PACS, Constitutional Framework & Cooperative Expansion Target - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

PACS, Constitutional Framework & Cooperative Expansion Target
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
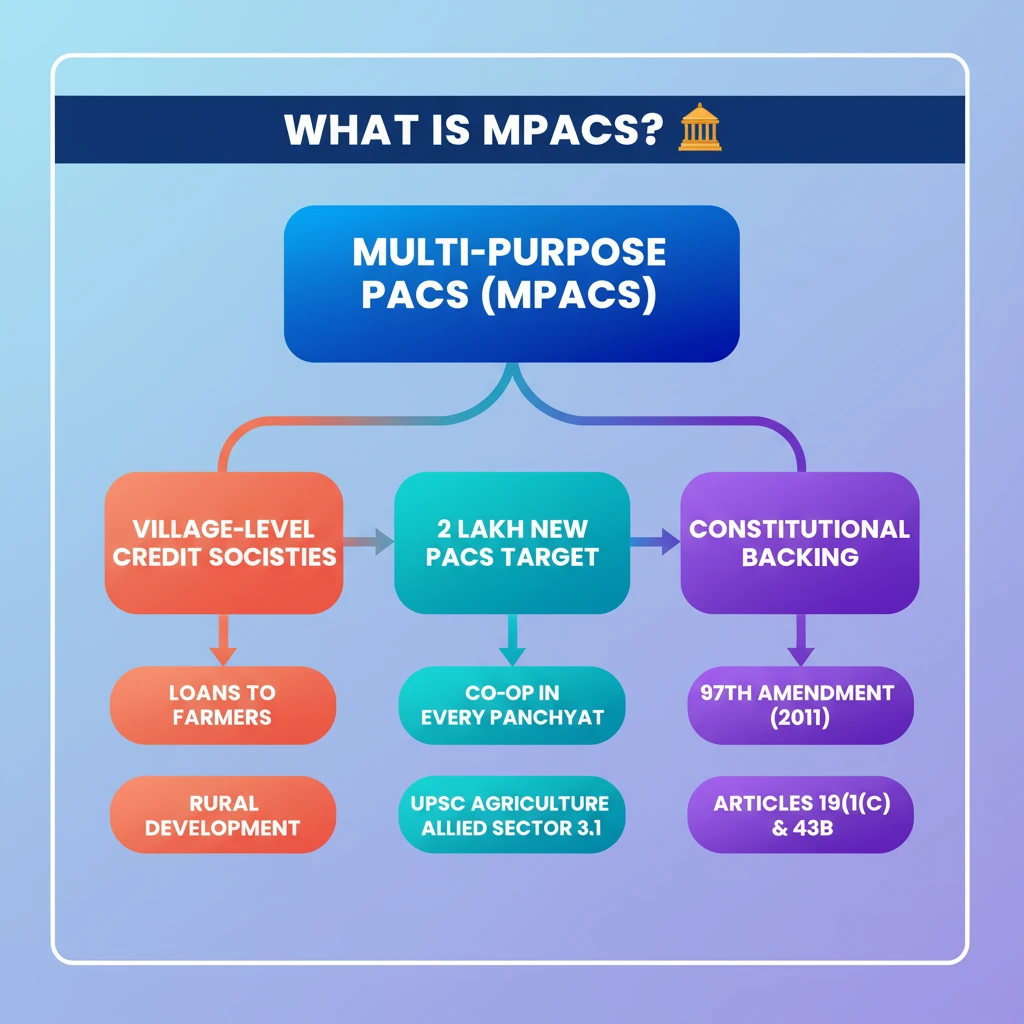
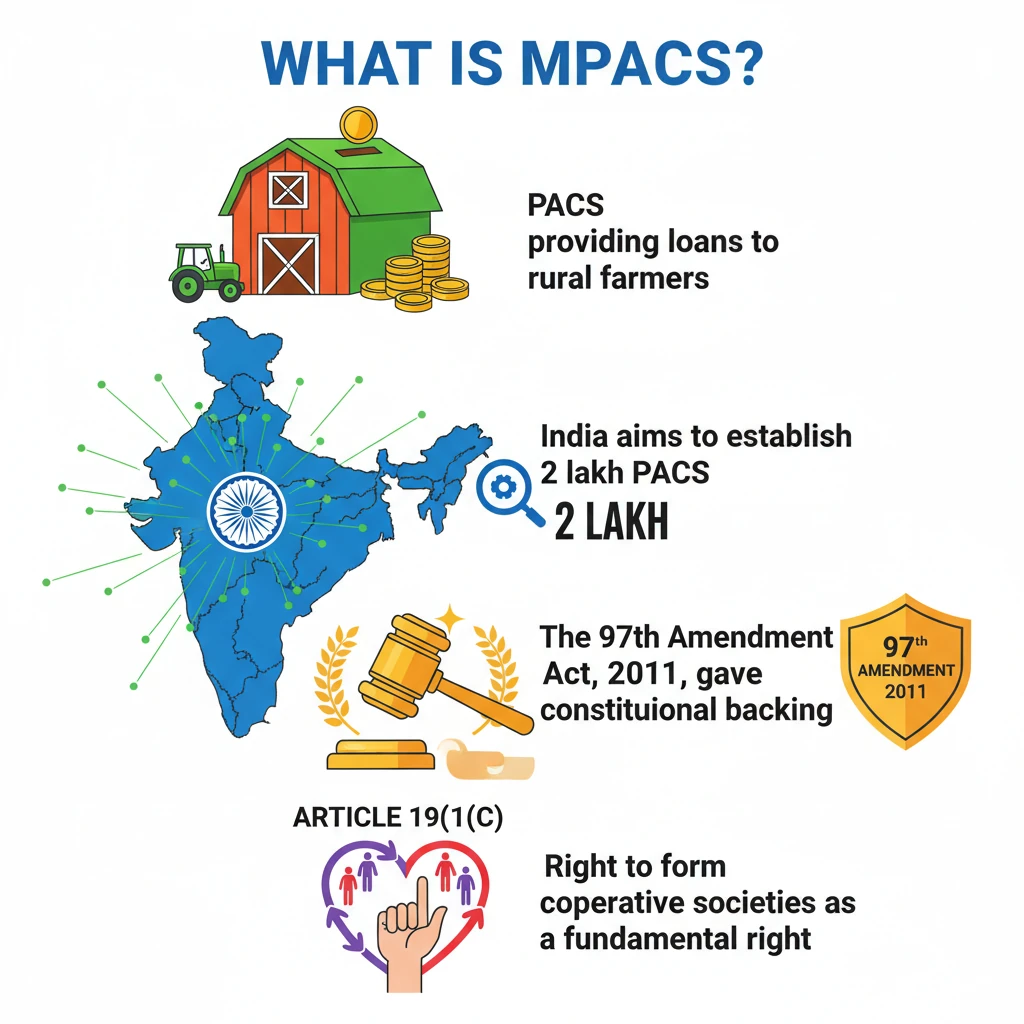
<h4>Introduction to Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)</h4><p><strong>Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)</strong> are vital <strong>village-level cooperative credit societies</strong> in India. Their primary role is to provide essential <strong>loans</strong> to rural agricultural borrowers and collect repayments.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Government Vision:</strong> India aims to create <strong>2 lakh PACS</strong> in 5 years.<br><strong>Goal:</strong> Ensure a presence of cooperatives in <strong>every panchayat</strong> across the country.</div><h4>Administration and Registration of PACS</h4><p>PACS are registered under the specific <strong>State Cooperative Societies Act</strong> of the state in which they operate. This legal framework governs their establishment and functioning.</p><p>They are administered by the <strong>State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS)</strong>. The RCS plays a crucial role in overseeing their compliance and operations.</p><h4>Constitutional Framework for Cooperatives</h4><p>The cooperative movement in India received significant constitutional backing through the <strong>97th Amendment Act, 2011</strong>. This amendment strengthened the legal and policy framework for cooperatives.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Key Constitutional Changes:</strong><ul><li>The word <strong>"cooperatives"</strong> was added in <strong>Article 19(1)(c)</strong> under <strong>Part III</strong> (Fundamental Rights) of the Constitution. This ensures the right to form cooperative societies.</li><li>A new <strong>Article 43B</strong> was inserted in the <strong>Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV)</strong>. This article mandates the state to endeavor to promote voluntary formation, autonomous functioning, democratic control, and professional management of cooperative societies.</li></ul></div><h4>What are Multi-Purpose Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (MPACS)?</h4><p><strong>Multi-Purpose Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (MPACS)</strong> represent an evolution of the traditional PACS model. They are designed to offer a broader spectrum of services to rural communities.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Beyond Credit:</strong> MPACS provide a wide range of services <strong>beyond agricultural credit</strong>, addressing multiple needs of rural communities.</div><h4>Diverse Activities of MPACS</h4><p>MPACS encompass not only credit societies but also other vital rural cooperatives, such as <strong>dairy and fisheries cooperatives</strong>. This integrated approach enhances their utility.</p><p>They are engaged in a diverse set of <strong>32 activities</strong>. This versatility makes them more effective in serving the holistic needs of rural populations.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Examples of MPACS Activities:</strong><ul><li><strong>Storage and distribution</strong> of agricultural produce.</li><li>Distribution of essential inputs like <strong>gas, fertilisers, and water</strong>.</li><li>Providing credit for various agricultural and allied activities.</li></ul></div><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the distinction between <strong>PACS</strong> and <strong>MPACS</strong>, along with their constitutional backing, is crucial for questions on rural development, cooperative federalism, and agricultural reforms in <strong>GS Paper III</strong> and <strong>GS Paper II</strong>.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •PACS are village-level cooperative credit societies providing loans to rural farmers.
- •India aims to establish 2 lakh PACS to ensure cooperative presence in every panchayat.
- •The 97th Amendment Act, 2011, gave constitutional backing to cooperatives.
- •Article 19(1)(c) now includes the right to form cooperative societies as a fundamental right.
- •Article 43B promotes the autonomous functioning and democratic control of cooperatives.
- •MPACS are an evolved form of PACS, offering a wide range of 32 services beyond credit.
- •MPACS integrate services like input distribution, storage, and support for dairy and fisheries.
🧠 Memory Techniques
100% Verified Content