Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) - economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Easy⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
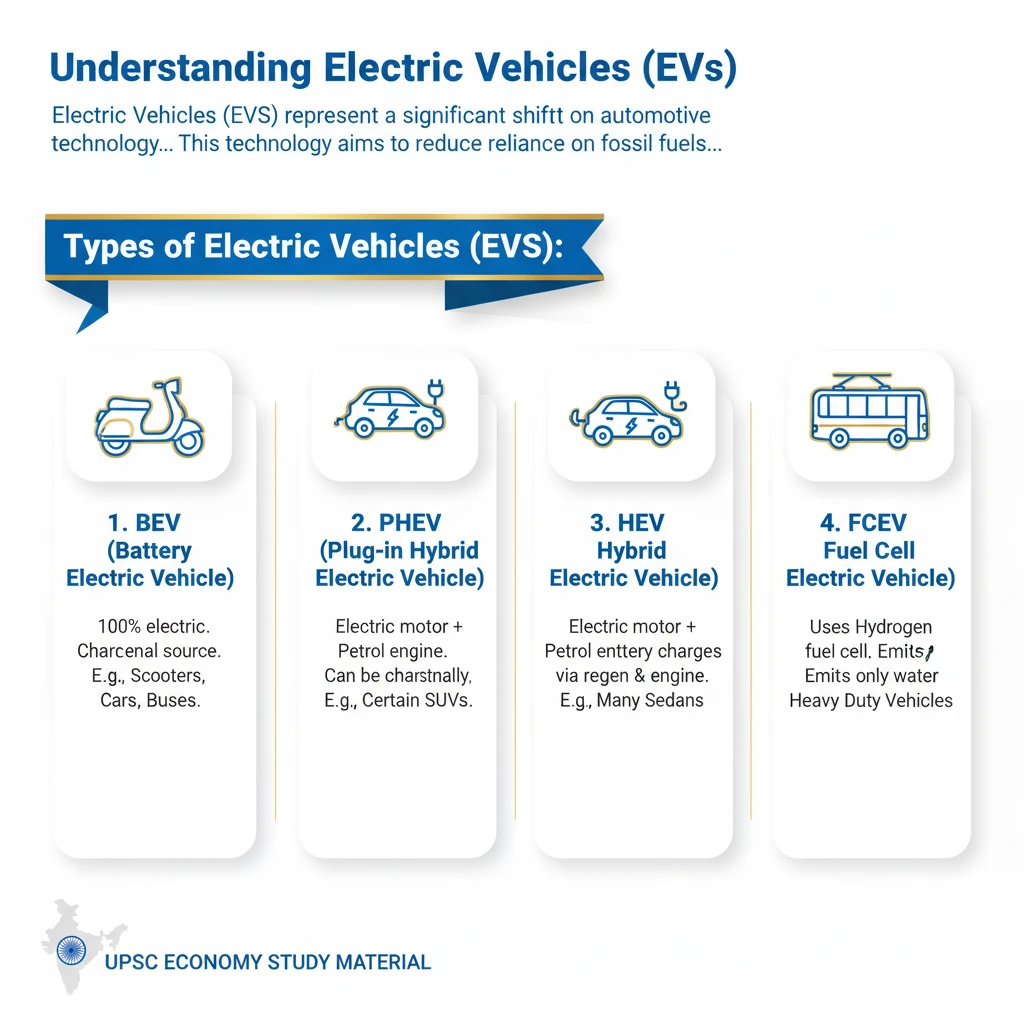
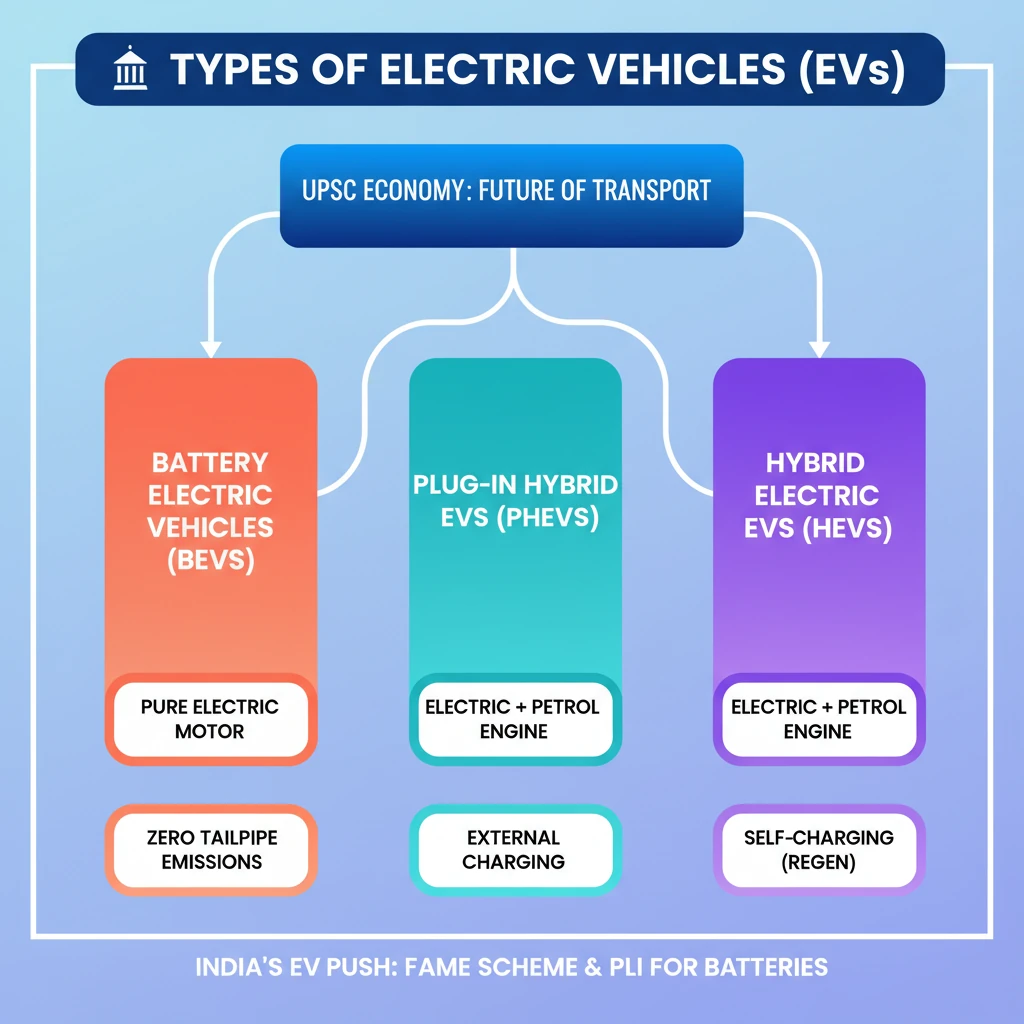
<h4>Understanding Electric Vehicles (EVs)</h4><p><strong>Electric Vehicles (EVs)</strong> represent a significant shift in automotive technology, moving away from traditional internal combustion engines. They utilize one or more electric motors for propulsion, drawing power from a rechargeable battery pack.</p><p>This technology aims to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby mitigating air pollution and carbon emissions. EVs are a cornerstone of global efforts towards sustainable transportation and energy security.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Mains GS3: Economy, Environment.</strong> Understanding EV types is crucial for questions on energy, infrastructure, and sustainable development. Focus on their operational differences and policy implications.</p></div><h4>Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): The Fully Electric Option</h4><p><strong>Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)</strong> are a category of EVs that are <strong>fully powered by electricity</strong>. They rely exclusively on an electric motor for propulsion, with no secondary power source like a gasoline engine.</p><p>These vehicles store energy in a large battery pack, which is charged by plugging into an external power source. The stored electricity then drives the electric motor, which in turn powers the wheels.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of BEVs:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Zero Tailpipe Emissions:</strong> Produce no exhaust gases, contributing to cleaner air.</li><li><strong>Electric Motor:</strong> Propelled solely by an electric motor.</li><li><strong>Battery Pack:</strong> Equipped with a large rechargeable battery.</li><li><strong>External Charging:</strong> Requires charging from the grid.</li><li><strong>No Internal Combustion Engine:</strong> Completely devoid of a gasoline or diesel engine.</li></ul></div><p>A significant advantage of BEVs is their superior <strong>efficiency</strong> compared to other types of electric vehicles. They convert a higher percentage of electrical energy from the grid directly into power for the wheels.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Efficiency Advantage:</strong> BEVs are <strong>more efficient compared to hybrid and plug-in hybrids</strong> because they avoid the energy losses associated with converting fuel to electricity or managing two distinct propulsion systems.</p></div><h4>Other Categories of Electric Vehicles (Brief Overview)</h4><p>While <strong>Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)</strong> are fully electric, other categories exist that combine electric and conventional propulsion. These include <strong>Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)</strong> and <strong>Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)</strong>.</p><p>These alternative types integrate an electric motor and battery with an internal combustion engine, offering different balances of electric range and fuel efficiency. BEVs stand out for their pure electric operation.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are fully powered by electricity, with no internal combustion engine.
- •BEVs are more efficient than hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles due to their pure electric powertrain.
- •They produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced carbon footprint.
- •Key components include an electric motor, a large rechargeable battery pack, and an external charging system.
- •India is actively promoting BEV adoption through policies like the FAME India scheme and PLI for battery manufacturing.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Heavy Industries, Government of India (FAME India Scheme documents)
•NITI Aayog reports on Electric Mobility
•Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) International publications on EV technology