Cotton Cultivation in North India - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Cotton Cultivation in North India
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
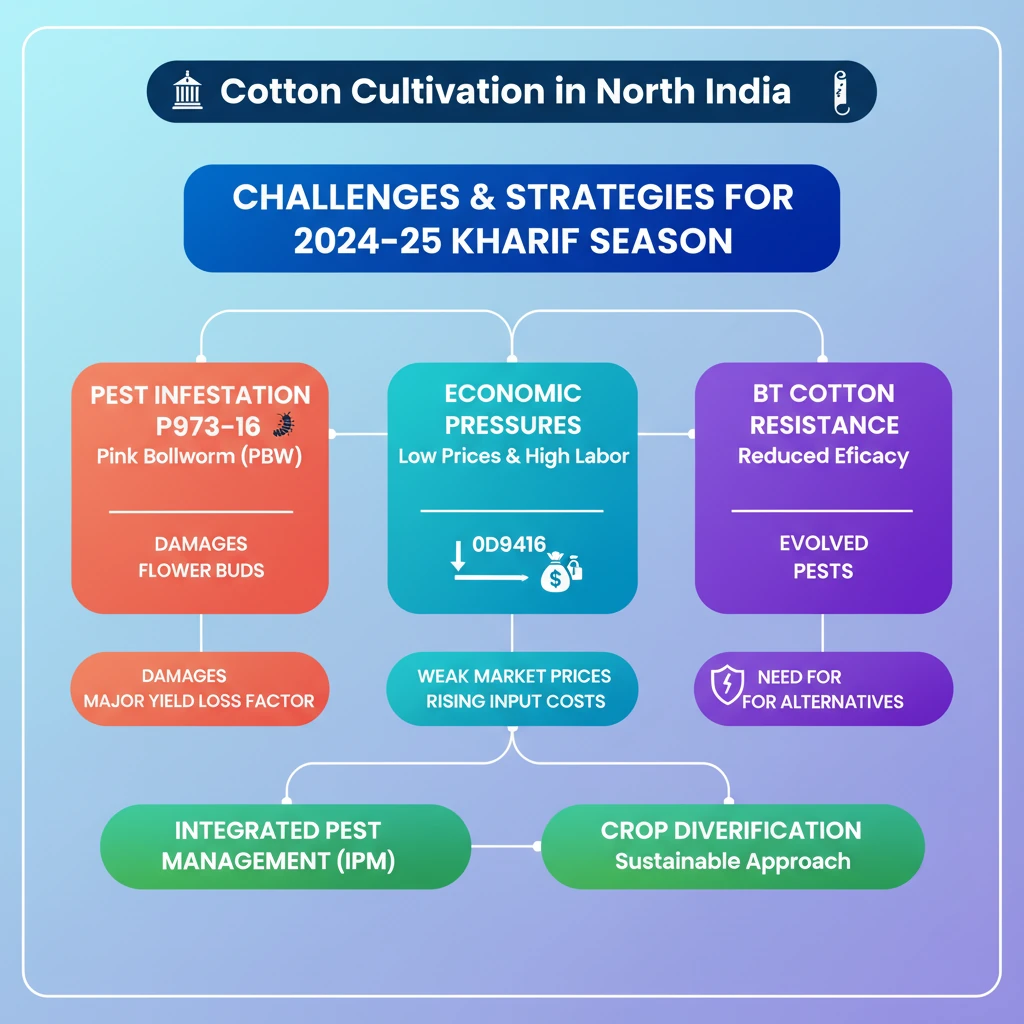
<h4>Outlook for Cotton Cultivation in North India (2024-25)</h4><p>The upcoming <strong>2024-25 kharif cotton planting season</strong> in <strong>North India</strong> anticipates a significant shift. Stakeholders foresee a potential dip in <strong>cotton acreages</strong>, signaling challenges for the region's agricultural landscape.</p><h4>Key Factors Driving Acreage Dip</h4><p>Several critical factors are converging to influence this projected decline in cotton cultivation:</p><ul><li><strong>Severe Pink Bollworm (PBW) infestation:</strong> A persistent and damaging pest affecting cotton crops.</li><li><strong>Weak prices for the fibre crop:</strong> Low market prices reduce profitability for farmers.</li><li><strong>Rising labour costs:</strong> Increasing operational expenses make cotton cultivation less viable.</li></ul><div class="exam-tip-box">📍 <strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> This scenario highlights the multifaceted challenges faced by the agricultural sector, often asked in <strong>GS-III (Agriculture)</strong>, linking pest management, market dynamics, and input costs.</div><h4>Understanding Pink Bollworm (PBW) Infestation</h4><p>The <strong>Pink Bollworm (PBW)</strong>, scientifically known as <strong><em>Pectinophora gossypiella</em></strong>, is a notorious pest. It is a major component of the <strong>American bollworm complex</strong>, specifically targeting cotton crops.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>PBW Identification:</strong> Also referred to as <strong>Saunders</strong>. This pest primarily damages the developing fruits of the cotton plant.</div><p>The damage caused by <strong>PBW</strong> is critical as it affects the plant's reproductive parts. It targets the <strong>flower bud (square)</strong> and the <strong>seed-containing boll</strong>, which are essential for cotton fibre production.</p><h4>Historical Context: Bt Cotton and Pest Management</h4><p>Historically, the introduction of <strong>Bt Cotton</strong> was a significant step in pest management. This genetically modified crop was engineered specifically to resist pests like the <strong>Pink Bollworm</strong>, aiming to mitigate infestation risks and improve yields.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Bt Cotton's Role:</strong> While initially effective, the emergence of resistance in pests like <strong>PBW</strong> has necessitated continuous research and integrated pest management strategies.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •North India anticipates a potential decline in cotton acreage for the 2024-25 kharif season.
- •Key factors driving this dip include severe Pink Bollworm (PBW) infestation, weak market prices, and rising labor costs.
- •Pink Bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) is a major pest that damages cotton flower buds and bolls.
- •Bt Cotton was introduced to combat pests like PBW, but resistance has emerged over time, reducing its efficacy.
- •Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and crop diversification are crucial strategies for sustainable cotton cultivation.
- •The economic viability of cotton farming is under pressure due to pest challenges and market fluctuations.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content