Pests of Cotton - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
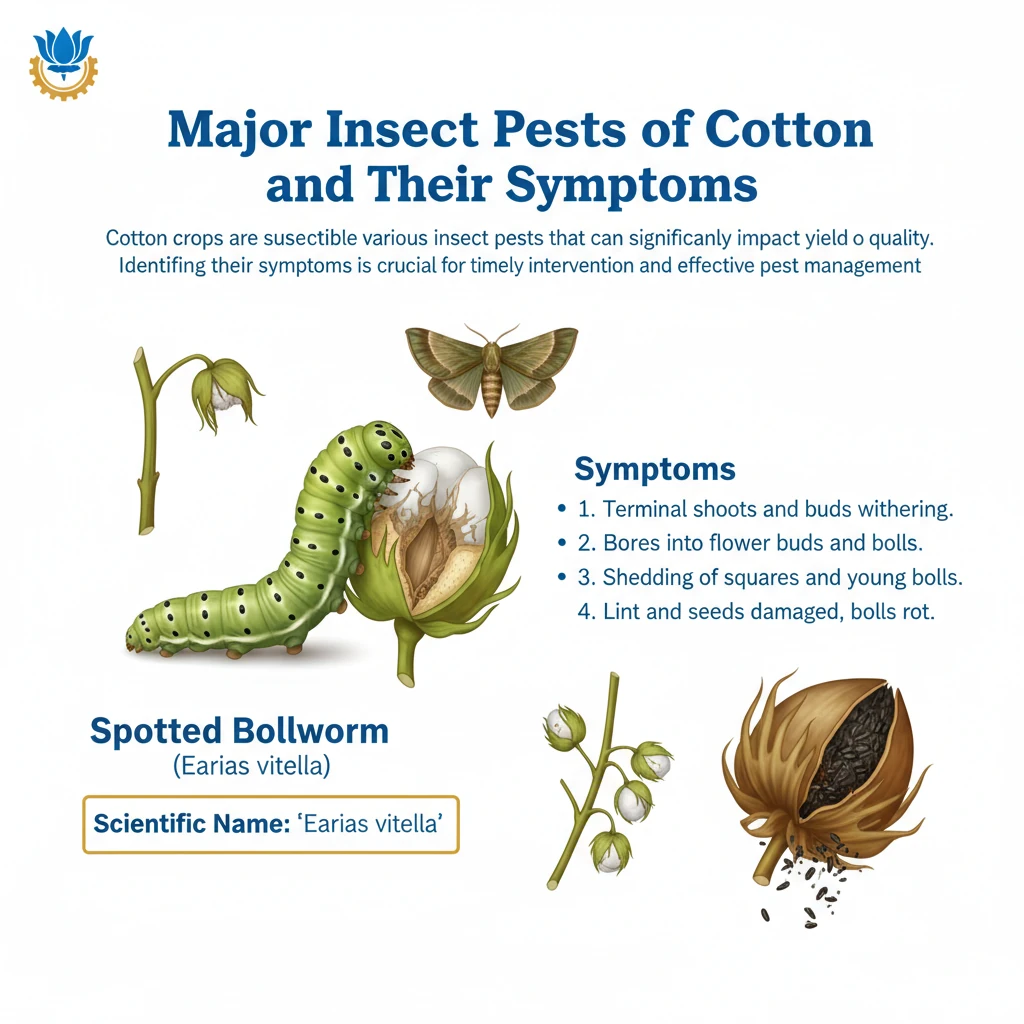
Pests of Cotton
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
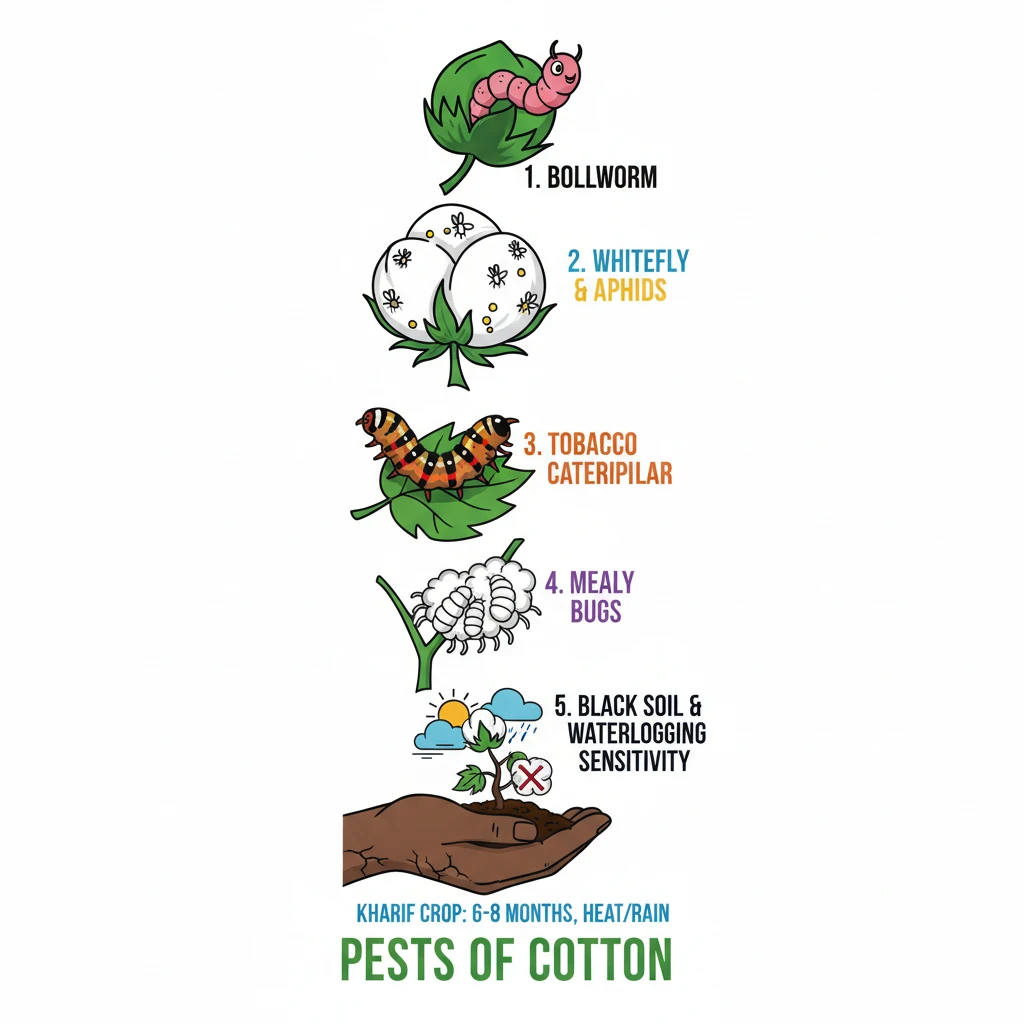
<h4>Major Insect Pests of Cotton and Their Symptoms</h4><p>Cotton crops are susceptible to various insect pests that can significantly impact yield and quality. Identifying their symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and effective pest management.</p><h4>Spotted Bollworm (<em>Earias vitella</em>)</h4><p>The <strong>Spotted Bollworm</strong> is a notorious pest causing damage to cotton plants at different growth stages.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Earias vitella</em></div><ul><li>Initially, it causes <strong>central shoots to dry, wither, and drop down</strong>.</li><li>Later, the larvae bore into <strong>flower buds</strong> and <strong>bolls</strong>, leading to their shredding and destruction.</li></ul><h4>American Bollworm (<em>Helicoverpa armigera</em>)</h4><p>The <strong>American Bollworm</strong> is another major pest, known for its destructive feeding habits on cotton.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Helicoverpa armigera</em></div><ul><li>A characteristic symptom is the <strong>flaring up of bracts</strong>, which are the leaf-like structures surrounding the flower bud.</li><li>It creates <strong>bore holes</strong> on squares (immature flower buds) that are typically filled with <strong>frass</strong> (insect excrement).</li></ul><h4>Tobacco Caterpillar (<em>Spodoptera litura</em>)</h4><p>The <strong>Tobacco Caterpillar</strong> can cause severe defoliation, impacting the plant's photosynthetic capacity.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Spodoptera litura</em></div><ul><li>Symptoms include <strong>irregular bore holes</strong> on leaves.</li><li>It leads to <strong>skeletonization of leaves</strong>, where only the veins remain.</li><li>Heavy infestation results in significant <strong>defoliation</strong> of the plant.</li></ul><h4>White Fly (<em>Bemisia tabaci</em>)</h4><p>The <strong>White Fly</strong> is a sap-sucking insect that can cause multiple issues, including reduced lint quality.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Bemisia tabaci</em></div><ul><li>Both nymphs and adults <strong>suck sap</strong> from the leaves, weakening the plant.</li><li>Infestation results in <strong>low quality lint</strong>.</li><li>In severe cases, it can lead to premature <strong>boll shedding</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Cotton Aphid (<em>Aphis gossypii</em>)</h4><p><strong>Cotton Aphids</strong> are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap and excrete honeydew.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Aphis gossypii</em></div><ul><li>Both <strong>nymphs and adults suck sap</strong> from the leaves.</li><li>Their feeding leads to a <strong>shiny appearance</strong> on leaves due to the secretion of <strong>honeydew</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Cotton Mealy Bug (<em>Phenacoccus solenopsis</em>)</h4><p>The <strong>Cotton Mealy Bug</strong> is a relatively newer pest that can cause significant damage and stunting.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Scientific Name:</strong> <em>Phenacoccus solenopsis</em></div><ul><li>Symptoms include the formation of <strong>bushy shoots</strong>.</li><li>At an early stage of cotton planting, <strong>crop senescence</strong> (premature ageing) may be observed.</li><li>The honeydew secreted by mealy bugs often leads to the growth of <strong>sooty mould</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Cotton Growing Conditions</h4><p><strong>Cotton</strong> is a vital <strong>kharif crop</strong> that requires specific climatic conditions for optimal growth and maturation.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Crop Cycle:</strong> Requires <strong>6 to 8 months</strong> to mature.</div><p>Ideal conditions include a long, sunny, and frost-free period.</p><ul><li><strong>Temperature:</strong> Best between <strong>21-30°C</strong>.</li><li><strong>Rainfall:</strong> Around <strong>50-100 cm</strong>. It thrives in warm and humid environments.</li></ul><h4>Soil Requirements for Cotton</h4><p>Cotton can be cultivated in a diverse range of soils, but certain types are more conducive to its growth.</p><div class="key-point-box">The most ideal soil for cotton cultivation is <strong>black cotton soil</strong>.</div><p>It can tolerate a wide <strong>pH range of 5.5 to 8.5</strong>. However, cotton plants are highly sensitive to <strong>waterlogging</strong> conditions.</p><h4>Geographic Distribution of Cotton in India</h4><p>India is a major global producer of cotton, with cultivation spread across distinct agro-climatic zones.</p><ul><li><strong>Northern Zone:</strong> Key states include <strong>Punjab</strong>, <strong>Haryana</strong>, and <strong>Rajasthan</strong>.</li><li><strong>Central Zone:</strong> Comprises <strong>Gujarat</strong>, <strong>Maharashtra</strong>, and <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong>.</li><li><strong>Southern Zone:</strong> Includes <strong>Telangana</strong>, <strong>Andhra Pradesh</strong>, <strong>Karnataka</strong>, and <strong>Tamil Nadu</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Economic Significance: India's "White-Gold"</h4><p>Cotton holds immense economic importance for India, impacting both agriculture and industry.</p><div class="key-point-box">Cotton is often referred to as <strong>“White-Gold”</strong> due to its significant economic contribution.</div><p>It serves as the <strong>primary source</strong> for the <strong>textile industry</strong>, accounting for approximately <strong>two-thirds</strong> of India’s total textile fibre consumption.</p><p>India is a global leader in cotton production, contributing about <strong>25% of the world's total cotton output</strong>.</p><p>Beyond fibre, cotton provides valuable by-products:</p><ul><li><strong>Cottonseed oil:</strong> Used for cooking and is India’s <strong>third-largest domestically-produced vegetable oil</strong>.</li><li><strong>Cottonseed cake/meal:</strong> Utilized as feed for <strong>livestock and poultry</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Government Initiatives for Cotton Sector</h4><p>The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to support cotton farmers and enhance the sector's productivity and quality.</p><ul><li><strong>Kasturi Cotton:</strong> A branding and certification initiative to establish Indian cotton as a premium product globally.</li><li><strong>Minimum Support Price (MSP):</strong> Ensures a guaranteed price for cotton, protecting farmers from market fluctuations.</li><li><strong>Cotton Corporation of India (CCI):</strong> A public sector undertaking responsible for procurement, distribution, and price stabilization of cotton.</li><li><strong>National Food Security Mission - Commercial Crops (NFSM-CC):</strong> Aims to increase production and productivity of various commercial crops, including cotton, through area expansion and improved technologies.</li></ul>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Cotton is a major kharif crop requiring 6-8 months to mature with specific temperature and rainfall needs.
- •Key insect pests include bollworms, whiteflies, aphids, tobacco caterpillar, and mealy bugs, each with distinct symptoms.
- •Black cotton soil is ideal for cultivation, and the crop is sensitive to waterlogging.
- •India has three major cotton growing zones: Northern, Central, and Southern.
- •Cotton is economically significant as the primary textile fibre source and for cottonseed oil, India's third-largest domestic vegetable oil.
- •Government initiatives like Kasturi Cotton, MSP, CCI, and NFSM-CC support the cotton sector.
- •Effective pest management is crucial for maintaining yield and lint quality in cotton farming.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India reports
•NCERT Textbooks (Geography, Economics)
•Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) publications