What is the Process for the UNESCO World Heritage List nomination? - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the Process for the UNESCO World Heritage List nomination?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
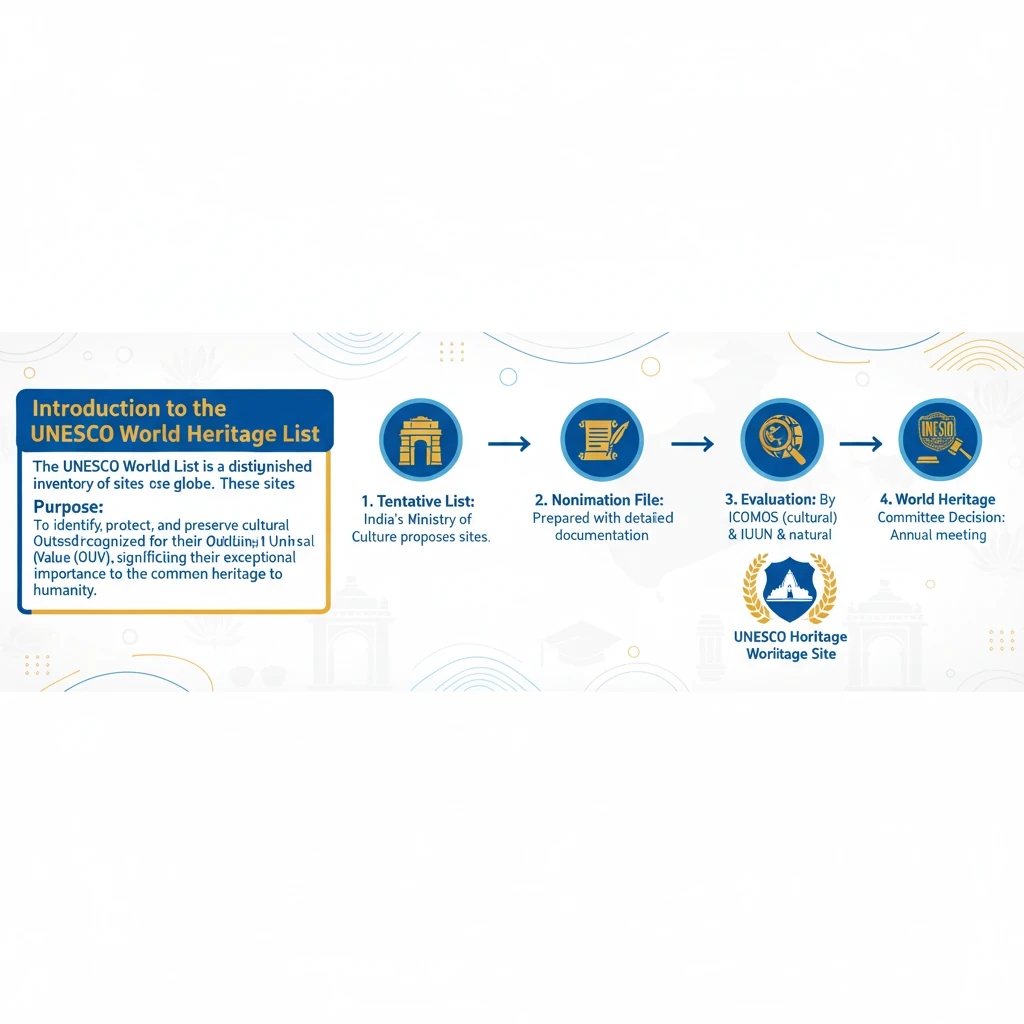
<h4>Introduction to the UNESCO World Heritage List</h4><p>The <strong>UNESCO World Heritage List</strong> is a distinguished inventory of sites across the globe. These sites are recognized for their <strong>Outstanding Universal Value (OUV)</strong>, signifying their exceptional importance to the common heritage of humanity.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Purpose:</strong> To identify, protect, and preserve cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity.</div><h4>Understanding Outstanding Universal Value (OUV)</h4><p>A site must meet at least one of ten specific criteria to be considered for <strong>Outstanding Universal Value</strong>. These criteria encompass both cultural and natural aspects, ensuring a broad representation of global heritage.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Key Concept:</strong> <strong>Outstanding Universal Value (OUV)</strong> is the central principle of the World Heritage Convention. It means a site's cultural and/or natural significance is so exceptional as to transcend national boundaries and be of common importance for present and future generations of all humanity.</div><h4>The Nomination Process: Step-by-Step</h4><p>The nomination of a site to the World Heritage List involves a rigorous, multi-stage process designed to ensure only sites of true global significance are inscribed. This process typically takes several years.</p><ol><li><strong>Inclusion in the Tentative List:</strong></li><ul><li>A country must first include a site in its <strong>Tentative List</strong>. This is an inventory of properties that a State Party intends to consider for nomination over the next 5 to 10 years.</li><li>It is a crucial first step, as a site cannot be nominated unless it has been on the Tentative List for at least one year.</li></ul><li><strong>Preparation of the Nomination File:</strong></li><ul><li>The State Party then prepares a comprehensive <strong>Nomination File</strong>. This document is extensive, detailing the site's OUV, integrity, authenticity, management plan, and protection measures.</li><li>It requires significant research, documentation, and stakeholder consultation.</li></ul><li><strong>Evaluation by Advisory Bodies:</strong></li><ul><li>Once submitted, the Nomination File is evaluated by two independent advisory bodies: the <strong>International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS)</strong> for cultural sites and the <strong>International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)</strong> for natural sites.</li><li>These bodies conduct field missions, review documentation, and provide recommendations to the World Heritage Committee.</li></ul><li><strong>Decision by the World Heritage Committee:</strong></li><ul><li>The <strong>World Heritage Committee</strong>, comprising representatives from 21 State Parties, makes the final decision during its annual session.</li><li>The Committee can decide to inscribe the site, defer the decision (requesting more information), refer it back (requesting substantial revisions), or reject the nomination.</li></ul><li><strong>Monitoring and Reporting:</strong></li><ul><li>After inscription, the State Party is responsible for the site's protection and management. Regular reporting on the site's condition and conservation efforts is required.</li><li>The Committee monitors inscribed sites, and in extreme cases, a site can be placed on the <strong>List of World Heritage in Danger</strong> or even delisted.</li></ul></ol><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the specific criteria for OUV and the multi-stage nomination process is vital. Questions often focus on the roles of <strong>ICOMOS</strong>, <strong>IUCN</strong>, and the <strong>World Heritage Committee</strong>, as well as the significance of the <strong>Tentative List</strong>.</div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The World Heritage List identifies sites of Outstanding Universal Value (OUV) for humanity.
- •OUV means a site's significance transcends national boundaries, making its preservation a global responsibility.
- •The nomination process involves a Tentative List, a detailed Nomination File, and evaluation by ICOMOS/IUCN.
- •The World Heritage Committee makes the final decision on inscription.
- •Post-inscription, State Parties are responsible for monitoring and reporting on the site's conservation.
- •UNESCO status brings benefits like enhanced conservation, tourism, and national prestige.
- •Challenges include managing tourism, climate change impacts, and ensuring local community benefits.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Culture, Government of India reports on heritage sites
•NCERT textbooks on Indian Art and Culture
•Standard UPSC preparation guides on Art and Culture