Historical Group of Dhamnar - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Historical Group of Dhamnar
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Gwalior Fort: A Historical Stronghold</h4><p>The <strong>Gwalior Fort</strong>, often referred to as 'the pearl amongst fortresses in India' by <strong>Mughal emperor Babur</strong>, stands majestically on a rocky outcrop in <strong>Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh</strong>. Its strategic location and formidable structure have made it a witness to centuries of Indian history, invasions, and architectural evolution.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Key Point:</strong> Gwalior Fort is renowned for its strategic importance and rich cultural heritage, reflecting diverse dynastic influences.</div><h4>Historical Genesis and Early Legends</h4><p>The origins of <strong>Gwalior Fort</strong> are steeped in legend. Local chieftain <strong>Suraj Sen</strong>, suffering from severe leprosy, was miraculously healed by a hermit-saint named <strong>Gwalipa</strong>. In gratitude, <strong>Suraj Sen</strong> established the city of <strong>Gwalior</strong>, named after the saint.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Founder:</strong> Suraj Sen<br><strong>Named After:</strong> Hermit-saint Gwalipa<br><strong>Location:</strong> Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh</div><h4>Evolution Through Dynasties: A Tumultuous History</h4><p>The fort has endured a tumultuous history, marked by numerous invasions and subsequent reconstructions. Each ruling dynasty left its indelible mark on the fort's architecture and cultural landscape.</p><ol><li><strong>Tomar Rule:</strong> The fort witnessed significant development under the <strong>Tomar ruler Maan Singh</strong>, who in <strong>1398 CE</strong>, added several monuments to its premises, enhancing its grandeur.</li><li><strong>Mughal Sultanate:</strong> Following <strong>Maan Singh's</strong> reign, <strong>Tomar</strong> control over <strong>Gwalior</strong> was briefly usurped by <strong>Ibrahim Lodi</strong> of the <strong>Mughal Sultanate</strong>. However, <strong>Akbar</strong> regained control in <strong>1550 CE</strong>.</li><li><strong>Maratha Empire:</strong> Later, the <strong>Marathas</strong>, under the leadership of the <strong>Scindias</strong>, took control of the fort, adding another layer to its rich history.</li><li><strong>British Interventions:</strong> The fort briefly fell to <strong>General White</strong> during the <strong>Second Maratha War</strong> but was returned to <strong>Scindia</strong> control in <strong>1805 CE</strong>. British rule lasted until <strong>1886 CE</strong>, when it was exchanged for <strong>Jhansi</strong> and once again returned to the <strong>Scindias</strong>.</li></ol><h4>Architectural Marvels: Key Temples and Structures</h4><p>The <strong>Gwalior Fort</strong> complex is home to several ancient temples, each possessing unique architectural and cultural significance. These structures showcase the diverse religious and artistic traditions that flourished within its walls.</p><h5>Teli ka Mandir</h5><p>This unique temple is dedicated to a trinity of deities: <strong>Shiva, Vishnu, and Matrikas</strong>. Its distinctive architectural style, often described as a blend of North and South Indian influences, makes it a prominent feature of the fort.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Deities:</strong> Shiva, Vishnu, Matrikas<br><strong>Architectural Style:</strong> Blend of North and South Indian influences</div><h5>Chaturbhuj Temple</h5><p>The <strong>Chaturbhuj Temple</strong> holds immense mathematical significance. It features one of the oldest known references to the concept of <strong>zero</strong> in mathematics, inscribed within its premises. This highlights the advanced scientific knowledge of ancient India.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Mathematical Significance:</strong> Contains one of the oldest references to the numeral <strong>zero</strong>.</div><h5>Sas Bahu Temples</h5><p>Dating back to <strong>1150 CE</strong>, the <strong>Sas Bahu temples</strong> are a pair of intricately carved structures. The larger of the two is dedicated to <strong>Vishnu</strong> and is renowned for its elaborate sculptures and detailed inscriptions, providing insights into the period's art and religious practices.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Construction Date:</strong> 1150 CE<br><strong>Primary Deity (Larger Temple):</strong> Vishnu<br><strong>Notable Feature:</strong> Intricate inscriptions and sculptures</div><h4>Spiritual Significance: Gurudwara Data Bandi Chhor</h4><p>Beyond Hindu temples, the fort also houses the <strong>Gurudwara Data Bandi Chhor</strong>. This sacred Sikh shrine commemorates <strong>Guru Hargobind Sahib</strong>, the <strong>sixth Sikh Guru</strong>, who was imprisoned here by <strong>Mughal emperor Jahangir</strong>. It symbolizes religious tolerance and historical intermingling.</p><h4>Strategic Importance and Ancient Nomenclature</h4><p>The fort's strategic location atop <strong>basalt rock hills</strong> made it a formidable defensive structure. This importance is reflected in ancient Sanskrit inscriptions, where it is referred to as <strong>Gopachala</strong> and <strong>Gopagiri</strong>, highlighting its elevated and protected position.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>Gwalior Fort</strong> often focus on its architectural diversity, historical evolution through different dynasties, and specific monuments like the <strong>Chaturbhuj Temple's</strong> mathematical significance.</div>
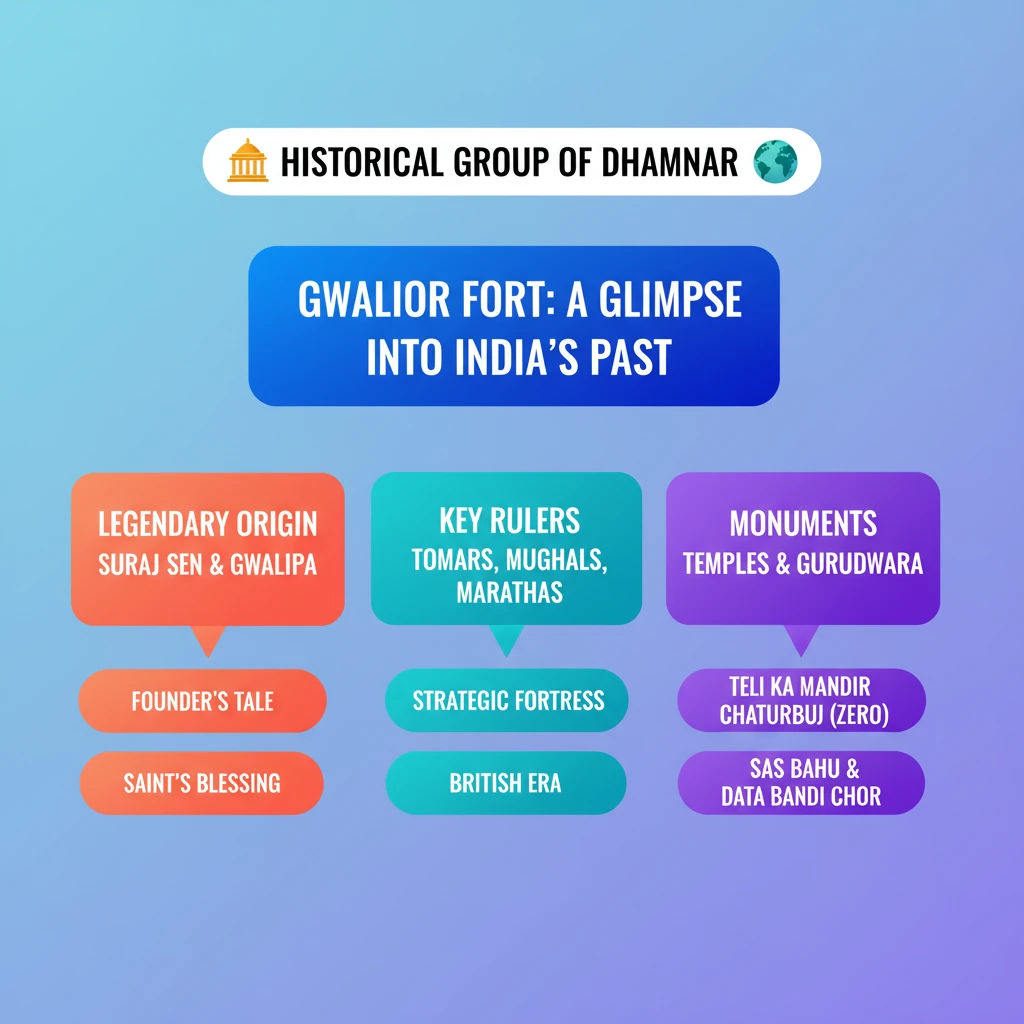
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Gwalior Fort is a historic hill fort in Madhya Pradesh, renowned for its strategic importance.
- •Its legendary origin involves chieftain Suraj Sen and hermit-saint Gwalipa.
- •The fort's history saw control by Tomars, Mughals, Marathas (Scindias), and the British.
- •Key monuments include Teli ka Mandir, Chaturbhuj Temple (with an early reference to zero), and Sas Bahu Temples.
- •Gurudwara Data Bandi Chhor commemorates Guru Hargobind Sahib's imprisonment.
- •Ancient Sanskrit inscriptions refer to the fort as Gopachala and Gopagiri.
- •It represents a blend of diverse architectural styles and cultural influences.
🧠 Memory Techniques
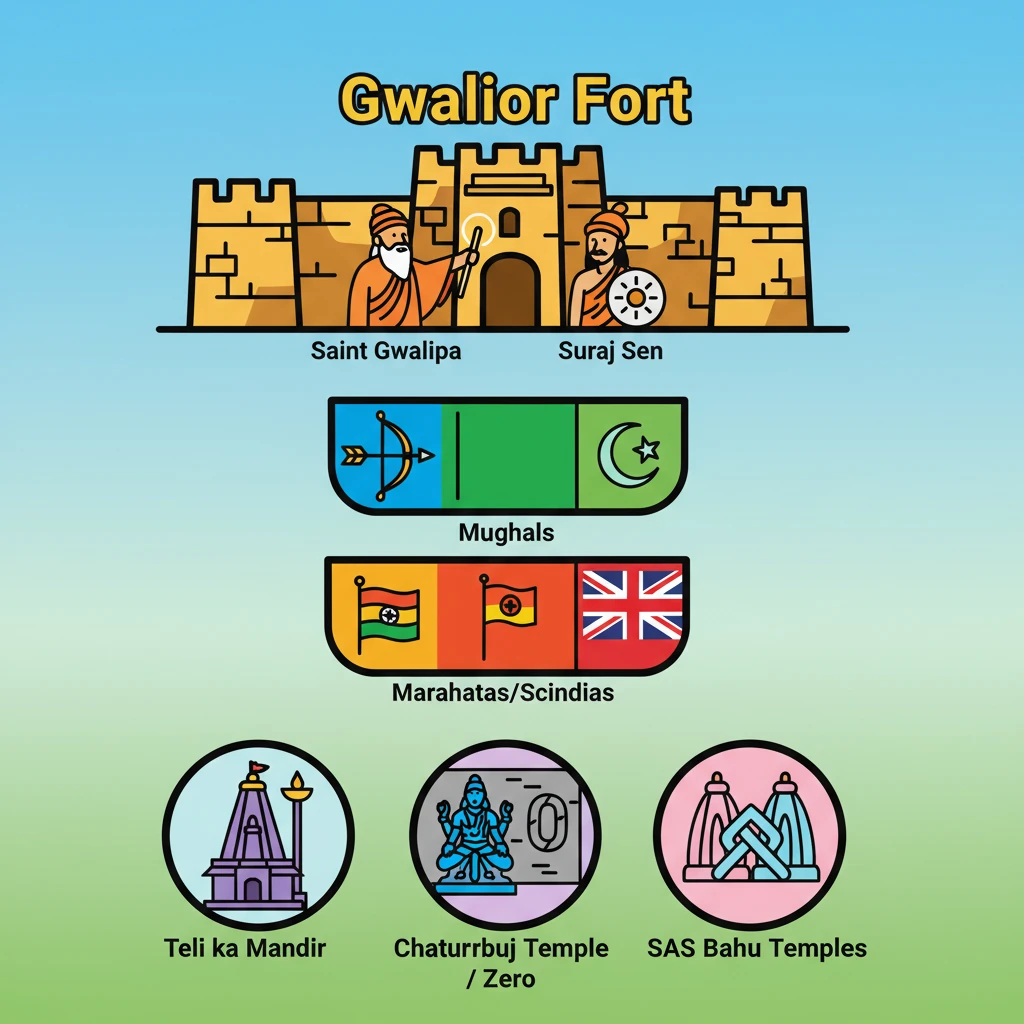
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) official records on Gwalior Fort
•Culturalindia.net - Gwalior Fort
•Madhya Pradesh Tourism official website
•Wikipedia - Gwalior Fort (for cross-referencing dates and rulers)