Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act) - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act)
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the AMASR Act, 1958</h4><p>The <strong>Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958</strong> (often referred to as the <strong>AMASR Act</strong>) is a pivotal piece of legislation in India. It was enacted to provide for the preservation of <strong>ancient and historical monuments</strong> and <strong>archaeological sites and remains</strong> of national importance.</p><p>This Act also regulates <strong>archaeological excavations</strong> and protects <strong>sculptures, carvings, and other like objects</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Full Name:</strong> The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958<br><strong>Enactment Year:</strong> 1958</div><h4>Core Objective of the Act</h4><p>The primary aim of the <strong>AMASR Act</strong> is to <strong>protect and preserve ancient monuments</strong> and archaeological sites for future generations. This ensures that India's rich cultural heritage is safeguarded against damage, encroachment, and illicit trade.</p><div class="key-point-box">The Act establishes a framework for declaring certain sites and remains as being of <strong>national importance</strong>, thereby bringing them under the purview of central protection.</div><h4>Key Provisions and Scope</h4><p>The Act defines what constitutes an <strong>ancient monument</strong> and an <strong>archaeological site and remains</strong>. It empowers the Central Government, through the <strong>Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)</strong>, to take measures for their upkeep and maintenance.</p><p>It also outlines regulations for construction activities in <strong>prohibited and regulated areas</strong> around protected monuments, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity and visual setting of these sites.</p><div class="exam-tip-box">Understanding the <strong>AMASR Act</strong> is crucial for UPSC as it forms the legal backbone for heritage preservation in India. Questions often relate to its provisions, amendments, and challenges in implementation.</div>
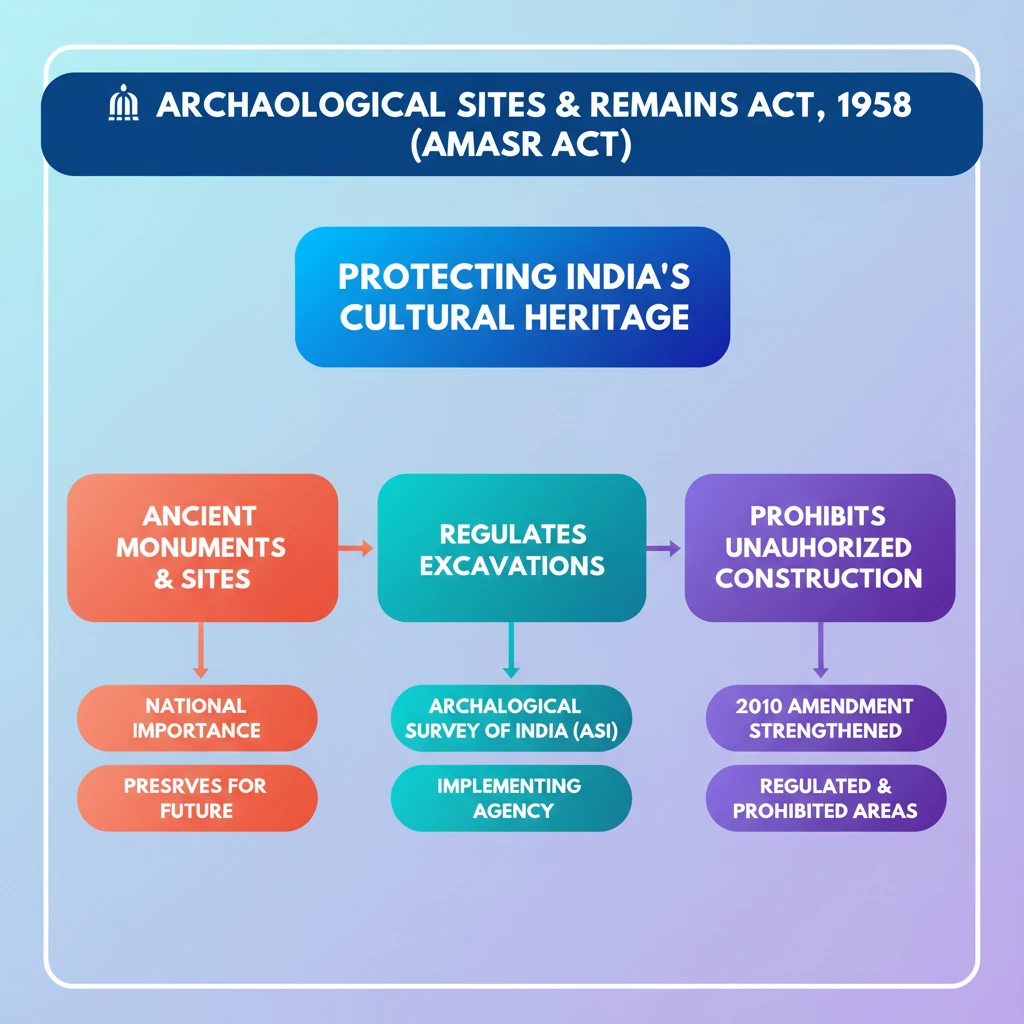
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The AMASR Act, 1958, protects ancient monuments and archaeological sites of national importance.
- •Its main objective is to preserve India's cultural heritage for future generations.
- •The Act regulates archaeological excavations and prohibits unauthorized construction near protected sites.
- •The 2010 amendment strengthened provisions regarding prohibited and regulated areas around monuments.
- •The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is the primary agency responsible for implementing the Act.
- •The Act faces challenges in balancing development needs with heritage preservation.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) official website
•Drishti IAS study material on Art & Culture
•Ministry of Culture, Government of India publications