International Models Addressing Food Waste - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

International Models Addressing Food Waste
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
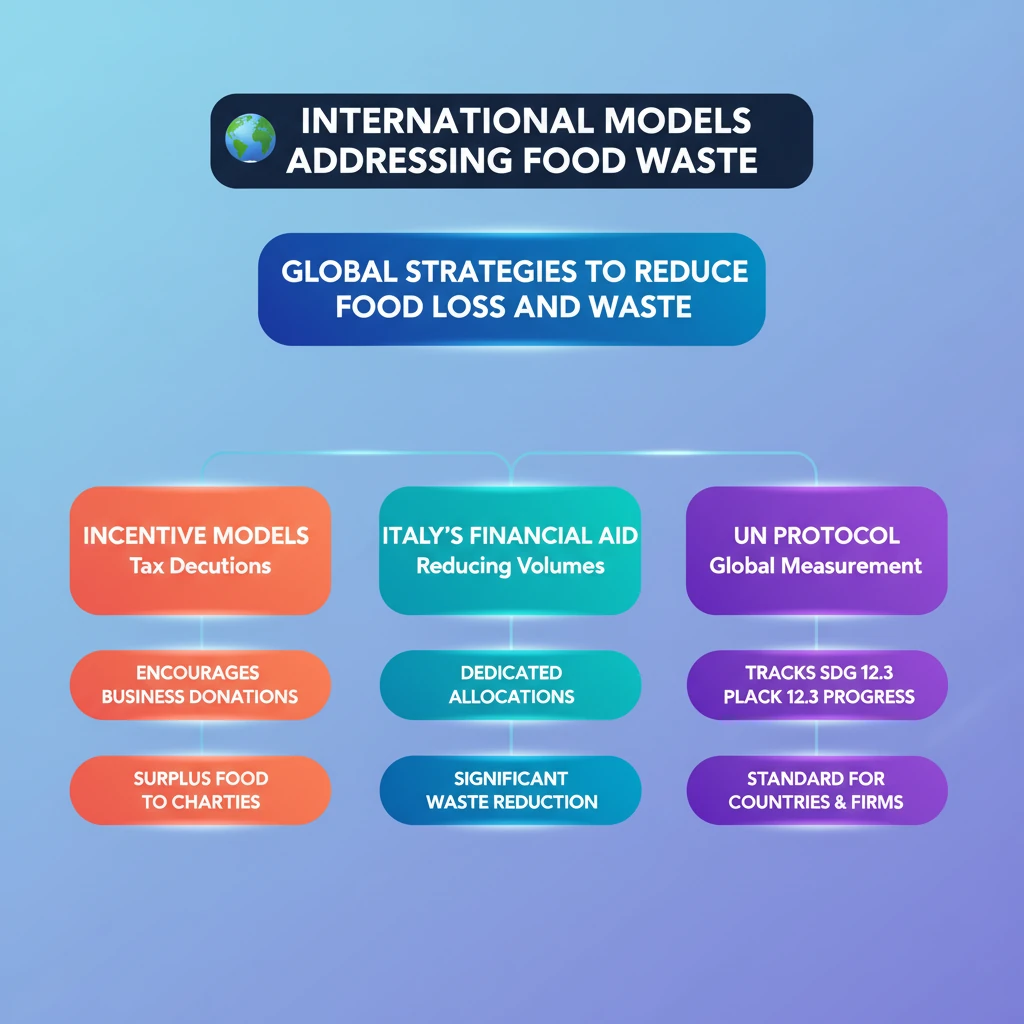
<h4>National Incentive Models for Food Waste Reduction</h4><p>Governments worldwide are implementing various strategies to combat <strong>food waste</strong>, often through incentive-based models. These models aim to encourage businesses and individuals to reduce, reuse, and redistribute excess food.</p><h4>US: Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes (PATH) Act of 2015</h4><p>The <strong>United States</strong> introduced significant incentives through the <strong>Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes (PATH) Act of 2015</strong>. This landmark legislation aimed to encourage businesses to donate their excess food rather than discarding it.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Key Provision:</strong> Enhanced tax deductions for food donations.</div><p>This act made it more financially attractive for companies to divert edible surplus food to charities, thereby reducing landfill waste and supporting food security initiatives.</p><h4>Italy's Incentive Model</h4><p><strong>Italy</strong> has also adopted a proactive approach to food waste reduction, demonstrating a strong commitment through financial incentives and streamlined donation processes.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Annual Allocation:</strong> Approximately <strong>USD 10 million</strong>.<br><strong>Target:</strong> Reduce <strong>one million tonnes</strong> of food waste annually.<br><strong>Mechanism:</strong> Offering businesses incentives to donate food to charities.</div><p>Italy's model simplifies the donation process for businesses, removing bureaucratic hurdles and providing financial encouragement, leading to substantial reductions in food waste.</p><h4>UN Global Food Loss and Waste Protocol</h4><p>Beyond national incentives, international standards play a crucial role in harmonizing efforts to measure and address food loss and waste globally. Consistent measurement is fundamental for effective policy-making.</p><div class="key-point-box">The <strong>UN Global Food Loss and Waste Protocol</strong> is a universal standard designed for the consistent measurement of <strong>food loss and waste (FLW)</strong>. It provides a common language and methodology for reporting.</div><p>This protocol was proposed as a key indicator for <strong>Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target 12.3</strong>. This target specifically addresses reducing food loss along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses, and reducing food waste at the retail and consumer levels.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Purpose:</strong> Provides a standardized methodology for measuring FLW.<br><strong>Applicability:</strong> Can be utilized by both <strong>countries</strong> and <strong>companies</strong>.<br><strong>Scope:</strong> Measures FLW within national borders and across complex supply chains.</div><p>By using a common protocol, global progress on food waste reduction can be accurately tracked, and best practices can be more easily identified and shared among nations and corporations.</p><div class="exam-tip-box">Understanding these international models is crucial for <strong>UPSC GS Paper III (Agriculture, Economy, Environment)</strong>. Be prepared to cite examples like the <strong>PATH Act</strong> or <strong>Italy's model</strong> when discussing policy solutions for food waste in India. The <strong>UN Global Food Loss and Waste Protocol</strong> is an excellent point to mention for international cooperation and standardization.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
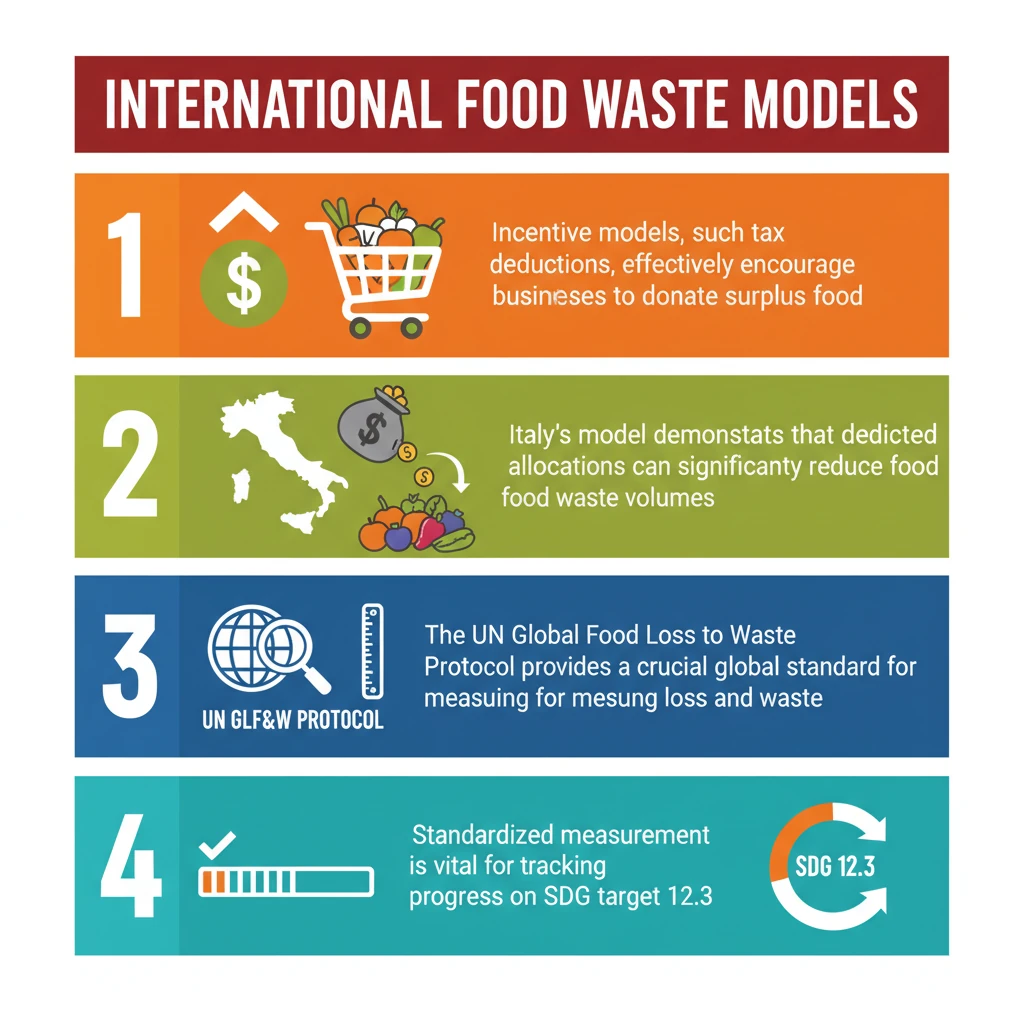
- •Incentive models, such as tax deductions, effectively encourage businesses to donate surplus food.
- •Italy's model demonstrates that dedicated financial allocations can significantly reduce food waste volumes.
- •The UN Global Food Loss and Waste Protocol provides a crucial global standard for measuring food loss and waste.
- •Standardized measurement is vital for tracking progress on SDG target 12.3.
- •Both countries and companies can use the UN Protocol to measure FLW within their borders and supply chains.
- •Reducing food waste contributes significantly to global food security and environmental sustainability.
- •These international models offer valuable lessons for India in developing its own food waste reduction policies.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content