Rice Cultivation in India: Conditions, Production & Government Initiatives - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Rice Cultivation in India: Conditions, Production & Government Initiatives
Easy⏱️ 5 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
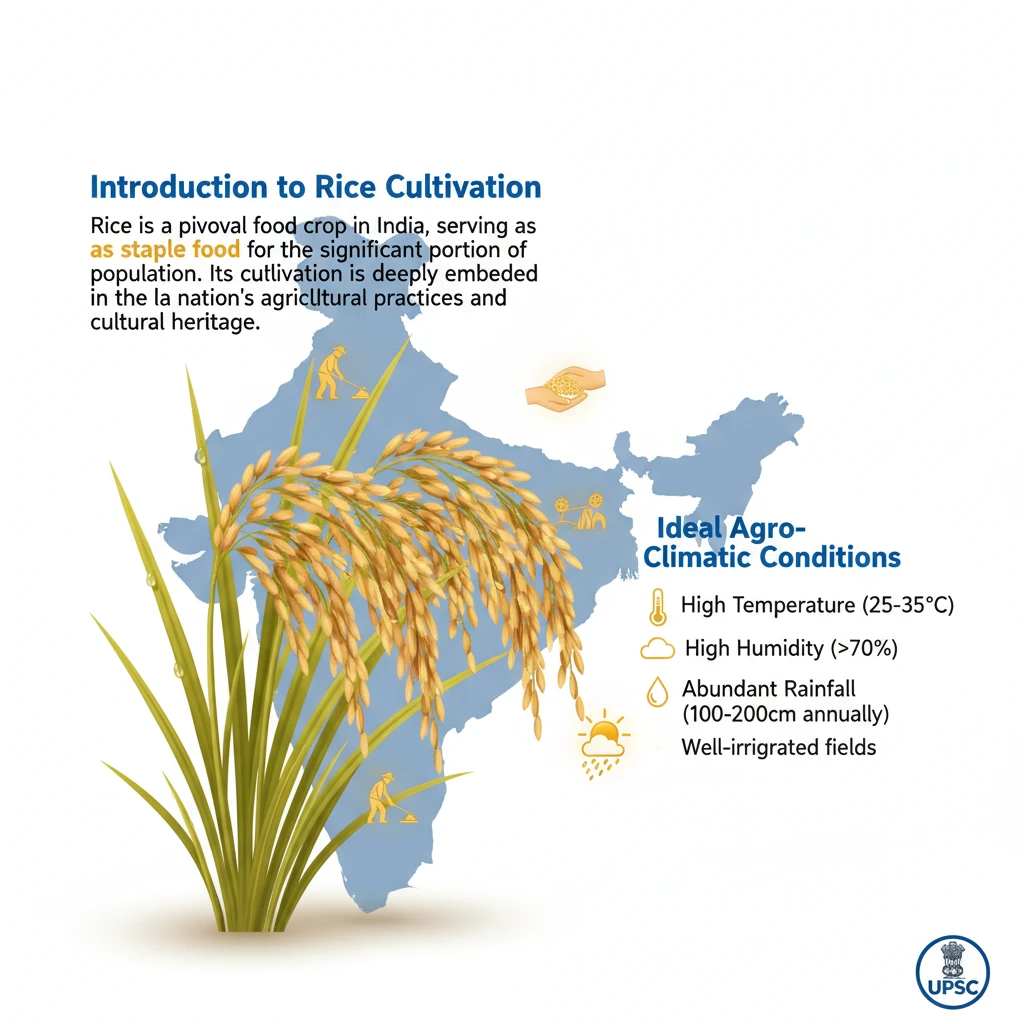
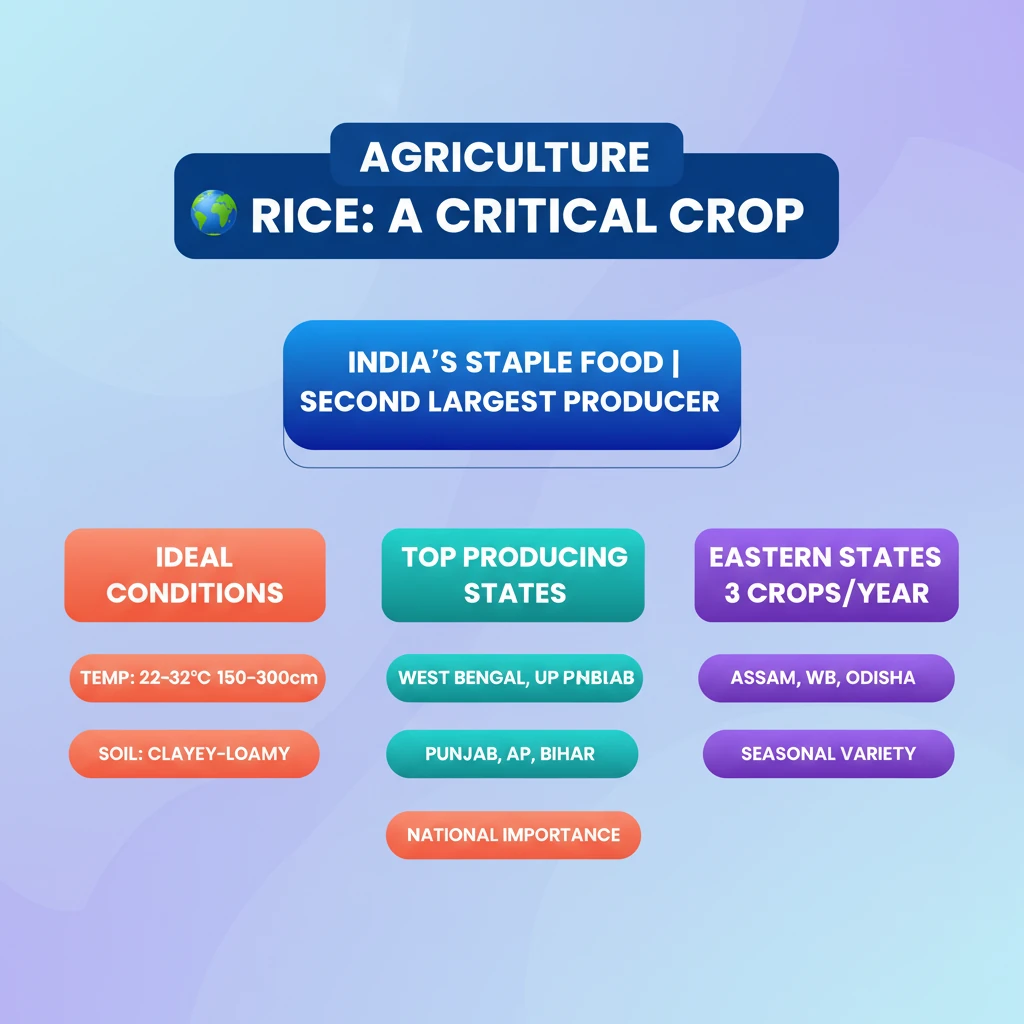
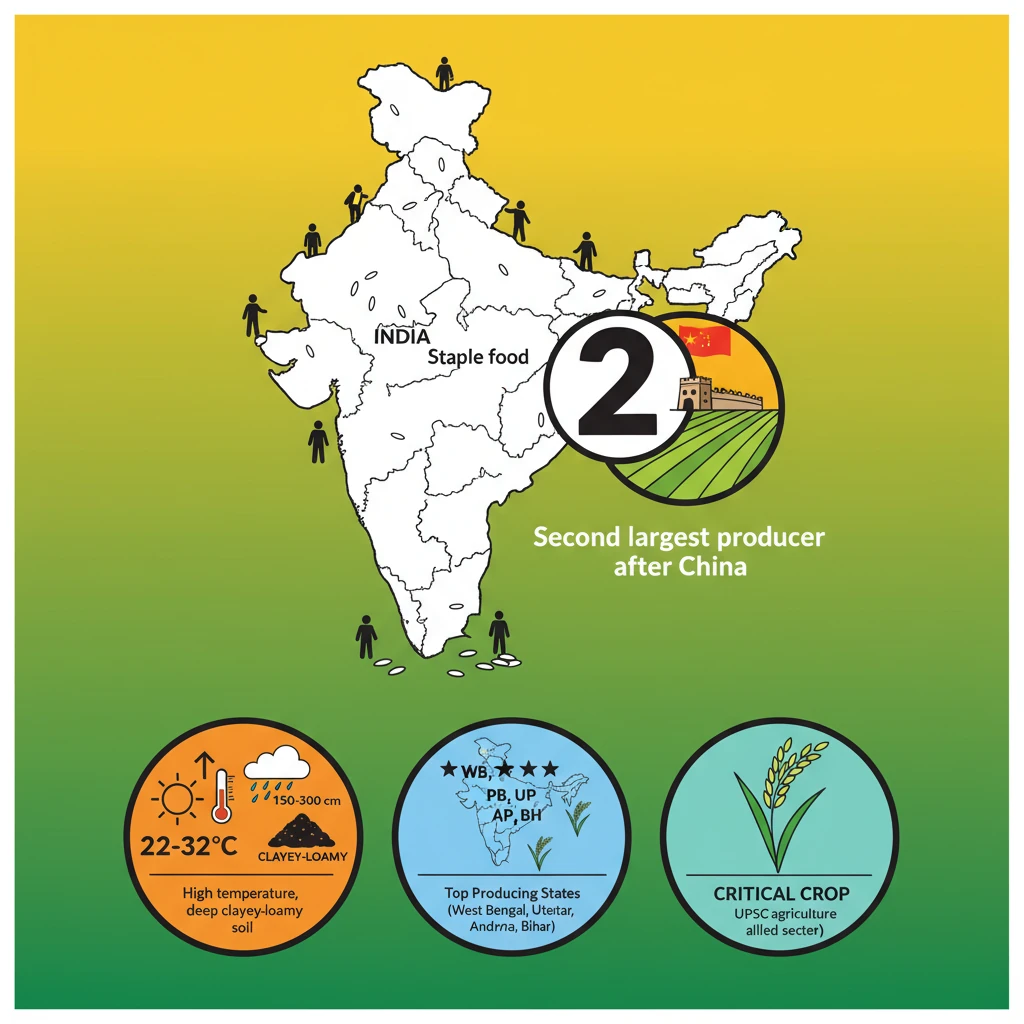
<h4>Introduction to Rice Cultivation</h4><p><strong>Rice</strong> is a pivotal <strong>food crop</strong> in India, serving as the <strong>staple food</strong> for a significant portion of the population. Its cultivation is deeply embedded in the nation's agricultural practices and cultural heritage.</p><h4>Ideal Agro-Climatic Conditions</h4><p>Successful <strong>rice cultivation</strong> requires specific environmental parameters to thrive. These conditions ensure optimal growth and yield for this vital crop.</p><div class="info-box"><ul><li><strong>Temperature:</strong> Between <strong>22-32 °C</strong>, requiring high humidity.</li><li><strong>Rainfall:</strong> Approximately <strong>150-300 cm</strong> annually.</li><li><strong>Soil Type:</strong> Prefers deep <strong>clayey and loamy soil</strong>, which can retain water effectively.</li></ul></div><h4>Major Producing States in India</h4><p>Several Indian states lead in <strong>rice production</strong>, contributing significantly to the nation's food basket. Their diverse agro-climatic zones support extensive cultivation.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Top Rice Producing States:</strong><ul><li><strong>West Bengal</strong></li><li><strong>Punjab</strong></li><li><strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong></li><li><strong>Andhra Pradesh</strong></li><li><strong>Bihar</strong></li></ul></div><h4>India's Global Standing and Crop Cycles</h4><p>India holds a prominent position in global <strong>rice production</strong>. Domestically, certain regions practice multiple cultivation cycles within a single year.</p><div class="info-box"><p>India is the <strong>second largest producer of rice</strong> in the world, following <strong>China</strong>.</p></div><p>In eastern states like <strong>Assam, West Bengal</strong>, and <strong>Odisha</strong>, farmers successfully cultivate <strong>three crops of paddy</strong> in a year. This practice maximizes land utility and food output.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><p>The three distinct rice crops grown annually in these states are known as <strong>Aus, Aman</strong>, and <strong>Boro</strong>. Understanding these crop cycles is crucial for analyzing regional agricultural patterns and food security strategies.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Rice is the staple food for the majority of Indians, making it a critical crop.
- •India is the second largest rice producer globally, after China.
- •Ideal conditions for rice include high temperature (22-32°C), high rainfall (150-300 cm), and deep clayey-loamy soil.
- •West Bengal, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Bihar are among the top rice producing states.
- •Eastern states like Assam, West Bengal, and Odisha grow three rice crops annually: Aus, Aman, and Boro.
- •Government initiatives such as the National Food Security Mission and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana support rice cultivation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India
•Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAOSTAT)