Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) - Agriculture Allied Sector | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
agriculture allied sector
📖 Introduction
<h4>Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in Agriculture</h4><p>The concept of <strong>Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)</strong> is crucial for modernizing agricultural extension services. It aims to create a unified digital ecosystem to support farmers effectively.</p><div class="key-point-box"><strong>DPI</strong> integrates various digital tools, including chatbots and <strong>Agristack</strong>, to provide real-time farmer support and feedback mechanisms.</div><h4>Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS)</h4><p>The <strong>Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS)</strong> is a vital component of digital outreach, focusing on weather and crop-related information dissemination. It operates through a network of specialized units.</p><div class="info-box"><ul><li><strong>130 Agromet Field Units (AMFUs)</strong> are responsible for gathering and disseminating localized information.</li><li>Information is shared via multiple channels: <strong>SMS</strong>, <strong>radio</strong>, and <strong>social media</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>Additionally, mobile applications like <strong>Kisan Suvidha</strong> and <strong>Bhuvan</strong> further assist farmers in accessing critical weather updates directly on their devices.</p><h4>Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)</h4><p>The <strong>Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)</strong> is a flagship scheme promoting organic farming practices in India. It focuses on cluster-based implementation to maximize impact.</p><div class="info-box"><ul><li>Since <strong>2015-16</strong>, <strong>PKVY</strong> has covered <strong>14.99 lakh hectares</strong>.</li><li>The scheme has benefited over <strong>25 lakh farmers</strong> by promoting certified organic production.</li></ul></div><h4>Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)</h4><p>The formation and promotion of <strong>Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)</strong> are central to empowering farmers by enhancing their collective bargaining power and market access.</p><div class="info-box">As of <strong>December 2024</strong>, <strong>9268 FPOs</strong> have been registered under the scheme to form and promote <strong>10,000 FPOs</strong>. These organizations help farmers with input sourcing, credit access, and marketing their produce.</div><h4>Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PMKMY)</h4><p>The <strong>Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PMKMY)</strong> is a social security scheme designed to provide a safety net for small and marginal farmers in their old age.</p><div class="info-box"><ul><li>As of <strong>November 2024</strong>, <strong>24.66 lakh farmers</strong> are enrolled.</li><li>The scheme provides a minimum pension of <strong>Rs 3,000 per month</strong> upon reaching <strong>60 years of age</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Per Drop More Crop (PDMC)</h4><p>The <strong>Per Drop More Crop (PDMC)</strong> component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) emphasizes efficient water use through micro-irrigation techniques.</p><div class="info-box">The government provides significant financial assistance for the installation of <strong>drip and sprinkler systems</strong>:<ul><li><strong>55%</strong> of project cost for <strong>small and marginal farmers</strong>.</li><li><strong>45%</strong> of project cost for <strong>other farmers</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)</h4><p>The <strong>Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)</strong> aims to bolster post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets, thereby reducing losses and improving farmer incomes.</p><div class="info-box">Key features of <strong>AIF</strong> include:<ul><li>Enhancing <strong>post-harvest infrastructure</strong> and reducing losses.</li><li>Eliminating intermediaries, allowing farmers to sell directly for better prices.</li><li>Interest rate for loans capped at <strong>9%</strong>.</li><li><strong>3% interest subvention</strong> for loans up to <strong>Rs 2 crore</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Skill Development Initiatives for Rural Youth</h4><p>Various programs are in place to enhance the skills of rural youth and farmers in the agricultural and allied sectors, fostering self-employment and modern practices.</p><div class="key-point-box">These initiatives are crucial for bridging the skill gap and promoting sustainable agricultural development.</div><ul><li><strong>Skill Training of Rural Youth (STRY)</strong>: Offers <strong>7-day short-term skill training</strong> in agriculture and allied sectors, specifically targeting self-employment opportunities.</li><li><strong>Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK)</strong>: Provides comprehensive training in agriculture, horticulture, livestock, and allied sectors to strengthen rural skills and knowledge.</li><li><strong>Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA)</strong>: Delivers decentralized extension services, keeping farmers updated on new technologies and best practices.</li><li><strong>Student READY Programme</strong>: Focuses on practical skill development and hands-on learning through training, rural awareness programs, internships, and projects for agricultural students.</li></ul><div class="exam-tip-box"><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the objectives and implementation status of these schemes is vital for questions on <strong>agricultural policy</strong>, <strong>rural development</strong>, and <strong>farmer welfare</strong> in <strong>GS Paper III</strong>. Note the specific targets and beneficiaries.</div>
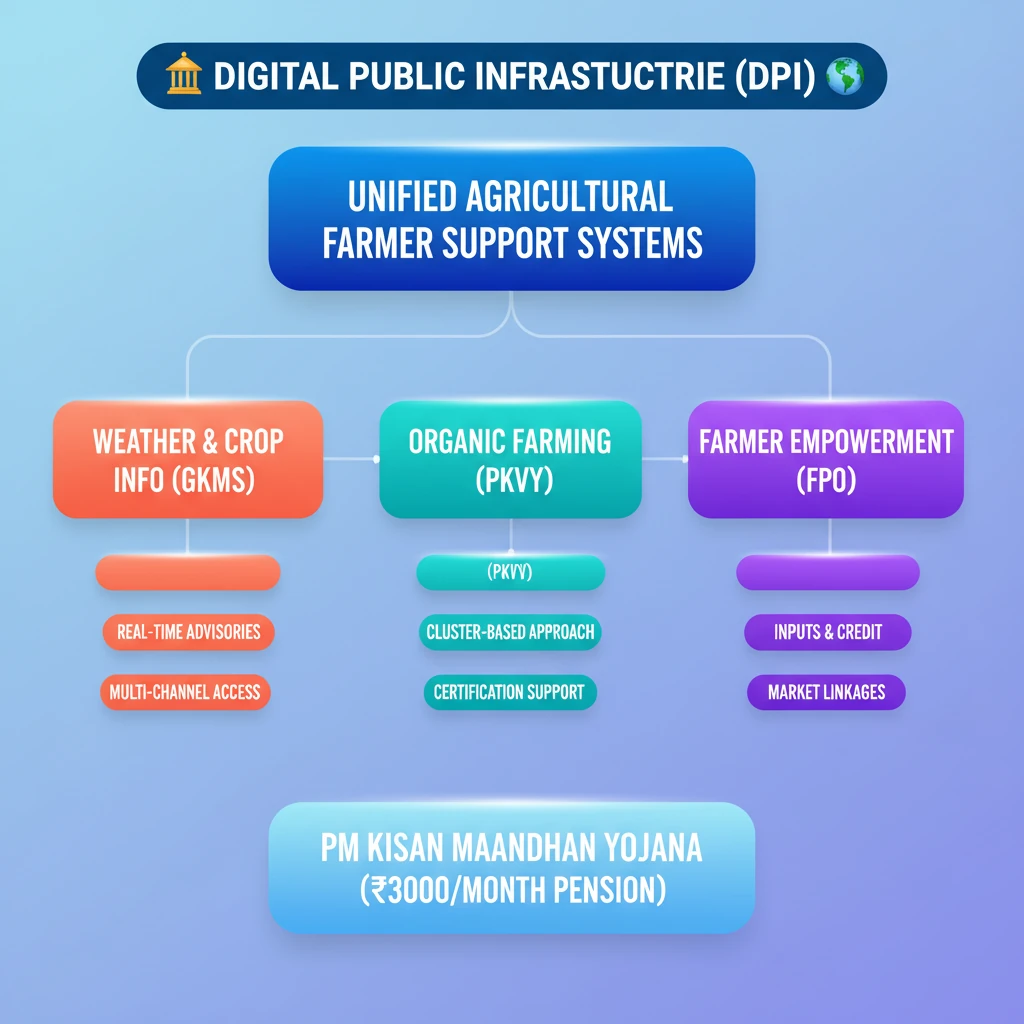
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) aims to unify agricultural extension services for real-time farmer support.
- •Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS) provides crucial weather and crop information through various channels.
- •Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) promotes organic farming through a cluster-based approach.
- •Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) empower farmers by improving input sourcing, credit access, and marketing.
- •Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PMKMY) offers a minimum pension of Rs 3,000 to eligible farmers at 60 years.
- •Per Drop More Crop (PDMC) incentivizes micro-irrigation systems with significant financial assistance.
- •Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) enhances post-harvest infrastructure with interest subvention for loans.
- •Skill development programs like STRY, KVK, and ATMA are vital for rural youth and farmers to adopt modern agricultural practices.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Drishti IAS Summary: Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PMKMY)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Per Drop More Crop (PDMC)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Skill Training of Rural Youth (STRY)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA)
•Drishti IAS Summary: Student READY Programme