South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) agreement - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) agreement
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
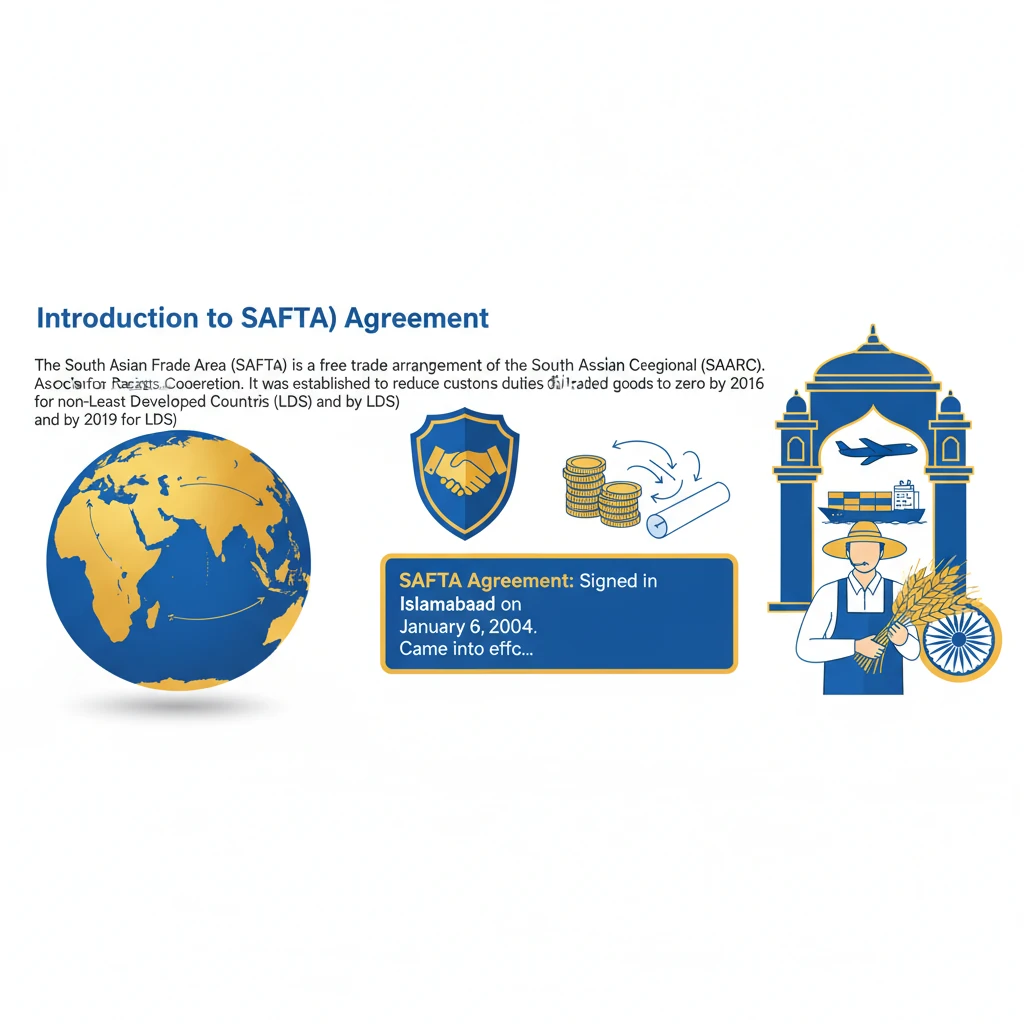
<h4>Introduction to SAFTA</h4><p>The <strong>South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)</strong> is a free trade arrangement of the <strong>South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)</strong>. It was established to reduce customs duties of all traded goods to zero by 2016 for non-Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and by 2019 for LDCs.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>SAFTA Agreement:</strong> Signed in <strong>Islamabad</strong> on <strong>January 6, 2004</strong>.<br><strong>Came into effect:</strong> <strong>January 1, 2006</strong>.<br><strong>Member States:</strong> Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka.</div><h4>Understanding Duty-Free Import Provisions</h4><p><strong>Duty-free import provisions</strong> under SAFTA mean that goods originating from member countries can be imported into other member countries without incurring customs duties. This aims to boost intra-regional trade and economic cooperation among <strong>SAARC nations</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box">The core idea is to eliminate trade barriers, making goods cheaper and more accessible across the region. This fosters economic integration and mutual benefit.</div><h4>The Issue of Misuse of SAFTA's Provisions</h4><p>The provided information highlights a concern regarding the <strong>misuse of SAFTA's duty-free import provisions</strong>. This implies that certain entities or practices are exploiting the agreement's benefits in ways unintended by its framers.</p><p>Such misuse can undermine the integrity of the trade agreement, distort regional trade patterns, and lead to revenue losses for member states. It often involves circumventing rules of origin or other regulatory frameworks.</p><div class="exam-tip-box">When discussing SAFTA, UPSC often looks for a nuanced understanding, including its successes, failures, and challenges like misuse of provisions. Focus on how such issues impact regional cooperation and India's trade policy.</div>
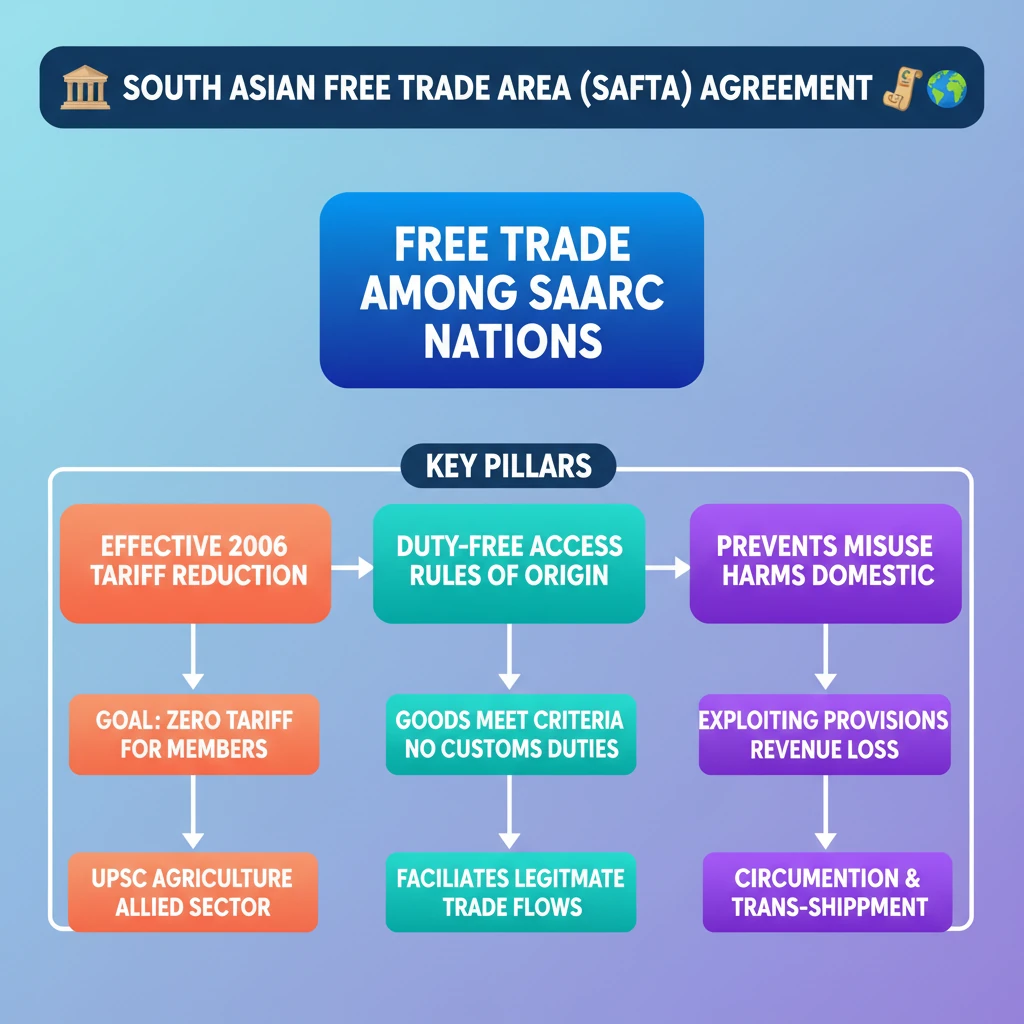
💡 Key Takeaways
- •SAFTA is a free trade agreement among SAARC nations, aiming for duty-free trade.
- •It came into effect in 2006, with goals to reduce tariffs to zero for member countries.
- •Duty-free import provisions allow goods meeting Rules of Origin to enter without customs duties.
- •Misuse involves exploiting these provisions, often by circumventing Rules of Origin or through illegal transshipment.
- •Such misuse leads to revenue loss for governments and harms domestic industries.
- •Effective enforcement of Rules of Origin and regional cooperation are crucial to prevent misuse.
- •The issue highlights challenges in achieving genuine economic integration in South Asia.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India Reports
•World Trade Organization (WTO) Publications on Regional Trade Agreements
•Economic Surveys of India (various years)
•Academic papers on South Asian economic integration