corridor projects for Vishnupad and Mahabodhi Temples.
- •These projects aim to boost pilgrimage and tourism, modeled after the Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
- •Rashtrapati Bhavan renamed Durbar Hall to Gyanatantra Mandap and Ashok Hall to Ashok Mandap.
- •The renaming reflects a move towards Indian cultural values and away from colonial influences.
- •Vishnupad Temple is dedicated to Lord Vishnu, built by Queen Ahilyabai Holkar, and significant for Pitra Paksha.
- •Mahabodhi Temple is where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment, originally built by Emperor Ashoka.
- •The Konark wheels demonstrate ancient Indian sundial functionality for precise time measurement.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content