What are Key Facts About Martand Sun Temple? - Art And Culture | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Key Facts About Martand Sun Temple?
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
art and culture
📖 Introduction
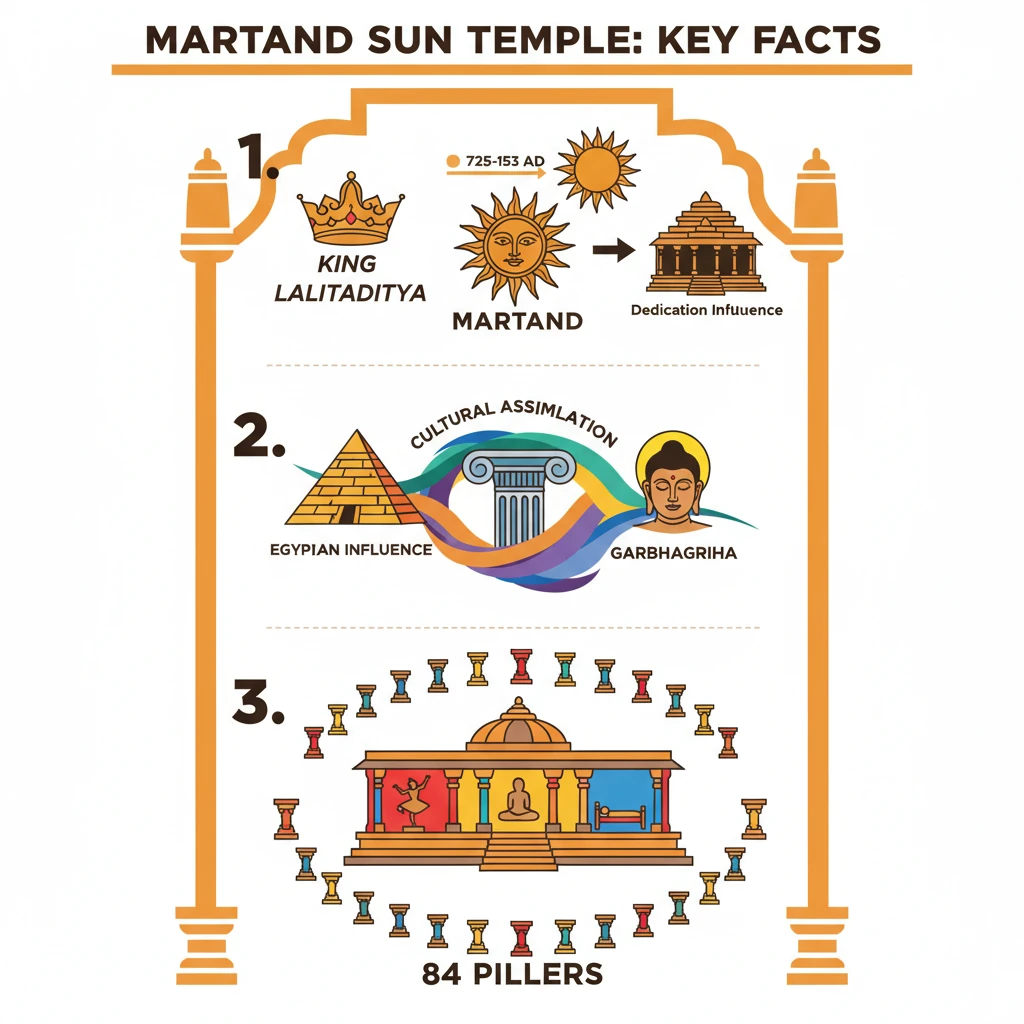
<h4>Introduction to Martand Sun Temple</h4><p>The <strong>Martand Sun Temple</strong> is a significant ancient temple located in <strong>Kashmir</strong>, renowned for its architectural grandeur and historical importance.</p><p>It stands as a testament to the rich cultural and artistic heritage of the region during the early medieval period.</p><h4>Construction and Dedication</h4><p>The temple was constructed approximately <strong>1200 years ago</strong>, making it a pivotal architectural marvel of its time.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Builder:</strong> King <strong>Lalitaditya Muktapida</strong><br><strong>Dynasty:</strong> <strong>Karkota dynasty</strong><br><strong>Reign:</strong> <strong>725 AD to 753 AD</strong> (Kashmir)<br><strong>Dedication:</strong> <strong>Martand</strong>, the <strong>Sun god</strong></div><p>Its dedication to the Sun god reflects the prevalence of solar worship in ancient India and the syncretic nature of religious practices.</p><h4>Grand Architecture and Influences</h4><p>The temple featured a grand architectural style, showcasing a remarkable synthesis of various cultural influences.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Architectural Influences:</strong><ul><li><strong>Egyptian</strong></li><li><strong>Greek</strong></li><li><strong>Gandharan</strong></li></ul>This blend highlights Kashmir's historical connections and cultural exchanges.</div><p>The structure boasted massive <strong>grey stone walls</strong>, indicating robust construction and a majestic presence.</p><p>A notable feature was a <strong>courtyard filled with river water</strong>, symbolizing its grandeur and spiritual significance within <strong>Kashmiri architecture</strong>.</p><h4>Historical Documentation</h4><p>The historical existence and significance of the <strong>Martand Sun Temple</strong> are well-documented in ancient texts.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Historical Reference:</strong> <strong>Rajatarangini</strong><br><strong>Author:</strong> <strong>Kalhana</strong><br><strong>Period:</strong> <strong>12th century</strong></div><p>This chronicle provides valuable insights into the temple's construction, patronage, and cultural context.</p><h4>Distinct Architectural Features</h4><p>The temple's design incorporated unique elements that set it apart from other temples in the region.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Unique Chamber Layout:</strong><br>The temple comprised three distinct chambers, a characteristic uncommon in many Kashmiri temples:<ol><li><strong>Mandapa</strong> (assembly hall)</li><li><strong>Garbhagriha</strong> (sanctum sanctorum)</li><li><strong>Antalaya</strong> (antechamber)</li></ol></div><p>The ruins suggest the temple was surrounded by a <strong>peristyle of 84 pillars</strong>, a hallmark of <strong>Kashmiri temple architecture</strong>.</p><p>An unusual construction material, <strong>lime mortar</strong>, was employed, suggesting advanced building techniques for its era.</p><p>The use of <strong>lime mortar</strong> also points towards the potential involvement of <strong>immigrant Byzantine architects</strong>, indicating international architectural exchange.</p><h4>Cultural Assimilation in Design</h4><p>The architecture of the <strong>Martand Temple</strong> vividly demonstrates a profound confluence of diverse cultural styles.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Confluence of Styles:</strong><ul><li><strong>Classical Greco-Roman</strong></li><li><strong>Buddhist-Gandhara</strong></li><li><strong>North Indian</strong></li></ul></div><p>This architectural syncretism reflects <strong>Kashmir's historical connections</strong> with various cultures and empires, serving as a crossroads of civilizations.</p>
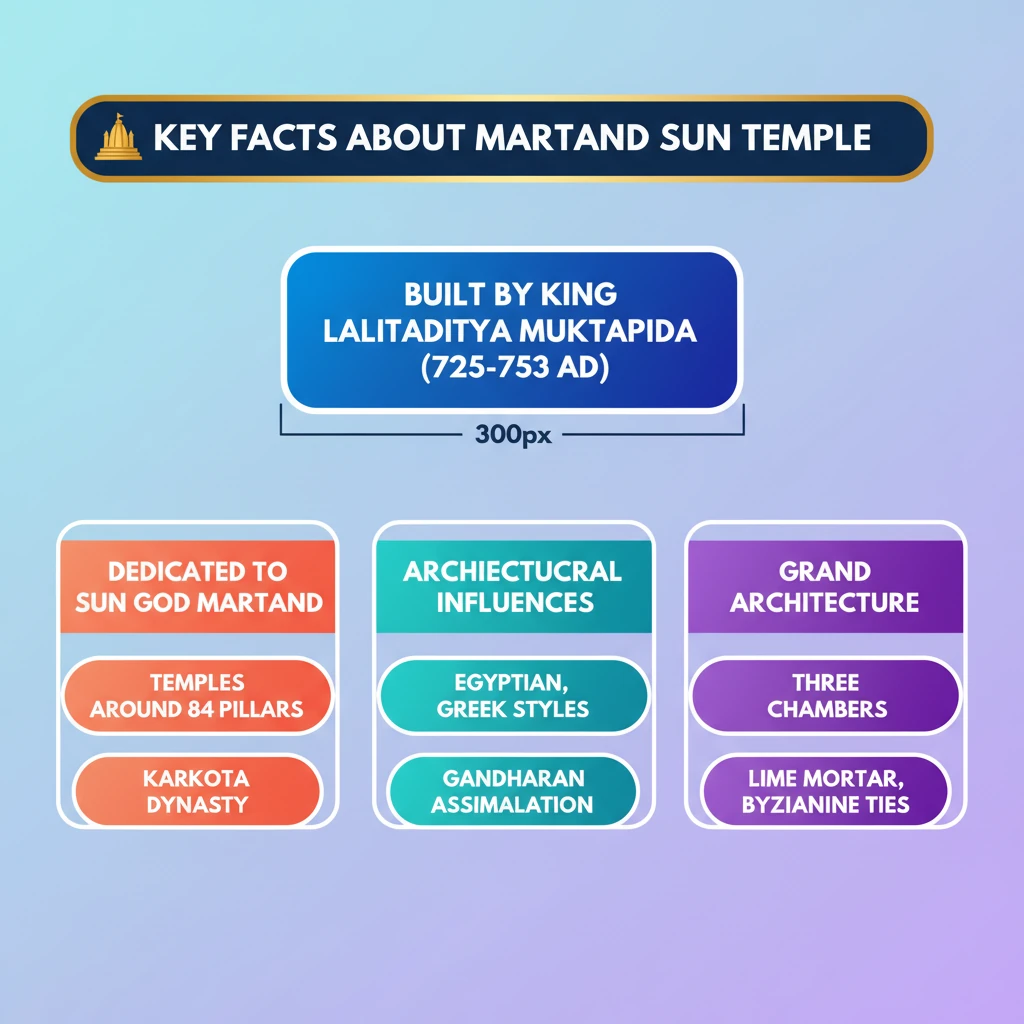
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Martand Sun Temple was built by King Lalitaditya Muktapida of the Karkota dynasty around 725-753 AD.
- •It was dedicated to the Sun god Martand and featured grand architecture.
- •The temple's design shows influences from Egyptian, Greek, and Gandharan styles, reflecting cultural assimilation.
- •It had three distinct chambers: mandapa, garbhagriha, and antalaya, and was surrounded by 84 pillars.
- •The use of lime mortar suggests advanced building techniques and possibly Byzantine architectural involvement.
- •Its history is documented in Kalhana's 12th-century text, Rajatarangini.
- •Martand Sun Temple is a significant example of Kashmir's rich pre-Islamic architectural heritage.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content