South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to SAFTA</h4><p>The <strong>South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)</strong> represents a significant regional trade agreement. It functions as the free trade arrangement under the umbrella of the <strong>South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)</strong>.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>SAFTA Overview:</strong><ul><li><strong>Purpose:</strong> Free trade arrangement for SAARC member states.</li><li><strong>Inception:</strong> Came into force on <strong>January 1, 2006</strong>.</li><li><strong>Predecessor:</strong> Succeeded the <strong>1993 SAARC Preferential Trading Arrangement (SAPTA)</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Membership of SAFTA</h4><p>SAFTA encompasses all member states of SAARC. This broad membership aims to foster greater economic integration across the South Asian region.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>SAFTA Member Countries:</strong><ul><li><strong>Afghanistan</strong></li><li><strong>Bangladesh</strong></li><li><strong>Bhutan</strong></li><li><strong>India</strong></li><li><strong>Maldives</strong></li><li><strong>Nepal</strong></li><li><strong>Pakistan</strong></li><li><strong>Sri Lanka</strong></li></ul></div><h4>Key Provisions of SAFTA</h4><p>SAFTA's primary objective is to liberalize trade among its members. This is achieved through a structured approach to tariff reduction on traded goods.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Trade Liberalization Policy:</strong><p>SAFTA's policy ensures a <strong>gradual reduction of tariffs</strong> on traded goods. The target range for these tariffs is between <strong>0% and 5%</strong>, significantly lowering trade barriers.</p></div><h4>Special Treatment for LDCs</h4><p>Recognizing the varying economic capacities of its members, SAFTA incorporates provisions for special and differential treatment. This is particularly crucial for the <strong>Least Developed Countries (LDCs)</strong> within the bloc.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>LDC Members in SAFTA:</strong><ul><li><strong>Afghanistan</strong></li><li><strong>Bangladesh</strong></li><li><strong>Nepal</strong></li></ul></div><p>These LDCs receive several benefits to support their economic development and integration into the free trade area.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Benefits for LDCs:</strong><ul><li><strong>Longer implementation period</strong> for tariff reductions.</li><li><strong>Greater exemptions</strong> from various trade restrictions.</li></ul></div><h4>Safeguard Measures</h4><p>To protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports or other adverse impacts of trade liberalization, SAFTA includes provisions for safeguard measures.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Safeguard Measures:</strong><p>These measures allow for the <strong>temporary suspension</strong> of trade concessions. This mechanism helps member states protect their local industries from potential harm caused by increased imports under SAFTA.</p></div><h4>Major Export Destinations (Contextual)</h4><p>While SAFTA focuses on intra-regional trade, understanding the broader export landscape for South Asian countries provides context. Many regional economies also engage significantly with markets beyond South Asia.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Common Export Destinations (Non-SAFTA focused, as per source):</strong><ul><li><strong>Indonesia</strong></li><li><strong>Vietnam</strong></li><li><strong>Philippines</strong></li><li><strong>Malaysia</strong></li><li><strong>Thailand</strong></li><li><strong>UAE</strong></li></ul><p><strong>Within SAARC:</strong> <ul><li><strong>Bangladesh</strong> is also a major destination.</li></ul></div>
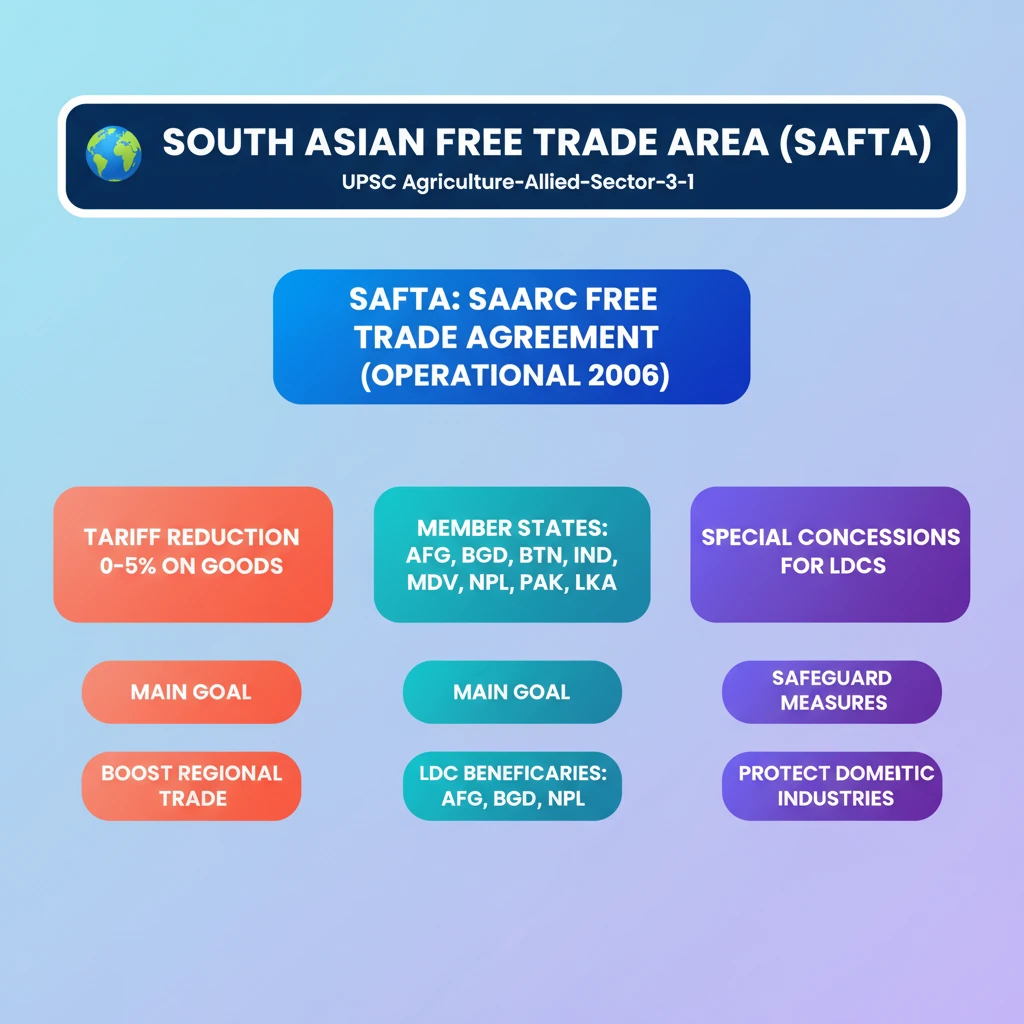
💡 Key Takeaways
- •SAFTA is the free trade agreement of SAARC, operational since 2006.
- •Its main goal is to reduce tariffs to 0-5% on traded goods among member states.
- •Member countries include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- •Least Developed Countries (LDCs) like Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal receive special concessions.
- •Safeguard measures allow temporary suspension of trade concessions to protect domestic industries.
- •SAFTA succeeded the earlier SAARC Preferential Trading Arrangement (SAPTA) from 1993.
- •Despite challenges, SAFTA aims to enhance regional economic integration and trade.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•SAARC Secretariat official website (for SAFTA agreement details and membership)
•World Trade Organization (WTO) definitions of Free Trade Area and LDCs