Edible Oil Imports and SAFTA Agreement - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Edible Oil Imports and SAFTA Agreement
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
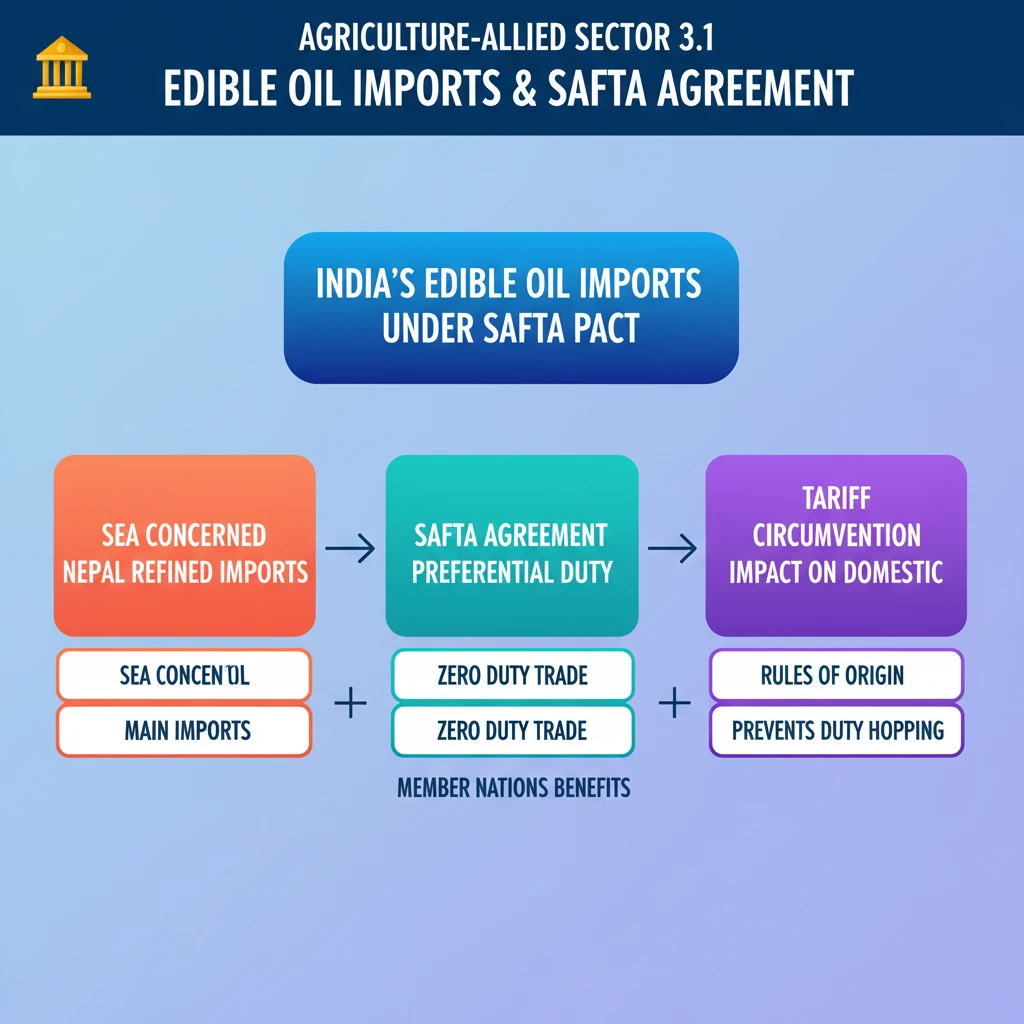
<h4>Concerns Over Edible Oil Imports from Nepal</h4><p>The <strong>Solvent Extractors’ Association of India (SEA)</strong> has expressed significant concerns regarding a substantial influx of <strong>refined Edible Oil</strong> into India. This oil, primarily <strong>soybean</strong> and <strong>palm oil</strong>, is being imported from <strong>Nepal</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box">This issue highlights potential challenges arising from regional trade agreements and their impact on domestic industries. The concerns are rooted in the implications for India's domestic edible oil sector.</div><h4>Role of SAFTA Agreement</h4><p>The imports are occurring under the framework of the <strong>South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) Agreement</strong>. SAFTA aims to reduce tariffs among member countries, facilitating smoother trade within the South Asian region.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>SAFTA Members:</strong> Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka.</div><p>While SAFTA promotes regional trade, the <strong>SEA's concerns</strong> likely stem from the possibility of tariff arbitrage or the circumvention of import duties that would otherwise apply to edible oil imports from non-SAFTA countries.</p><h4>Nature of the Imports</h4><p>The specific oils causing concern are <strong>refined soybean oil</strong> and <strong>refined palm oil</strong>. These are widely consumed edible oils in India, making the volume of imports a critical factor for the domestic market.</p><ul><li><strong>Soybean Oil:</strong> A major cooking oil, India is a significant consumer and importer.</li><li><strong>Palm Oil:</strong> The most widely consumed edible oil globally, India is its largest importer.</li></ul><div class="exam-tip-box">Understanding the mechanics of <strong>Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)</strong> like SAFTA, especially the role of <strong>Rules of Origin</strong>, is crucial for <strong>UPSC GS Paper 2 (International Relations)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper 3 (Economy)</strong>. Questions often revolve around their impact on domestic industry.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Solvent Extractors’ Association of India (SEA) is concerned about refined edible oil imports from Nepal.
- •These imports, mainly soybean and palm oil, occur under the SAFTA Agreement.
- •SAFTA allows preferential or zero-duty trade among member countries.
- •SEA's concern likely stems from potential tariff circumvention impacting India's domestic refiners.
- •Rules of Origin are crucial in FTAs to prevent duty hopping.
- •India is a major importer of edible oils, making domestic production a strategic priority.
- •Government initiatives like NEOM-OP aim to reduce India's edible oil import dependency.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official SAFTA Agreement documents
•Reports from Solvent Extractors’ Association of India (SEA)
•Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India publications on edible oils
•Economic Survey of India