Maratha Military Landscapes - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Maratha Military Landscapes
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
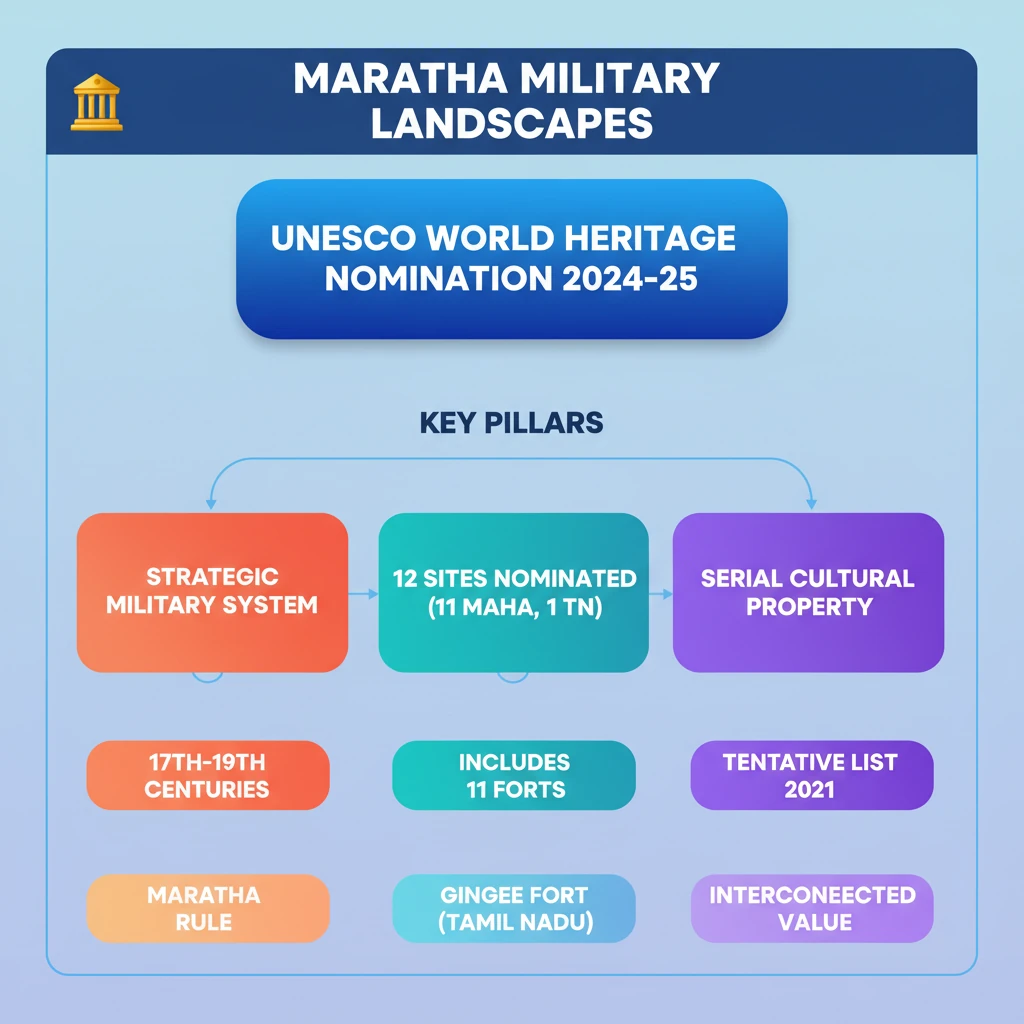
<h4>India's UNESCO Nomination for Maratha Military Landscapes</h4><p>India has formally nominated the <strong>“Maratha Military Landscapes”</strong> for <strong>UNESCO World Heritage recognition</strong> for the <strong>2024-25 cycle</strong>. This significant nomination highlights the unique strategic military system of the Maratha rulers.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Nomination Year:</strong> 2024-25 Cycle<br><strong>Purpose:</strong> UNESCO World Heritage recognition<br><strong>Focus:</strong> Strategic military prowess of Maratha rule</div><h4>Overview of Maratha Military Landscapes</h4><p>The <strong>‘Maratha Military Landscapes’</strong> represent a vast network of <strong>12 forts and fortifications</strong>. These structures collectively showcase the extraordinary military system and strategic genius employed by <strong>Maratha rulers</strong> between the <strong>17th and 19th centuries</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box">This network is not just a collection of forts, but a demonstration of an integrated military defense strategy across diverse geographical terrains.</div><h4>Components of the Nomination</h4><p>The nomination includes <strong>12 specific forts</strong>, strategically located across different regions. These forts are crucial examples of Maratha military architecture and planning.</p><ul><li><strong>Maharashtra Forts:</strong> <strong>Salher Fort</strong>, <strong>Shivneri Fort</strong>, <strong>Lohgad</strong>, <strong>Khanderi Fort</strong>, <strong>Raigad</strong>, <strong>Rajgad</strong>, <strong>Pratapgad</strong>, <strong>Suvarnadurg</strong>, <strong>Panhala Fort</strong>, <strong>Vijaydurg</strong>, <strong>Sindhudurg</strong>.</li><li><strong>Tamil Nadu Fort:</strong> <strong>Gingee Fort</strong>.</li></ul><p>The <strong>Maratha Military Landscapes of India</strong> were initially included in the <strong>Tentative List of World Heritage Sites in 2021</strong>. This is the <strong>sixth cultural property</strong> nominated from <strong>Maharashtra</strong> for inclusion in the World Heritage List.</p><h4>Features and Typology of Maratha Forts</h4><p>The network of forts exhibits diverse hierarchies, scales, and typological features. Their design brilliantly integrates the natural landscape, terrain, and physiographic characteristics of their locations.</p><ul><li><strong>Geographical Integration:</strong> Forts are found across the <strong>Western Ghats (Sahyadri Hills)</strong>, the <strong>Konkan Coast</strong>, the <strong>Deccan Plateau</strong>, and the <strong>Eastern Ghats</strong>.</li><li><strong>Total Forts:</strong> Maharashtra boasts <strong>more than 390 forts</strong>, but only 12 are selected for this specific nomination.</li></ul><h4>Protection and Administration of Forts</h4><p>Out of the 12 nominated forts, <strong>8 are protected by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)</strong>, ensuring their preservation and historical integrity.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>ASI Protected Forts:</strong> <strong>Shivneri Fort</strong>, <strong>Lohgad</strong>, <strong>Raigad</strong>, <strong>Suvarnadurg</strong>, <strong>Panhala Fort</strong>, <strong>Vijaydurg</strong>, <strong>Sindhudurg</strong>, and <strong>Gingee Fort</strong>.</div><p>The remaining <strong>four forts</strong> are under the protection of the <strong>Directorate of Archaeology and Museums, Government of Maharashtra</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Maharashtra State Protected Forts:</strong> <strong>Salher Fort</strong>, <strong>Rajgad</strong>, <strong>Khanderi Fort</strong>, and <strong>Pratapgarh</strong>.</div><h4>Classification of Forts by Location</h4><p>The forts within the Maratha Military Landscapes demonstrate a variety of strategic locations and designs:</p><ul><li><strong>Hill Forts:</strong> <strong>Salher Fort</strong>, <strong>Shivneri Fort</strong>, <strong>Lohgad</strong>, <strong>Raigad</strong>, <strong>Rajgad</strong>, and <strong>Gingee Fort</strong>.</li><li><strong>Hill-Forest Fort:</strong> <strong>Pratapgad</strong>.</li><li><strong>Hill-Plateau Fort:</strong> <strong>Panhala</strong>.</li><li><strong>Coastal Fort:</strong> <strong>Vijaydurg</strong>.</li><li><strong>Island Forts:</strong> <strong>Khanderi Fort</strong>, <strong>Suvarnadurg</strong>, and <strong>Sindhudurg</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Historical Origin of Maratha Military Ideology</h4><p>The distinctive <strong>Maratha Military ideology</strong> and its associated fort-building tradition originated in the <strong>17th century</strong>. It began under the visionary rule of <strong>Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj</strong> around <strong>1670 CE</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Founding Figure:</strong> <strong>Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj</strong><br><strong>Period:</strong> 17th century (c. 1670 CE) to 1818 CE (Peshwa rule conclusion)</div><p>This military system continued to evolve and expand through subsequent Maratha rulers, culminating with the conclusion of the <strong>Peshwa rule in 1818 CE</strong>.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India has nominated 'Maratha Military Landscapes' for UNESCO World Heritage status for 2024-25.
- •The nomination comprises 12 forts, including 11 in Maharashtra and 1 in Tamil Nadu (Gingee Fort).
- •These forts represent the strategic military system of Maratha rulers from the 17th to 19th centuries.
- •Forts are diverse, including hill, hill-forest, hill-plateau, coastal, and island types, integrating natural terrain.
- •The Maratha military ideology originated under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj around 1670 CE.
- •The landscapes were added to India's Tentative List of World Heritage Sites in 2021.
- •The nomination is under UNESCO Cultural Criteria (iii), (iv), and (vi).
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•UNESCO World Heritage Centre official website
•Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) records