Why are RRBs Facing High Attrition Rates? - economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Why are RRBs Facing High Attrition Rates?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
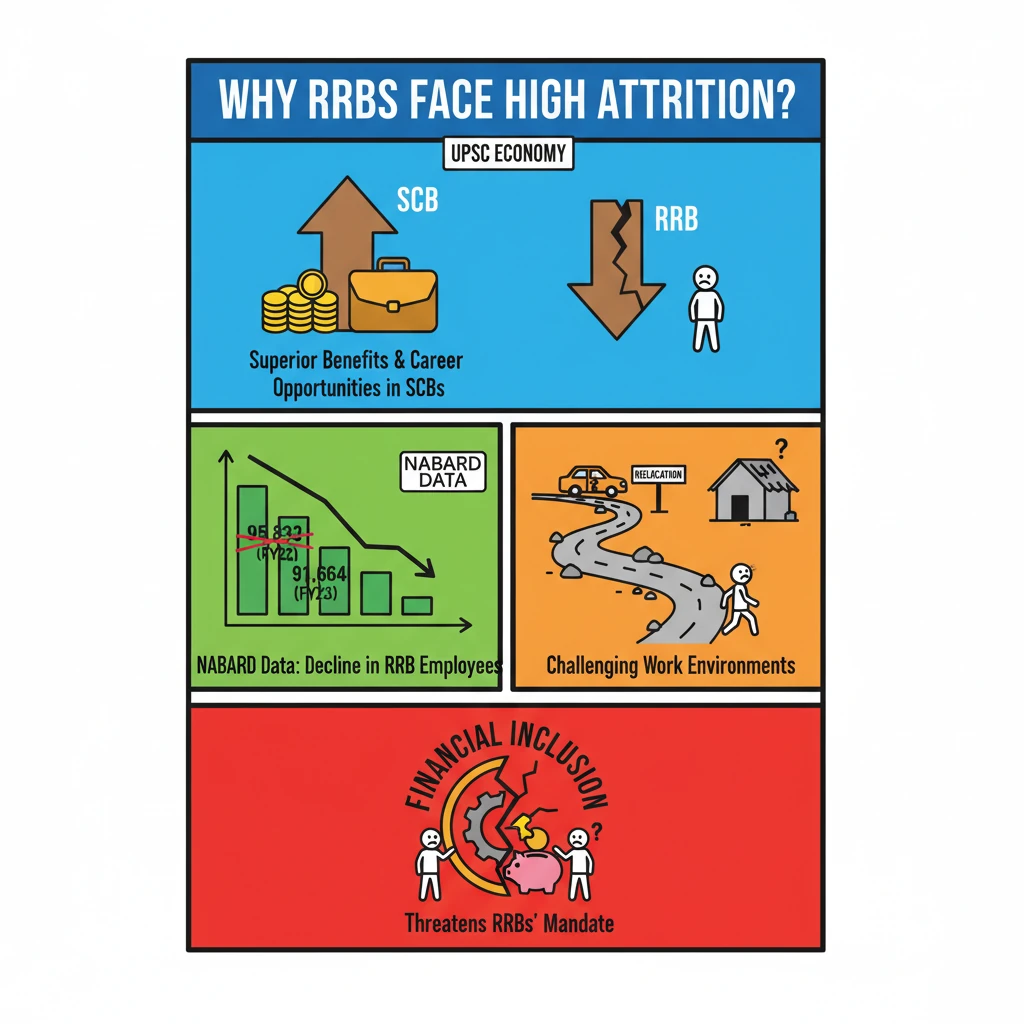
<h4>Understanding High Attrition in Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)</h4><p><strong>Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)</strong> play a crucial role in India's rural financial landscape. However, they are currently grappling with significant challenges, notably high <strong>employee attrition rates</strong>. This phenomenon impacts their operational efficiency and ability to serve their target demographic effectively.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>High attrition</strong> in <strong>RRBs</strong> is a critical issue, threatening their mandate of financial inclusion and rural development. Understanding its root causes is essential for policy intervention.</p></div><h4>Lack of Employee Benefits and Career Progression</h4><p>One of the primary drivers of attrition in <strong>RRBs</strong> is the perceived <strong>lack of superior employee benefits</strong> compared to <strong>Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs)</strong>. Despite often similar pay scales, <strong>SCBs</strong> typically offer better perks, housing, transfer policies, and overall career growth opportunities.</p><p>This disparity makes <strong>SCBs</strong> more attractive to banking professionals, leading to a continuous outflow of talent from <strong>RRBs</strong>. Employees seek environments that provide greater job satisfaction and long-term career prospects.</p><h4>Statistical Evidence of Attrition</h4><p>Data from the <strong>National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)</strong> substantiates the rising attrition. The total number of employees in <strong>RRBs</strong> has shown a noticeable decline over recent financial years.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>NABARD Data (43 RRBs):</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Total Employees FY22:</strong> 95,833</li><li><strong>Total Employees FY23:</strong> 91,664 (a decrease of 4,169 employees)</li><li><strong>Number of Branches FY22:</strong> 21,892</li><li><strong>Number of Branches FY23:</strong> 21,895 (a minor increase, indicating higher workload per employee)</li></ul></div><p>This data highlights a worrying trend where the workforce is shrinking while the branch network, and thus the operational burden, remains constant or slightly increases.</p><h4>Challenging Work Environment and Relocation Issues</h4><p>Another significant factor contributing to attrition is the <strong>challenging work environment</strong> often associated with <strong>RRBs</strong>. Many employees are required to relocate from their home states to work in remote rural areas, which can present substantial personal and professional difficulties.</p><p>Employees face issues such as language barriers, lack of urban amenities, limited educational opportunities for children, and social isolation. These factors collectively contribute to dissatisfaction and a desire to seek employment elsewhere.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>When analyzing challenges like <strong>RRB attrition</strong>, remember to consider both <strong>structural issues</strong> (benefits, career path) and <strong>operational issues</strong> (work environment, relocation). This holistic approach is crucial for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III</strong> answers on the Indian Economy.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •RRBs face high attrition due to superior benefits and career opportunities in SCBs.
- •NABARD data confirms a significant decline in RRB employees (95,833 in FY22 to 91,664 in FY23).
- •Challenging work environments, including relocation issues and lack of amenities, push employees away.
- •Attrition threatens RRBs' mandate of financial inclusion and rural development.
- •Addressing HR issues, career paths, and work environment is crucial for RRB sustainability.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Publications on Regional Rural Banks
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India Reports
•Narasimham Committee Report (1975)