What are Weeds? - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Weeds?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
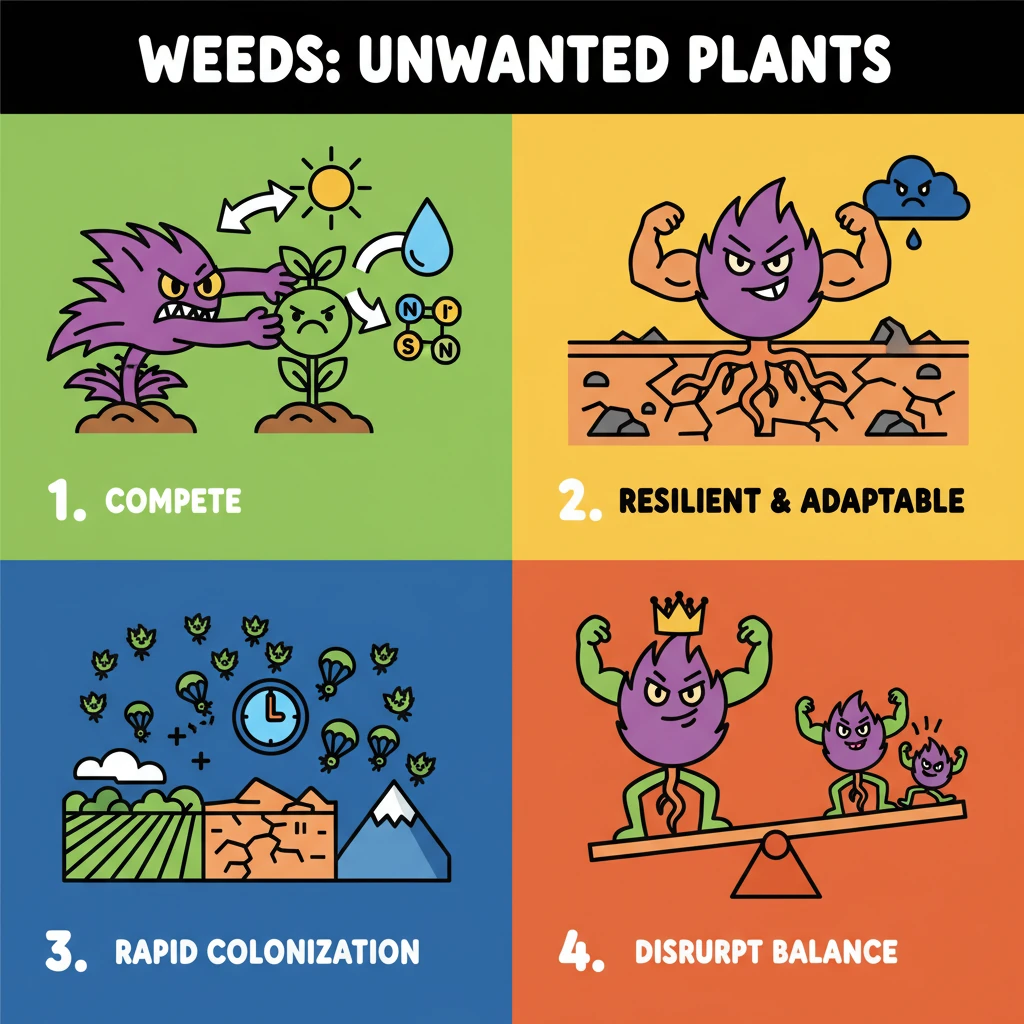
<h4>Understanding Weeds: An Overview</h4><p><strong>Weeds</strong> are typically defined as plants growing where they are not wanted, particularly in agricultural fields or managed ecosystems. They are considered undesirable because they interfere with human activities or the health of desired plants.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Core Definition:</strong> An <strong>unwanted plant</strong> that thrives in an ecosystem, disrupting agricultural or ecological balance by competing with cultivated crops or other vegetation.</div><h4>Common Examples of Weeds</h4><p>Various plant species are classified as weeds due to their disruptive nature. These can range from grasses to broad-leaved plants, adapted to different environments.</p><ul><li><strong>Nut Grass</strong> (<em>Cyperus rotundus</em>): A highly persistent perennial weed, notorious for its deep root system and tubers.</li><li><strong>Portulaca</strong> (<em>Portulaca oleracea</em>): Also known as <strong>purslane</strong>, it's a succulent annual weed common in gardens and cultivated areas.</li><li><strong>Common Couch</strong> (<em>Elymus repens</em>): A widespread perennial grass weed, known for its extensive rhizome system that spreads aggressively.</li><li><strong>Leucaena</strong> (<em>Leucaena leucocephala</em>): While sometimes used as fodder, it can become an invasive weed in certain ecosystems due to its rapid growth and prolific seeding.</li></ul><h4>Key Characteristics of Weeds</h4><p>Weeds possess specific traits that enable their survival and proliferation, making them a significant challenge in agriculture and natural ecosystems.</p><div class="key-point-box"><ul><li><strong>Aggressive Competition:</strong> Weeds fiercely compete with cultivated crops and other desired vegetation for vital resources such as <strong>sunlight, water, nutrients, and space</strong>. This competition directly impacts crop yield and quality.</li><li><strong>Resilience and Adaptability:</strong> They exhibit remarkable resilience and adaptability, allowing them to thrive in diverse environmental conditions. This includes tolerance to drought, poor soil, and even some herbicides.</li><li><strong>Rapid Colonization:</strong> Their ability to rapidly colonize various habitats is a defining characteristic, often facilitated by efficient seed dispersal mechanisms and vegetative propagation.</li></ul></div><div class="exam-tip-box">For <strong>UPSC Mains (GS-III Agriculture)</strong>, understanding weed characteristics is crucial for discussing <strong>weed management strategies</strong> and their impact on <strong>food security</strong>. Mentioning specific examples adds value to your answers.</div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Weeds are unwanted plants that disrupt agricultural and ecological balance.
- •They aggressively compete with cultivated crops for essential resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- •Weeds exhibit significant resilience and adaptability to diverse environmental conditions.
- •Rapid colonization of various habitats is a defining characteristic of weeds.
- •Common examples include Nut Grass, Portulaca, Common Couch, and Leucaena.
- •Effective weed management is crucial for ensuring food security and promoting sustainable agriculture.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research) publications on Weed Science
•FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) reports on crop protection
•Standard textbooks on Agronomy and Plant Protection