High-Yielding Seeds - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

High-Yielding Seeds
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
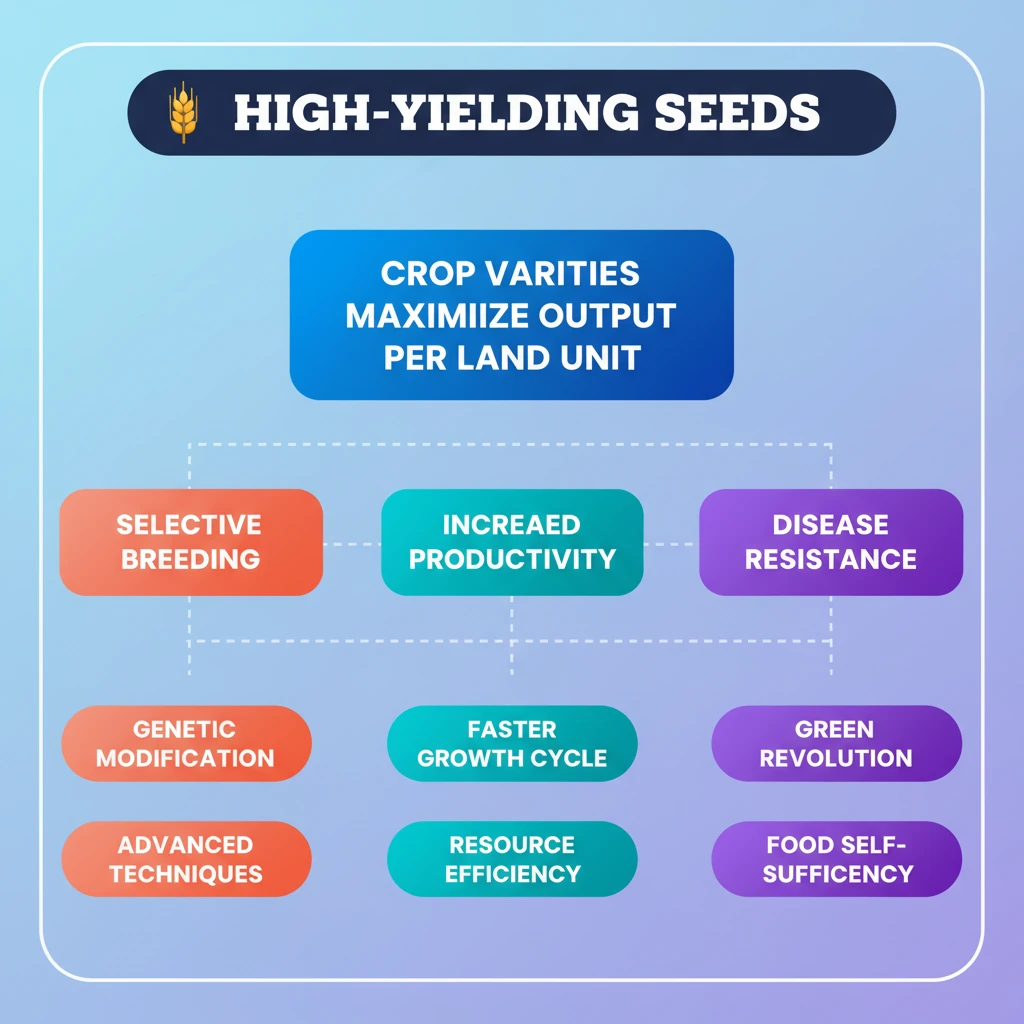
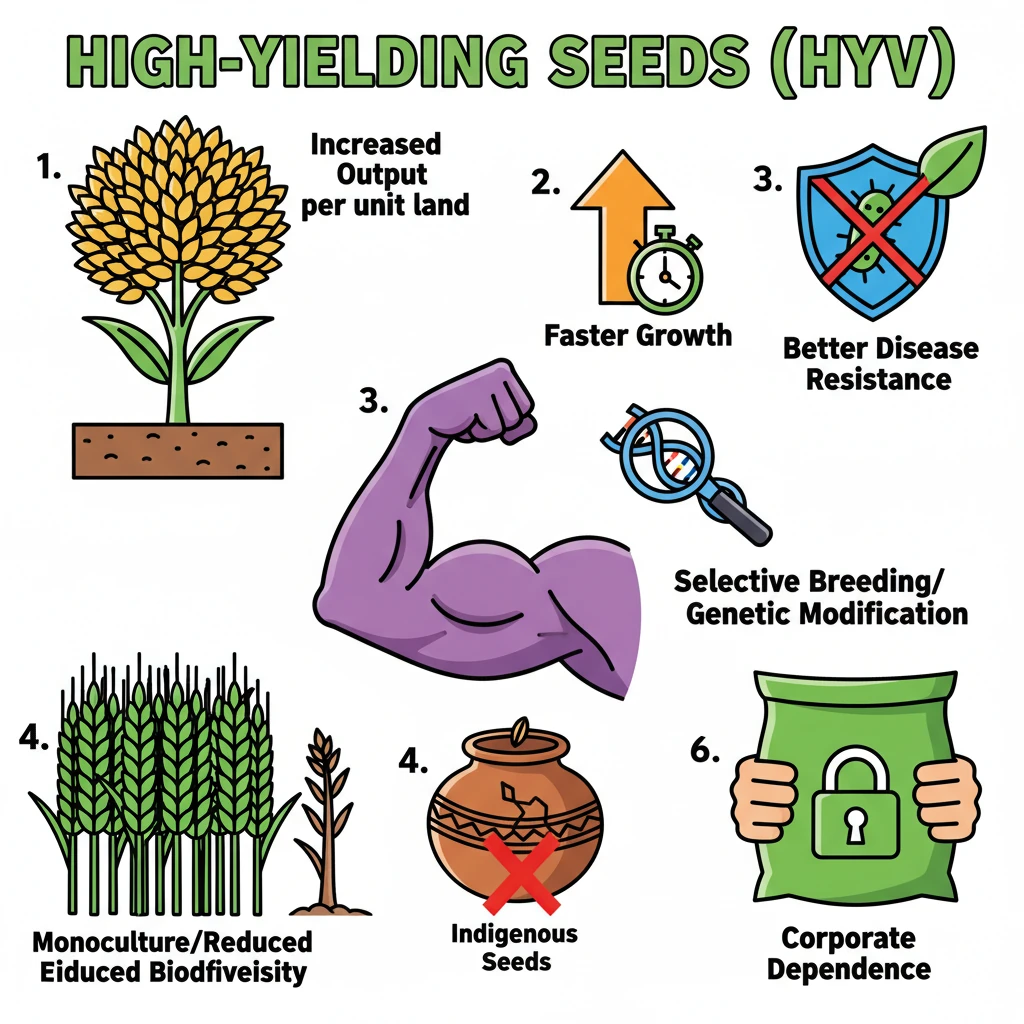
<h4>Introduction to High-Yielding Seeds (HYVs)</h4><p><strong>High-yielding seeds (HYVs)</strong> are a category of seeds specifically developed to significantly increase crop output per unit of land. These seeds are a cornerstone of modern agriculture, aiming to enhance productivity and address global food demands.</p><div class="info-box"><strong>Definition:</strong> Seeds engineered through selective breeding, genetic modification, or advanced techniques to produce substantially more yield than traditional varieties.</div><h4>Methods of Development</h4><p>The development of HYVs involves sophisticated agricultural science. Farmers utilize various methods to achieve the desired traits:</p><ul><li><strong>Selective Breeding:</strong> Identifying and propagating plants with desirable characteristics over generations.</li><li><strong>Genetic Modification:</strong> Directly altering the genetic makeup of seeds to introduce specific traits, such as pest resistance.</li><li><strong>Advanced Agronomic Techniques:</strong> Employing modern cultivation practices that complement the genetic potential of HYVs.</li></ul><h4>Key Benefits of High-Yielding Seeds</h4><p>HYVs offer numerous advantages that have transformed agricultural landscapes globally. Their adoption has been critical for improving food security in many regions.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>Primary Advantages:</strong><ul><li><strong>Increased Output:</strong> Produce a much larger quantity of crops from the same land area.</li><li><strong>Faster Growth Cycle:</strong> Often mature more quickly, allowing for multiple cropping seasons in a year.</li><li><strong>Enhanced Disease Resistance:</strong> Bred to withstand common plant diseases, reducing crop loss.</li><li><strong>Resource Efficiency:</strong> Can be optimized to utilize water and nutrients more efficiently, though sometimes requiring specific inputs.</li></ul></div><h4>Concerns Associated with High-Yielding Seeds</h4><p>Despite their benefits, the widespread adoption of HYVs also raises several ecological, economic, and social concerns that warrant careful consideration.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> The debate around HYVs often appears in <strong>GS-III (Agriculture, Economy, Environment)</strong>, focusing on their impact on food security, biodiversity, and farmers' livelihoods.</div><ul><li><strong>Promotion of Monocultures:</strong> Encourages the cultivation of single crop varieties over vast areas, increasing vulnerability to specific pests and diseases.</li><li><strong>Reduction in Biodiversity:</strong> Leads to the displacement and loss of traditional, indigenous seed varieties, diminishing genetic diversity.</li><li><strong>Threat to Indigenous Seeds:</strong> Local varieties, often well-adapted to specific regional conditions, are sidelined in favor of commercially viable HYVs.</li><li><strong>Increased Dependence on Corporate Seed Companies:</strong> Farmers often become reliant on a few large corporations for seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, impacting their autonomy and input costs.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •High-Yielding Seeds (HYVs) are crop varieties developed to produce significantly more output per unit of land.
- •They are created through selective breeding, genetic modification, or advanced techniques.
- •Key benefits include increased output, faster growth, better disease resistance, and potential for resource efficiency.
- •Concerns include promotion of monocultures, reduction in biodiversity, threat to indigenous seeds, and increased corporate dependence.
- •HYVs were crucial to India's Green Revolution, leading to food self-sufficiency.
- •Examples include hybrid rice (PRH 10), hybrid wheat (HD 3086), and Bt Cotton.
- •Current relevance involves balancing food security with environmental sustainability and farmer welfare.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Textbooks (Agriculture, Economics)
•Government of India reports on Agriculture and Seed Policy
•International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) publications