Floriculture in India - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Floriculture in India
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Floriculture in India</h4><p>The <strong>Jujumara region</strong> in <strong>Odisha’s Sambalpur district</strong> is home to one of the first <strong>Farmer Producer Organizations (FPO)</strong> in the state dedicated exclusively to <strong>floriculture</strong>. This marks a significant transition for farmers from traditional <strong>paddy farming</strong>.</p><p>With crucial support from the <strong>National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI)</strong>, local farmers are actively adopting <strong>flower cultivation</strong>. This strategic shift has resulted in significant <strong>economic improvements</strong> for the community.</p><div class="exam-tip-box">This example highlights the role of <strong>FPOs</strong> and research institutes like <strong>NBRI</strong> in promoting agricultural diversification and rural development, a key theme for <strong>UPSC GS Paper III</strong>.</div><h4>Defining Floriculture</h4><div class="info-box"><strong>Floriculture Definition:</strong> Floriculture involves the cultivation of <strong>flowering and ornamental plants</strong>. These plants are grown for various purposes, including <strong>direct sale</strong>, and as raw materials for the <strong>cosmetics, perfume, and pharmaceutical industries</strong>.</div><h4>Key Cultivation Techniques</h4><p>Floriculture encompasses the production of <strong>seed and plant material</strong>. This process is achieved through several specialized techniques:</p><ul><li><strong>Cutting:</strong> Propagating plants from a section of the stem, root, or leaf.</li><li><strong>Grafting:</strong> Joining two plant parts (scion and rootstock) to grow as one.</li><li><strong>Budding:</strong> A form of grafting where a single bud is used instead of a scion.</li></ul><h4>Nodal Agency for Promotion and Export</h4><p>The <strong>Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)</strong> serves as the primary nodal organization. Its mandate is to promote <strong>agri-exports</strong>, a category that prominently includes <strong>flowers and floriculture products</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>APEDA's Role:</strong> Facilitates export promotion, market development, and quality control for various agricultural products, including floriculture.</div><h4>Floriculture Market in India: A Sunrise Industry</h4><p>The <strong>Government of India</strong> has officially identified <strong>floriculture</strong> as a <strong>“sunrise industry”</strong>. This designation underscores its significant growth potential and economic importance for the nation.</p><div class="key-point-box">A <strong>"sunrise industry"</strong> is a new or emerging sector experiencing rapid growth, characterized by high innovation, job creation, and significant future potential.</div><h4>Key Statistics and Market Trends (2023-24)</h4><p>The floriculture sector in India demonstrates robust growth and expansion:</p><ul><li><strong>Area Under Cultivation:</strong> Approximately <strong>297 thousand hectares</strong> were dedicated to floriculture in <strong>2023-24</strong> (based on 2nd advance estimates).</li><li><strong>Export Volume:</strong> India exported around <strong>20,000 metric tonnes</strong> of floriculture products.</li><li><strong>Export Value:</strong> These exports were valued at <strong>Rs 717.83 crores</strong> in the <strong>2023-24</strong> fiscal year.</li></ul><div class="info-box"><strong>Projected Growth:</strong> The sector is expected to grow to <strong>USD 5.9 billion by 2030</strong>, exhibiting a <strong>Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.4%</strong> between 2023 and 2030.</div><h4>Major Export Destinations</h4><p>Indian floriculture products find significant markets globally. The primary importers include:</p><ul><li><strong>United States of America (USA)</strong></li><li><strong>The Netherlands</strong></li><li><strong>United Arab Emirates (UAE)</strong></li><li><strong>The United Kingdom (UK)</strong></li><li><strong>Canada</strong></li><li><strong>Malaysia</strong></li></ul><h4>Diverse Floriculture Varieties</h4><p>India's floriculture industry cultivates a wide range of products, catering to various market demands:</p><ul><li><strong>Cut Flowers:</strong> Roses, carnations, gerberas, etc., for bouquets and arrangements.</li><li><strong>Pot Plants:</strong> Ornamental plants grown in containers for indoor and outdoor decoration.</li><li><strong>Bulbs:</strong> Underground storage organs used for propagation (e.g., gladiolus, lilies).</li><li><strong>Tubers:</strong> Swollen underground stems for propagation (e.g., dahlias).</li><li><strong>Dried Flowers:</strong> Preserved flowers used for decorative purposes and crafts.</li></ul>
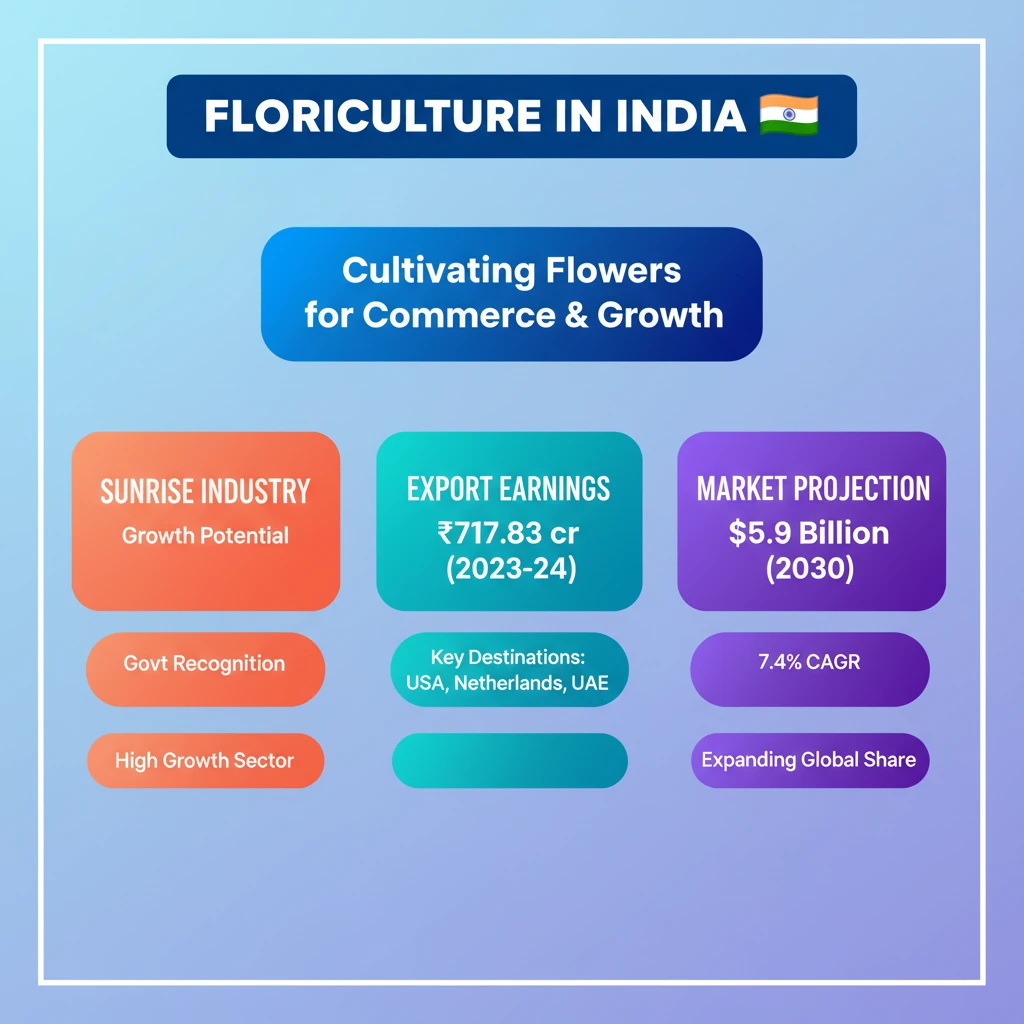
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Floriculture involves cultivating flowering and ornamental plants for various commercial uses.
- •The Government of India recognizes floriculture as a 'sunrise industry' due to its growth potential.
- •India exported Rs 717.83 crores worth of floriculture products in 2023-24.
- •Key export destinations include the USA, Netherlands, and UAE.
- •The sector is projected to reach USD 5.9 billion by 2030 with a 7.4% CAGR.
- •APEDA is the nodal agency promoting floriculture exports.
- •FPOs and research institutes like NBRI play a crucial role in its development.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content